Abstract
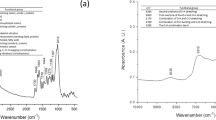
The contamination of animal feed with mycotoxins represents a worldwide problem for the animal industry. The most applied method for protecting animals against aflatoxicosis is the utilization of clay minerals. In the course of a research project adsorption experiments were performed in buffer solutions in order to evaluate the ability to bind Aflatoxin B1 (AfB1) at various pH-values. In order to investigate the strength of binding, the chemisorption index was calculated. Isothermal analysis was used to determine the values for the maximum adsorption capacity. Adsorption experiments in simulated gastrointestinal fluid and real gastric juice were carried out. Furthermore binding capability of the materials regarding selected vitamins was examined. Special attention was paid to the formation of AfB2a during experimental conditions. Based on the obtainedin vitro results, highly promising sorbent materials were ranked for furtherin vivo studies. Some adsorbing bentonites were also analysed mineralogically, but the results did not indicate which smectite property influences the adsorption process for AfB1
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CAST (Council for Agricultural Science and Technology) (2003) Mycotoxins: Risks in Plant, animal and human systems. Task Force Report No. 139: 13–85. CAST, Ames, IA
Agag BI (2004) Mycotoxins in foods and feeds. 1-Aflatoxins. Ass Univ Bull Environ Res 7 (1): 173–206
Huwig A, Freimund S, Kappeli O, Dutler H (2001) Mycotoxin detoxication of animal feed by different adsorbents. Toxicol Lett 122: 179–188
Evans AG (2004) Safety and efficacy of Nova Sil clay as a dietary supplement to prevent aflatoxicosis. Dissertation, Texas A&M University
Miazzo R, Peralta MF, Magnoli C, Salvano M, Ferrero S, Chiacchiera SM, Carvalho EC, Rosa CA, Dalcero A (2005) Efficacy of sodium bentonite as a detoxifier of broiler feed contaminated with aflatoxin and fumonisin. Poult Sci 84(1): 1–8
Lemke SL, Ottinger SE, Mayura K, Ake CL, Pimpukkdee K, Wang N, Phillips TD (2001) Development of a multi-tiered approach to the in vitro prescreening of clay-based enterosorbents. Animal Feed Sci Technol 93: 17–29
Grant PG, Lemke SL, Dwyer MR, Phillips TD (1998) Isothermal adsorption of aflatoxin B1 on HSCAS clay. J Agr Food Chem 46: 599–605
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Financial support: Christian Doppler Society
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vekiru, E., Fruhauf, S., Sahin, M. et al. Investigation of various adsorbents for their ability to bind aflatoxin B1 . Mycotox Res 23, 27–33 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02946021
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02946021