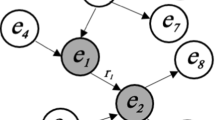
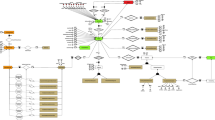
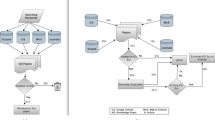
Abstract
Domain analysis is the activity of identifying and representing the relevant information in a domain, so that the information can be shared and reused in similar systems. But until now, no efficient approaches are available for capturing and representing the results of domain analysis and then for sharing and reusing the domain knowledge. This paper proposes an ontology-oriented approach for formalizing the domain models. The architecture for the multiple-layer structure of the domain knowledge base is also discussed. And finally, some genetic algorithm-based methods have been given for supporting the knowledge sharing and reusing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maymir-Ducharme F A. Varying domain engineering approaches — Business case perspectives. InProceedings of 5th Annual Workshop on Software Reuse Education and Training, Morgantown, WV, 1996.
Neighbors J. Software construction using components [Dissertation]. Information and Computer Science Department, University of California, 1981.
Domain Analysis. Technical Report, 1997. available from http://WWW.sern.enel.ucalgary.ca/charmi/Courses/97-98/ENEL619.02/FuSeminar.html
Prieto-Diaz R, Arango G: Domain Analysis and Software Systems Modeling. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos, California, 1991.
Simos M A. Organization domain modeling (ODM) guidebook. Technical Report STARS VC-A023/011, Unisys Corporation, 1995.
Kyo C Kang, Sholom G Cohen, James A Hess, William E Novak, A Spencer Peterson. Feature-Oriented Domain Analysis (FODA) Feasibility Study. Technical Report CMU/SEI-90-TR-21, Pittsburgh, PA: Software Engineering Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, 1990.
McCain R. Reusable software component construction — A product oriented paradigm. InProceedings of AIAA/ACM/NASA/IEEE Computers in aerospace Conference, 1985, pp. 125–135.
Yi X. Study on Software Development of Special Domains based on Architectures [Dissertation]. Peking University, 1996.
Yang F. Overview of the jade bird project. Technical Report, Department of Computer Science, Peking University, 1997.
Capilla R. Application of Domain Analysis to Knowledge Reuse. InProceedings of the 8th Annual Workshop on Institutionalizing Software Reuse (WISR’8), Ohio State, USA, 1997. http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/capilla97 application.html
Chandrasekaran B. Generic tasks in knowledge-based reasoning: High level building blocks for expert system design.IEEE Expert, 1986, 1 (3): 23–30.
Lu R, Jin Z. Domain Modelling-Based Software Engineering. Volume 8 of The Kluwer International Series on Asian Studies in Computer and Information Science, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000.
Lu R, Jin Z. Hierarchical software reuse.Chinese Journal of Advanced Software Research, 1999, 6(1): 1–11.
Lu R, Jin Z, Wan R. PROMIS: A knowledge-based tool for automatically prototyping management information systems. InProceedings of AVIGNON’94, Paris, France, 1994, 325–330.
Lu R, Jin Z, Wan R. Requirement specification in pseudo-natural language in PROMIS. InProceedings of 19th COMPSAC, USA, 1995, pp. 96–101.
Lu R, Jin Z, Wan R, Xie Y. Domain knowledge based requirements information acquisition.Journal of Software, 1996, 7(3): 137–144.
Lu R, Jin Z, Liu L, Jiang A, Lai H. PROMIS 2.0: An intelligent CASE tool for MIS in the client/server application. InProceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Future Computer Systems, Xiamen, P.R. China, 1997, pp.399–405.
Lu R, Jin Z, Liu L, Fan G, Chen G, Xun X, Wang S. OSNET: A Language for Domain Modeling. InTools Asia’98, Beijing, P.R. China, 1998, pp.198–203.
Lu R, Jin Z, Liu L, Jiang A, Lai H. NEWCOM: An architecture description language in client/server style.Chinese Journal of Computers, 1998, 21(12): 1103–1111.
Uschold M, Gruninger M. The enterprise ontology. Technical Report AIAI-TR-195, Artificial Intelligence Application Institute, University of Edinburgh, 1997.
TOVE Project. TOVE Manual. Technical Report, Enterprise Integration Laboratory, University of Toronto, available from http://www.ie.utoronto.ca/EIL/tove, 1995.
Chen P. The entity-relationship model — Towards a unified view of data.ACM Transactions on Database Systems, 1976, 1(1): 9–36.
Sowa J F. Conceptual Structure: Information Processing in Mind and Machine. Addison-Wesley Publisher, Reading, Mass, USA, 1984.
IEEE Standard for Developing Software Life Cycle Processes. IEEE Computer Society New York, 1996.
Fernandez M. Overview of methodologies for building ontologies. InProceedings of the IJCAI-99 Workshop on Ontologies and Problem-Solving Methods, 1999, pp.1–13.
A Gomez-Perez, V Richard Benjamins. Overview of knowledge sharing and reuse components: Ontologies and problem-solving methods. InProceedings of the IJCAI-99 Workshop on Ontologies and Problem-Solving Methods (KRR5), Stockholm, Sweden, 1999.
Natalya Fridman Noy, Carole D Hafner. The state of the art in ontology design.AI Magazine, Fall, 1997, pp.53–74.
Gruber T R. Towards principles for the design of ontologies used for knowledge sharing. Technical Report KSL-93-04, Knowledge Systems Laboratory, Stanford University, 1993.
Genesereth M R, Fikes R E. Knowledge interchange format. Technical Report KSL-92-86, Knowledge Systems Laboratory, Stanford University, 1992.
Lenat D B. CYC: A large scale investment in knowledge infrastructure.Communication of ACM, 1995, (11): 33–38.
Gruber T R, Olsen R. An ontology for engineering mathematics. Technical Report KSL-94-04, Knowledge Systems Laboratory, Stanford University, 1994.
Borst W N. Construction of Engineering Ontology [Dissertation]. University of Twente, Enschede, 1997.
Bateman J A, Magnini B, Fabris G. The generalized upper model knowledge base: Organization and use. Towards Very Large Knowledge Bases: Knowledge Building and Knowledge Sharing, Mars N J I (ed.), IOS Press, 1995, pp.60–72.
Miller G A. WordNet: A lexical database for English.Communications of ACM, 1995, 39–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.69983010), the National Natural Science Key Foundation of China (Grant No.69733020), the National High-Tech Project (Grant No.2001AA113130), the Pre-973 Project (Grant No.2001CCA03000), the CAS Project of Brain and Mind Science and the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
LU Ruqian, male, was born in Shanghai, China, in 1935. He received the degree of Diplom Mathematiker from the Friedlich Schiller University of Jena in 1959. He joined the Institute of Mathematics in 1959 and is now a professor of this institute. He is also a professor of Fudan University and a guest professor of Institute of Computing Technology. He is a academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. His research interests include artificial intelligence, knowledge engineering and knowledge science, and theoretical computer science.
JIN Zhi is a professor of computer science at the Academy of Mathematics and System Sciences. She received her Ph.D. degree in computer science from National University of Defense Technology in 1992. Her research interests include knowledge-based systems, ontology development, artificial intelligence, and requirements engineering. She has authored and co-authored one book and over 50 papers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, R., Jin, Z. Formal ontology: Foundation of domain knowledge sharing and reusing. J. Comput. Sci. & Technol. 17, 535–548 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02948822
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02948822