Summary
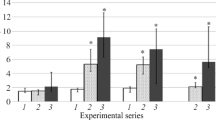
Immunoreactive substance P (iSP) has been measured in plasma in 77 normal subjects and in 125 hospital patients. Factors affectingin-vitro degradation of iSP were studied.In vivo, iSP is degraded in the liver and its level in the circulation is independent of kidney excretory function.
During insulin-induced hypoglycaemic stress and also during glucose-tolerance test, iSP in plasma decreased transiently. No circadian rhythm of iSP was observed, but in a study in sleeping volunteers episodic secretory bursts were seen, separated by one- to two-hour intervals, the first peak appearing about 90 minutes after the subjects fell asleep.
In a patient with carcinoid metastases in the liver, an elevated level of iSP was found in the general circulation with a marked gradient at the hepatic venous effluent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura, A., Sato, H., Dupont, A., Nishi, N. and Schally, A. V. 1975. Somatostatin: abundance of immunoreactive hormone in rat stomach and pancreas. Science 189, 1007.
Benuck, M. and Marks, N. 1975. Enzymatic inactivation of substance P by a partially purified enzyme from rat brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 65, 153.
Brown, M. and Vale, W. 1976. Effects of neurotensin and substance P on plasma insulin, glucagon and glucose levels. Endocrinology 98, 819.
Claybrook, D. L. and Pfiffner, J. J. 1968. Purification and properties of a substance Pinactivating enzyme from bovine brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 17, 281.
Collier, H. O. J. 1963. The action and antagonism of kinins on bronchioles. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 104, 290.
Duffy, M. J. and Powell, D. 1975. Stimulation of brain adenylate cyclase activity by the undecapeptide substance P and its modulation by the calcium ion. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 385, 275.
Efendic, S., Luft, R. and Pernow, B. 1976. Effect of substance P on arginine-induced insulin and glucagon release from the isolated perfused rat pancreas in “Substance P”, ed. by U. S. von Euler and B. Pernow, New York, Raven Press (in the press).
Erspamer, V., Erspamer-Falconieri, G. and Linari, G. 1976. Occurrence of tachykinins (substance P-like peptides) in the amphibian skin and their actions on isolated smooth muscle preparations in “Substance P”, ed. by U. S. von Euler and B. Pernow, New York, Raven Press (in the press).
Hallberg, D. and Pernow, B. 1975. Effect of substance P on various vascular beds in the dog. Acta Physiol. Scand. 93, 277.
Henry, J. L., Krnjevic, K. and Morris, M. E. 1975. Substance P and spinal neurones. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 53, 423.
Johnson, A. R. and Erdös, E. G. 1976. Peptidases in cultured endothelial cells in “Substance P”, ed. by U. S. von Euler and B. Pernow, New York, Raven Press (in the press).
Kocic-Mitrovic, D. 1959. Uber die Wirkung einiger physiologischer Reize auf die Konzentration der Substanz P in Gehirn und Retina. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs. Arch. exp. Path. Pharmakol. 236, 37.
Lembeck, F., Popper, H. and Juan, H. 1976. Release of prostaglandins by bradykinin as an intrinsic mechanism of its algesic effect. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 294, 69.
Melchiorri, P., Tonelli, F. and Negri, L. 1976. Comparative circulatory effects of eledoisin, physalaemin and substance P in the dog in “Substance P”, ed. by U. S. von Euler and B. Pernow, New York, Raven Press (in the press).
Mills, I. H., Macfarlane, N. A. A. and Ward, P. E. 1974. Increase in kallikrein excretion during the natriuresis produced by arterial infusion of substance P. Nature 247, 108.
Morson, B. C. and Dawson, I. M. P. 1972. in “Gastrointestinal Pathology”, Oxford, Blackwell, p. 467.
Oates, J. A. and Melmon, K. L. 1966. Biochemical and physiological studies of the kinins in carcinoid syndrome in “Hypotensive peptides”, ed. by E. G. Erdös, N. Back and F. Sicuteri, Berlin, Springer Verlag, p. 565.
O’Connell, R., Skrabanek, P., Cannon, D. and Powell, D. 1976. High-sensitivity radioimmunoassay for substance P. Irish J. Med. Sci. 145, 392.
Orci, L., Beatens, O., Rufener, C., Brown, M., Vale, W. and Guillemin, R. 1976. Evidence for immunoreactive neurotensin in dog intestinal mucosa. Life Sci. 19, 559.
Otsuka, M., Konishi, S., Takahashi, T. 1975. Hypothalamic substance P as a candidate for transmitter of primary afferent neurons. Fedn. Proc. 34, 1922.
Powell, D., Leeman, S., Tregear, G. W., Niall, H. D. and Potts, J. T. Jr. 1973. Radioimmunoassay for substance P. Nature New Biol. 241, 252.
Powell, D., Skrabanek, P. and Cannon, D. 1976. Substance P: radioimmunoassay studies in “Substance P”, ed. by U. S. von Euler and B. Pernow, New York, Raven Press (in the press).
Pearse, A. G. E. 1975. Neurocristopathy, neuroendocrine pathology and the APUD concept. Z. Krebsforsch. 84, 1.
Pearse, A. G. E. and Polak, J. M. 1975. Immunocytochemical localization of substance P in mammalian intestine. Histochemistry 41, 373.
Pearse, A. G. E. and Takor Takor, T. 1976. Neuroendocine embryology and the APUD concept. Clin. endocrinol. 5 Suppl. 229s.
Said, S. I. and Rosenberg, R. N. 1976. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: abundant immuno-reactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science 192, 907.
Stewart, J. M., Getto, C. J., Neldner, K., Reeve, E. B., Krivoy, W. A. and Zimmermann, E. 1976. Substance P and analgesia. Nature 262, 784.
Sundler, F., Bengmark, S., Brodin, E., Håkansson, R., Ingemansson, S., Larsson, L. I. and Nilsson, G. 1976. Demonstration of substance P-like immunoreactivity in carcinoid tumours in “Substance P”, ed. by U. S. von Euler and B. Pernow, New York, Raven Press (in the press).
Vanderhaegen, J. J., Signeau, J. C. and Gepts, W. 1975. New peptide in the vertebrate CNS reacting with antigastrin antibodies. Nature 257, 604.
Von Euler, U. S. and Gaddum, J. H. 1931. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J. Physiol. 72, 74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skrabanek, P., Cannon, D., Kirrane, J. et al. Circulating immunoreactive substance P in man. IJMS 145, 399–408 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02938979
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02938979