Abstract
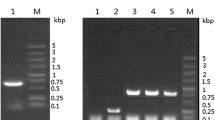
The human chemokine, the short version of leukotactin-1 (shLkn-1; molecular weight =7.2 kD and 66 amino acids), was expressed and secreted into a culture medium using the methylotrophic yeast,Pichia pastoris. The recombinant shLkn-1 was purified from the culture supernatant using a simple two-step procedure consisting of cation exchange and reverse phase chromatography (RPC), in which shLkn-1 was highly purified (99.5%) with a high recovery yield of 82.7%. The C-terminal truncated derivative of shLkn-1 was found in the supernatant and was separated by RPC. The physicochemical properties of the purified shLkn-1 were verified to be the same as expected. The biological activity of the purified recombinant shLkn-1 was also quantified using a chemotaxis assay. It was observed that the recombinant shLkn-1 had the maximum migration activity at a concentration of 10 nM, as potent as MIP-1α.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rollins, B. J. (1997) Chemokines.Blood 90: 909–928.
Pardigol, A., U. Forssmann, H. D. Zucht, P. Loetscher, P. Schulz-Knappe, M. Baggiolini, W. G. Forssmann, and H. J. Magert (1998) HCC-2, a human chemokine: Gene structure, expression pattern, and biological activity.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 6308–6313.
Coulin, F., C. A. Power, S. Alouani, M. C. Peitsch, J. M. Schroeder, M. Moshizuki, I. Clark-Lewis, and T. N. Wells (1997) Characterisation of macrophage inflammatory protein-5/human CC cytokine-2, a member of the macrophage-inflammatory-protein family of chemokines.Eur. J. Biochem. 248: 507–515.
Youn, B. S., S. M. Zhang, E. K. Lee, D.-H. Park, H. E. Broxmeyer, P. M. Murphy, M. Locati, J. E. Pease, K. K. Kim, K. Antol, and B. S. Kwon (1997) Molecular cloning of leukotactin-1: A novel human beta-chemokine, a chemoattractant for neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes, and and a potent agonist at CC chemokine receptors 1 and 3.J. Immunol. 159: 5201–5205.
Sticht, H., S. E. Escher, K. Schweimer, W. G. Forssmann, P. Rosch, and K. Adermann (1999) Solution structure of the human CC chemokine 2: A monomeric representative of the CC chemokine subtype.Biochemistry 38: 5995–6002.
Zhang, S., B. S. Youn, J. L. Gao, P. M. Murphy, and B. S. Kwon (1999) Differential effects of leukotactin-1 and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha on neutrophils mediated by CCR1.J. Immunol. 162: 4938–4942.
McAleer, B. and B. Rima (2000) Cloning and secreted expression of the extracellular domain of the mumps virus fusion protein inPichia pastoris.Virus Genes 20: 127–133.
Kim, K.-Y., H.-K. Lim, K.-J. Lee, D.-H. Park, K. W. Kang, S.-I. Chung, and K.-H. Jung (2000) Production and characterization of recombinant guamerin, an elastase-specific inhibitor, in the methylotrophic yeastPichia pastoris.Protein Expr. Purif. 20: 1–9.
Bidlingmer, B. A., S. A. Cohen, and T. L. Tarvin (1984) Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization.J. Chromatogr. 336: 93–104.
Heo, J. H., H. S. Won, H. A. Kang, S.-K. Rhee, and B. H. Chung. (2002) Purification of recombinant human epidermal growth factor secreted from the methylotrophic yeastHansenula polymorpha.Protein Expr. Purif. 24: 117–122.
Heim, J., K. Takabayashi, B. Meyhack, W. Marki, and G. Pohlig (1994) C-terminal proteolytic degradation of recombinant desulfato-hirudin and its mutants in the yeastSaccharomyces cerevisiae.Eur. J. Biochem. 226: 341–353.
Mizuno, K., T. Nakamura, T. Ohshima, S. Tanaka, and H. Matsuo (1989) Characterization of KEX2-encoded endopeptidase from yeastSaccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 159: 305–311.
Ohi, H., W. Ohtani, N. Okazaki, N. Furuhata, and T. Ohmura (1996) Cloning and characterization of thePichia pastoris PRC1 gene encoding carboxypeptidase Y.Yeast 12: 31–40.
Rosenfeld, S. A., D. Nadeau, J. Tirado, G. F. Hollis, R. M. Knabb, and S. Jia (1996) Production and purification of recombinant hirudin expressed in the methylotrophic yeastPichia pastoris.Protein Expr. Purif. 8: 476–482.
Maeda, Y., R. Kuroki, H. Suzuki, and H. Reilander (2000) High-level secretion of biologically active recombinant human macrophage inflammatory protein-1α by the methylotrophic yeast.Pichia pastoris.Protein Expr. Purif. 18: 56–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, I.H., Lee, K.J., Lee, E.K. et al. High-yield purification and characterization of recombinant human leukotactin-1 inPichia pastoris . Biotechnol Bioproc E 9, 1–6 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02949314
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02949314