Abstract
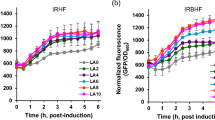
Promoters of the genesG3P, ICL1, POT1, POX1, POX2 andPOX5 of the yeastY. lipolytica were studied in respect to their regulations and activities during growth on different carbon sources. The aim of this study was to select suitable promoters for high expression of heterologous genes in this yeast. For this purpose the promoters were fused with the reporter genelacZ ofE. coli and integrated as single copies into the genome ofY. lipolytica strain PO1d. The measurement of expressed activities of β-galactosidase revealed thatpICL1, pPOX2 andpPOT1 are the strongest regulable promoters available forY. lipolytica, at present.pPOX2 andpPOT4 were highly induced during growth on oleic acid and were completely repressed by glucose and glycerol.pICL1 was strongly inducible by ethanol besides alkanes and fatty acids, however, not completely repressible by glucose or glycerol. Ricinoleic acid methyl ester appeared as a very strong inducer forpPOT1 andpPOX2, in spite of that it inhibited growth ofY. lipolytica transformants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barth, G. and C. Gaillardin (1996)Yarrowia lipolytica. pp. 313–388. In: K. Wolf (ed.):Nonconventional yeasts in biotechnology. A Handbook. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Barth, G. and C. Gaillardin (1997) Physiology and genetics of the dimorphic fungusYarrowia lipolytics.FEMS Micobiol. Rev. 19: 219–237.
Gaillardin, C. and H. Heslot (1988) Genetic engineering inYarrowia lipolytica.J. Basic Microbiol. 28: 161–174.
Romanos, M., C. Scorer, and J. Clare (1992) Foreign gene expression in yeast.Yeast 8: 423–488.
Sudbery, P. (1994) Non-Saccharomyces yeasts.Yeast 10: 1707–1726.
Müller, S., T. Sandal, P. Kamp-Hansen, and H. Dalboge (1998) Comparison of expression systems in the yeastsSaccharomyces cerevisiae, Hansenula polymorpha, Klyuveromyces lactis, Schizosaccharomyces pombe andYarrowia lipolyca.Yeast 14: 1267–1283.
Fournier, P., L. Guyaneux, M. Chasles, and C. Gaillardin (1991) Scarcity of ars sequences isolated in a morphogenesis mutant of the yeastYarrowia lipolytica.Yeast 7: 25–36.
Fournier, P., A. Abbas, M. Chasles, B. Kudla, D. M. Ogrydziak, D. Yaver, J.-W. Xuan, A. Peito, A.-M. Ribet, C. Feynerol, F. He, and C. Caillardin (1993) Colocalization of centromeric and replicative functions on autonomously replicating sequences isolated from the yeastYarrowia lipolytica.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 4912–4916.
Matsuoka, M., M. Matsubara, H. Daidoh, T. Imanaka, K. Uchida, and S. Aiba (1993) Analysis of regions essential for the function of chromosomal replicator sequences fromYarrowia lipolytica.Mol. Gen. Genet. 237: 327–333.
Vernis, L., A. Abbas, M. Chasles, G. M. Gaillardin, C. Brun, J. A. Huberman, and P. Fournier (1997) An origin of replication and a centromere are both needed to establish a replicative plasmid in the yeastYarrowia lipolytica.Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 1995–2004.
Vernis, L., M. Chasles, P. Pasero, A. Lepingle, C. Caillardin, and F. Fournier (1999) Short DNA fragments without sequence similarity are initiation sites for replication in the chromosome of the yeastYarrowia lipolytica.Mol. Cell. Biol. 10: 757–769.
Le Dall, M.-T., J.-M. Nicaud, and C. Gaillardin (1994) Multi-copy integration in the yeastYarrowia lipolytica.Curr. Genet. 26: 38–44.
Juretzek, T. M. T. Le Dall, S. Mauersberger, C. Gaillardin, G. Barth, and J. M. Nicaud (2000) Vectors for gene expression and amplification in the yeastYarrowia lipolytica. Yeast in press.
Matoba, S., J. Fukuyama, R. A. Wing, and D. M. Ogrydziak (1988) Intracellular precursors and secrition of alkaline extracellular protease ofYarrowia lipolytica.Mol. Cell. Biol. 8: 4904–4916.
Fabre, E., J. M. Nicaud, M. C. Lopez, and C. Caillardin (1991) Role of the proregion in the production and secretion of theYarrowia lipolytica alkaline extracellular protease.J. Biol. Chem. 266: 3782–3790.
Matoba, S., K. A. Morano, D. J. Klionsky, K. Kim, and D. M. Ogrydziak (1997) Dipeptidyl aminopeptidase processing and biosynthesis of extracellular protease fromYarrowia lipolytica.Microbiology 143: 3263–3272.
Blanchin-Roland, S., R. Cordero Otero, and C. Gaillardin (1994) Two upstream UAS control expression of theXPR2 gene encoding an extracellular alkaline protease in the yeastYarrowia lipolytica.Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 327–338.
Park, G. S., C. C. Chang, J. Y. Kim, D. M. Ogrydziak, and D. D. Ryu (1997) Expression, secretion, and processing of rice a-amylase in the yeastYarrowia lipolytica.J. Biol. Chem. 272: 6876–6881.
Chang, C. C., D. D. Ryu, C. S. Park, and J. Y. Kim (1998) Improvement of heterologous protein productivity using recombinantYarrowia lipolytica and cyclic fed-batch process strategy.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 59: 379–385.
Madzak, C., S. Blanchin-Roland, R. R. Cordero-Otero, and C. Gaillardin (1999) Functional analysis of upstream regulating regions from theYarrowia lipolytica XPR2 promoter.Microbiology 145: 75–87.
Barth, G. and T. Scheuber (1993) Cloning of the isocitrate lyase gene (ICL1) fromYarrowia lipolytica and characterization of the deduced protein.Mol. Gen. Genet. 241: 422–430.
Berninger, G., R. Schmidtchen, G. Casel, A. Knoerr, K. Rautenstrauss, W.-H. Kunau, and E. Schweizer (1993) Structure and metabolic control of theYarrowia lipolytica peroxisomal 3-oxoacyl-CoA-thiolase gene.Eur. J. Biochem. 216: 607–613.
Wang, H., A. Le Clainche, M. T. Le Dall, Y. Wache, Y. Pagot, J. M. Belin, C. Gaillardin, and J. M. Nicaud (1998) Cloning and characterization of the peroxisomal acyl CoA oxidaseACO3 gene from the alkane-utilizing yeastYarrowia lipolytica.Yeast 14: 1373–1386.
Wang, H. J., M. T. Le Dall, Y. Wach, C. Laroche, J. M. Belin, C. Gaillardin, and J. M. Nicaud (1999) Evaluation of acyl coenzyme A oxidase (Aox) isozyme function in the n-alkane-assimilating yeastYarrowia lipolytica.J. Bacteriol. 181: 5140–5148.
Sambrook, J., E. E. Fritsch, and T. Maniatis (1989)Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2nd ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA.
Mauersberger, S., M. Ohkuma, W-H. Schunck, and M. Takagi (1996)Candida maltosa. pp 411–580. In: K. Wolf (ed.);Nonconventional yeasts in biotechnology. A Hand-book. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. C. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (1993)Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, Vol. 1, Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts, USA.
Juretzek, T. (1999)Entwicklung von Wirts-Vektor-Systemen zur heterologen Expression von Proteinen in der micinkonventionellen Hefe Yarrowia lipolyticaund ihre Anwendung für die Cytochrom P450-katalysierte Stoffumwandlung, PhD thesis. Technische Universität Dresden, Germany.
Schmidtchen, R. (1994)Untersuchungen zur Regulation des 3-Oxcacyl-CoA-Thio-lacs-1-Gens aus Yarrowia lipoly-tica, PhD thesis, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität, Erlangen, Germany.
Madzak, C., B. Tréton, and S. Blanchin-Roland (2000) Strong hybrid promoters and integrative expression/secretion vectors for quasi-constitutive expression, of heterologous proteins in the yeastYarrowia lipolytic.J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2: 207–216.
Sanger, F., S. Nicklen, and A. R. Coulson (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74: 5463–5467.
Gaillardin, C. and A.-M. Ribet (1987)LEU2 directed expression of β-galactosidase activity and phleomycin resistance inYarrowia lipolytica.Curr. Genet. 11: 369–375.
Pagot, Y., A. Endrizzi, J. M. Nicaud, and J. M. Belin (1997) Utilization of an auxotrophic strain of the yeastYarrowia lipolytica to improve gamma-decalactone production yields.Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 25: 113–116.
Gerber, J. (1999)Untersuchungen zur Optimierung des Elektromentransportsystems für die Cytochrom P450 katalysierte Biotransformation von Steroiden in Yarrowia lipolytica. Diploma thesis, Technische Universität Dresden, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juretzek, T., Wang, HJ., Nicaud, JM. et al. Comparison of promoters suitable for regulated overexpression of β-galactosidase in the alkane-utilizing yeastYarrowia lipolytica . Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 5, 320–326 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02942206
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02942206