Abstract
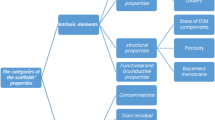
Tissue engineering scaffolds play a critical role in regulating the reconstructed human tissue development. Various types of scaffolds have been developed in recent years, including fibrous matrix and foam-like scaffolds. The design of scaffold materials has been investigated extensively. However, the design of physical structure of the scaffold, especially fibrous matrices, has not received much attention. This paper compares the different characteristics of fibrous and foam-like scaffolds, and reviews regulatory roles of important scaffold properties, including surface geometry, scaffold configuration, pore structure, mechanical property and bioactivity. Tissue regeneration, cell organization, proliferation and differentiation under different microstructures were evaluated. The importance of proper scaffold selection and design is further discussed with the examples of bone tissue engineering and stem cell tissue engineering. This review addresses the importance of scaffold microstructure and provides insights in designing appropriate scaffold structure for different applications of tissue engineering.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALP:
-
alkaline phosphatase
- BMP:
-
bone morphogenetic protein
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- GAG:
-
glycosaminoglycans
- PEG:
-
poly(ethylene glycol)
- PET:
-
polyethylene terephthalate
- PGA:
-
poly(glycolic acid)
- PLA:
-
poly(lactic acid)
- PGLA:
-
poly(glycolic-co-lactic acid)
- PLG:
-
poly(lactic-co-glycolide)
- PLGA:
-
poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
- PTFE:
-
polytetrafluoroethylene
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Langer, R. and J. P. Vacanti (1993) Tissue engineering.Science 260: 920–926.
Langer, R. (2000) Tissue engineering.Molecular Therapy 1: 12–15.
Shastri, V. P., I. Martin, and R. Langer (2000) Macroporous polymer foams by hydrocarbon templating.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 933–937.
Oberpenning, F., J. Meng, J. J. Yoo, and A. Atala (1999) De novo reconstitution of a functional mammalian urinary bladder by tissue engineering.Nature Biotechnol. 17: 149–155.
Niklason, L. E., J. Gao, W. M. Abbott, K. K. Hirschi, S. Houser, R. Marini, and R. Langer (1999) Functional arteries grown in vitro.Science 284: 489–493.
Griffith, M., R. Osborne, R. Munger, X. Xiong, C. J. Doillon, N. L. C. Laycock, M. Hakim, Y. Song, and M. A. Watsky (1999) Functional human corneal equivalents constructed from cell lines.Science 286: 2169–2172.
Boyan, B. D., T. W. Hummert, D. D. Dean, and Z. Schwartz (1996) Role of material surfaces in regulating bone and cartilage cell response.Biomaterials 17: 137–146.
Ingber, D. E. and J. Folkman (1989) Mechanical switching between growth and differentiation during fibroblast growth factor-stimulated angiogenesis in vitro: role of extracellular matrix.J. Cell Biol. 109: 317–330.
Mooney, D. J., L. Hansen, J. P. Vacanti, R. Langer, S. Farmer, and D. E. Ingber (1992) Switching from differentiation to growth in hepatocytes: control by extracellular matrix.J. Cellular Physiol. 151: 497–505.
Sittinger, M., D. Reitzel, M. Dauner, H. Hierlemann, C. Hammer, E. Kastenbauer, H. Planck, G. R. Burmester, and J. Bujia (1996) Resorbable polyesters in cartilage engineering: affinity and biocompatibility of polymer fiber structures to chondrocytes.I. Biomed. Mater. Res. (Appl. Biomater.) 33: 57–63.
Kim, B.-S., J. Nikolovski, J. Bonadio, E. Smiley, and D. J. Mooney (1999) Engineered smooth muscle tissues: regulating cell phenotype with the scaffold.Exp. Cell Res. 251: 318–328.
Walboomers, X. F., H. J. E. Croes, L. A. Ginsel, and J. A. Jansen (1999) Contact guidance of rat fibroblasts on various implant materials.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 47: 204–212.
Chinn, J. A., T. A. Horbett, B. D. Ratner, M. B. Schway, Y. Haque, and S. D. Hauschka (1989) Enhancement of serum fibronectin adsorption and the clonal plating efficiencies of Swiss Mouse 3T3 fibroblast and MM14 Mouse myoblast cells on polymer substrates modified by radiofrequency plasma deposition.J. Colloid Interface Sci. 127: 67–87.
Chen, W. and T. J. McCarthy (1998) Chemical surface modification of poly(ethylene terephthalate).Macromolecules 31: 3648–3655.
Madihally, S. V. and W. T. Matthew (1999) Porous chitosan scaffolds for tissue engineering.Biomaterials 20: 1133–1142.
James, K. and J. Kohn (1996) New biomaterials for tissue engineering.MRS Bulletin 21: 22–27.
Aigner, J., J. Tegeler, P. Hutzler, D. Campoccia, A. Pavesio, C. Hammer, E. Kastenbauer, and A. Naumann (1998) Cartilage tissue engineering with novel nonwoven structured biomaterial based on hyaluronic acid benzyl ester.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 42: 172–181.
Glicklis, R., L. Shapiro, R. Agbaria, J. C. Merchuk, and S. Cohen (2000) Hepatocyte behavior within three-dimensional porous alginate scaffolds.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 67: 344–353.
Temenoff, J. S. and A. G. Mikos (2000) Review: tissue engineering for regeneration of articular cartilage.Biomaterials 21: 431–440.
Angelova, N. and D. Hunkeler (1999) Rationalizing the design of polymeric biomaterials.Trends Biotechnol. 17: 409–421.
Chen, C. S., M. Mrksich, S. Huang, G. M. Whitesides, and D. E. Ingber (1998) Micropatterned surfaces for control of cell shape, position, and function.Biotechnol. Prog. 14: 356–363.
Chen, C. S., M. Mrksich, S. Huang, G. M. Whitesides, and D. E. Ingber (1997) Geometric control of cell life and death.Science 276: 1425–1428.
Singhvi, R., A. Kumar, G. P. Lopez, G. N. Stephanopoulos, D. I. C. Wang, G. M. Whitesides, and D. E. Ingber (1994) Engineering cell shape and function.Science 264: 696–698.
Braber, E. T. D., J. E. D. Ruijter, H. T. J. Smits, L. A. Ginsel, A. F. V. Recum, and J. A. Jansen (1995) Effect of parallel surface microgrooves and surface energy on cell growth.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29: 511–518.
van Kooten, T. G., J. F. Whitesides, and A. F. von Recum (1998) Influence of silicone (PDMS) surface texture on human skin fibroblast proliferation as determined by cell cycle analysis.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. (Appl. Biomater.) 43: 1–14.
Singhvi, R., G. Stephanopoulos, and D. I. C. Wang (1994) Review: Effects of substratum morphology on cell physiology.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 43: 764–771.
Rezania, A. and K. E. Healy (1999) Biomimetic peptide surfaces that regulate adhesion, spreading, cytoskeletal organization, and mineralization of the matrix deposited by osteoblast-like cells.Biotechnol. Prog. 15: 19–32.
Folch, A. and M. Toner (1998) Cellular micropatterns on biocompatible materials.Biotechnol. Prog. 14: 388–392.
Patel, N., R. Padera, G. H. W. Sanders, S. M. Cannizzaro, M. C. Davies, R. Langer, C. J. Roberts, S. J. B. Tendler, P. M. Williams, and K. M. Shakesheff (1998) Spatially controlled cell engineering on biodegradable polymer surfaces.FASEB J. 12: 1447–1454.
Cannizzaro, S. M., R. E. Padera, R. Langer, R. A. Rogers, F. E. Black, M. C. Davies, S. J. B. Tendler, and K. M. Shakeshef (1998) A novel biotinylated degradable polymer for cell-interactive applications.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 58: 529–535.
Ito, Y. (1998) Regulation of cell functions by micropattern-immobilized biosignal molecules.Nanotechnology 9: 200–204.
Wueller-Klieser, M. (1997) Three-dimensional cell cultures: from molecular mechanisms to clinical applications.Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 273: C1109-C1123.
Hoffman, R. M. (1994) The three-dimensional question: can clinically-relevant tumor drug resistance be measuredin vitro.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 13: 169–173.
Chen, G., T. Ushida, and T. Tateishi (2000) A biodegradable hybrid sponge nested with collagen microsponges.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 51: 273–279.
Kim, B.-S. and D. J. Mooney (1998) Development of biocompatible synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue engineering.Trends Biotechnol. 16: 224–230.
Sittinger, M., J. Bujia, N. Rotter, D. Reitzel, W. W. Minuth, and G. R. Burmester (1996) Tissue engineering and autologous transplant formation: practical approaches with resorbable biomaterials and new cell culture techniques.Biomaterials 17: 237–242.
Bhat, G. S. (1995) Nonwovens as three-dimensional textiles for composites.Materials Manufacturing Proc. 10: 667–688.
Wake, M. C., P. K. Gupta, and A. G. Mikos (1996) Fabrication of pliable biodegradable polymer foams to engineer soft tissues.Cell Transplantation 5: 465–473.
Lu, L. and A. G. Mikos (1996) The importance of new processing techniques in tissue engineering.MRS Bulletin 21: 28–32.
Harris, L. D., B. S. Kim, and D. J. Mooney (1998) Open pore biodegradable matrices foamed with gas foaming.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 42: 396–402.
Whang, K., C. H. Thomas, and K. E. Healy (1995) A novel method to fabricate bioasorbable scaffolds.Polymer 36: 837–842.
Kang, H.-W., Y. Tabata, and Y. Ikada (1999) Fabrication of porous gelatin scaffolds for tissue engineering.Biomaterials 20: 1339–1344.
Mooney, D. J., C. L. Mazzoni, C. Breuer, K. McNamara, D. Hern, J. P. Vacanti, and R. Langer (1996) Stabilized polyglycolic acid fibre-based tubes for tissue engineering.Biomaterials 17: 115–124.
Li, Y., T. Ma, S. T. Yang, and D. A. Kniss (2001) Thermal compression and characterization of three-dimensional nonwoven PET matrices as tissue engineering scaffolds.Biomaterials 22: 609–618.
Kim, S.-H. and C.-C. Chu (2000). Pore structure analysis of swollen dextran-methacrylate hydrogel by SEM and mercury intrusion porosimetry.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. (Appl. Biomater.) 53: 258–266.
Berthiaume, E., P. Moghe, M. Toner, and M. L. Yarmush (1996) Effect of extracellular matrix topology on cell structure, function, and physiological responsiveness: hepatocytes cultured in a sandwich configuration.FASEB J. 10: 1471–1478.
Freed, L. E., J. C. Marquis, G. Vunjak-Novakovic, J. Emmanual, and R. Langer (1994) Composition of cell-polymer cartilage implants.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 43: 605–614.
Sanders, J. E., C. E. Stiles, and C. L. Hayes (2000) Tissue response to single-polymer fibers of varying diameters: Evaluation of fibrous encapsulation and macrophage density.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52: 231–237.
Wintermantel, E., J. Mayer, K.-L. Eckert, P. Luscher, and M. Mathey (1996) Tissue engineering scaffolds using superstructures.Biomaterials 17: 83–91.
Ranucci, C. S. and P. V. Moghe (1999) Polymer substrate topography actively regulates the multicellular organization and liver-specific functions of cultured hepatocytes.Tissue Eng. 5: 407–420.
Ranucci, C. S., A. Kumar, S. P. Batra, and P. V. Moghe (2000) Control of hepatocyte function on collagen foams: sizing matrix pores toward selective induction of 2-D and 3-D cellulr morphogenesis.Biomaterials 21: 783–793.
Takagi, M., T. Sasaki, and T. Yoshida (1999) Spatial development of the cultivation of a bone marrow stromal cell line in porous carriers.Cytotechnology 31: 225–231.
Nehrer, S., H. A. Breinan, A. Ramappa, G. Young, S. Shortkroff, L. K. Louie, C. B. Sledge, I. V. Yannas, and M. Spector (1997) Matrix collagen type and pore size influence behaviour of seeded canine chondrocytes.Biomaterials 18: 769–776.
Brauker, J. H., V. E. Carr-Brendel, L. A. Martinson, J. Crudele, W. D. Johnston, and R. C. Johnson (1995) Neovascularization of synthetic membranes directed by membrane microarchitecture.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29: 1517–1524.
Wake, M. C., C. W. Patrick, and A. G. Mikos (1994) Pore morphology effects on the fibrovascular tissue growth in porous polymer substrates.Cell Transplantation 3: 339–343.
Yannas, I. V., E. Lee, O. P. Orgil, E. M. Krabut, and F. Murphy (1989) Synthesis and characterization of a model extracellular matrix that induces partial regeneration of adult mammalian skin.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 933–937.
Evans, G. R. D., K. Brandt, M. S. Widmer, L. Lu, R. K. Meszlenyi, P. K. Gupta, A. G. Mikos, J. Hodges, J. Williams, A. Gurlek, A. Nabawi, R. Lohman, and Jr. C. W. Patrick (1999) In vivo evaluation of poly(L-lactic acid) porous conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration.Biomaterials 20: 1109–1115.
Dillon, G. P., X. Yu, A. Sridharan, J. P. Ranieri, and R. V. Bellamkonda (1998) The influence of physical structure and charge on neurite extension in a 3D hydrogel scaffold.J. Biomaterials Sci. Polymer Edition 9: 1049–1069.
Patrick, C. W., P. B. Chauvin, J. Hobley, and G. P. Reece (1999) Preadipocyte seeded PLGA scaffolds for adipose tissue engineering.Tissue Eng. 5: 139–151.
Chang, B.-S., C.-K. Lee, K.-S. Hong, H.-J. Youn, H.-S. Ryu, S.-S. Chung, and K.-W. Park (2000) Osteoconduction at porous hydroxyapatite with various pore configurations.Biomaterials 21: 1291–1298.
Gauthier, O., J.-M. Bouler, E. Aguado, P. Pilet, and G. Daculsi (1998) Macroporous biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics: influence of macropore diameter and macroporosity percentage on bone ingrowth.Biomaterials 19: 133–139.
Whang, K., K. E. Healy, D. R. Elenz, E. K. Nam, D. C. Tsai, C. H. Thomas, G. W. Nuber, F. H. Glorieux, R. Travers, and S. M. Sprague (1999) Engineering bone regeneration with bioabsorbable scaffolds with novel microarchitecture.Tissue Eng. 5: 35–51.
Hayen, W., M. Goebeler, S. Kumar, R. Rieben, and V. Hehls (1999) Hyaluronan stimulates tumor cell migration by modulating the fibrin fiber architecture.J. Cell Sci. 112: 2241–2251.
Matsuda, T. and Y. Nakayama (1996) Surface microarchitectural design in biomedical applications: in vitro transmural endothelialization on microporous segmented polyurethane films fabricated using an excimer laser:J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 31: 235–242.
Ma, T., Y. Li, S. T. Yang, and D. A. Kniss (1999) Tissue engineering human placenta trophoblast cells in 3-D fibrous matrix: spatial effects on cell proliferation and function.Biotechnol. Prog. 15: 715–724.
Ma, T., Y. Li, S. T. Yang, and D. A. Kniss (2000) Effects of pore size in 3-D fibrous matrix on human trophoblast tissue development.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 70: 606–618.
Herbert, C. B., C. Nagaswami, G. D. Bittner, J. A. Hubbell, and J. W. Weisel (1998) Effects of fibrin micromorphology on neurite growth from dorsal root ganglia cultured in three-dimensional fibrin gels.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 40: 551–559.
Freed, L. E., G. Vunjak-Novakovic, and R. Langer (1993) Cultivation of cell-polymer cartilage implants in bioreactors.J. Cellular Biochem. 51: 257–264.
Ishaug, S. L., G. M. Crane, M. J. Miller, A. W. Yasko, M. J. Yaszemski, and A. G. Mikos (1997) Bone formation by three-dimensional stromal osteoblast culture in biodegradable polymer scaffolds.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 36: 17–28.
Ishaug-Riley, S. L., G. M. Crane, M. J. Yaszemski, and A. G. Mikos (1998) Three-dimensional culture of rat calvarial osteoblasts in porous biodegradable polymers.Biomaterials 36: 17–28.
Kino, Y., M. Sawa, S. Kasai, F. Nakazawa, K. Kato, T. Yamamoto, and M. Mito (1996) Immobilization of rat hepatocytes on multiporous microcarriers with larger pores and their metabolic activity.Cell Transplantation 5: S35-S37.
Kaufmann, P. M., S. Heimrath, B. S. Kim, and D. J. Mooney (1997) Highly porous polymer matrices as a three-dimensional culture system for hepatocytes: initial results.Transplantation Proceedings 29: 2032–2034.
Moghe, P. V., F. Berthiaume, R. M. Ezzell, M. Toner, R. G. Tompkins, and M. L. Yarmush (1996) Culture matrix configuration and composition in the maintenance of hepatocyte polarity and function.Biomaterials 17: 373–385.
Shea, L. D., E. Smiley, J. Bonadio, and D. J. Mooney (1999) DNA delivery from polymer matrices for tissue engineering.Nature Biotechnol. 17: 551–554.
Eiselt, P., B.-S. Kim, B. Chacko, B. Isenberg, M. C. Peters, K. G. Greene, W. D. Roland, A. B. Loebsack, K. J. L. Burg, C. Culberson, C. R. Halerstadt, W. D. Holder, and D. J. Mooney (1998) Development of technologies aiding large-tissue engineering.Biotechnol. Prog. 14: 134–140.
Hubbell, J. A. (1999) Bioactive biomaterials.Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 10: 123–129.
Maquet, V., D. Martin, B. Malgrange, R. Franzen, J. Schoenen, G. Moonen, and R. Jerome (2000) Peripheral nerve regeneration using bioresorbable macroporous polylactide scaffolds.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52: 639–651.
Freed, L. E. and G. Vunjak-Novakovic (1998) Culture of organized cell communities.Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 33: 15–30.
Goldstein, A. S., G. Zhu, G. E. Morris, R. K. Meszlenyi, and A. G. Mikos (1999) Effect of osteoblastic culture conditions on the structure of poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) foam scaffolds.Tissue Eng. 5: 421–433.
Shapiro, L. and S. Cohen (1997) Novel alginate sponges for cell culture and transplantation.Biomaterials 18: 583–590.
Kim, B.-S. and D. J. Mooney (1998) Engineering smooth muscle tissue with a predefined structure.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 41: 322–332.
Kellomaki, M., H. Niiranen, K. Puumanen, N. Ashammakhi, T. Waris, and P. Tormala (2000) Bioabsorbable scaffolds for guided bone regeneration and generation.Biomaterials 21: 2495–2505.
Hutmacher, D. W. (2000) Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.Biomaterials 21: 2529–2543.
Burg, K. J. L., S. Porter, and J. F. Kellam (2000) Biomaterial development for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials 21: 2347–2359.
Reddi, A. H. (2000) Morphogenesis and tissue engineering of bone and cartilage: inductive signals, stem cells, and biomimetic biomaterials.Tissue Eng. 6: 351–359.
Naughton, B. A., R. A. Preti, and G. K. Naughton (1987) Hematopoiesis on nylon mesh templates. I. Long-term culture of rat bone marrow cells.J. Med. 18: 219–250.
Wang, T.-Y., J. K. Brennan, and J. H. D. Wu (1995) Multilineal hematopoiesis in a three-dimensional murine long-term bone marrow culture.Exp. Hematol. 23: 26–32.
Bagley, J., M. Rosenzweig, D. F. Marks, and M. J. Pykett (1999) Extended culture of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors without cytokine augmentation in a novel three-dimensional device.Exp. Hematol. 27: 496–504.
Li, Y., T. Ma, S. T. Yang, D. A. Kniss, and L. C. Lasky (2000) Ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic progenitors from human cord blood cells in three-dimensional fibrous matrices.Blood 16 (Suppl): 777a.
Tomimori, Y., M. Takagi, and T. Yoshida (2000) The construction of an in vitro three-dimensional hematopoietic microenvironment for mouse bone marrow cells employing porous carriers.Cytotechnology 34: 121–130.
Thomson, J. A. and J. S. Odorico (2000) Human embryonic stem cell and embryonic germ cell lines.Trends Biotechnol. 18: 53–57.
Nakano, T. (1996)In vitro development of hematopoietic system from mouse embryonic stem cells: a new approach for embryonic hematopoiesis.Int. J. Hematol. 65: 1–8.
Schuldiner, M., O. Yanuka, J. Itskovitz-Eldor, D. A. Melton, and N. Benvenisty (2000) Effects of eight growth factors on the differentiation of cells derived from human embryonic stem cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 11307–11312.
Zandstra, P. W., H.-V. Le, G. O. Daley, L. G. Griffith, and D. A. Lauffenburger (2000) Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) concentration modulates embryonic stem cell selfrenewal and differentiation independently of proliferation.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 69: 607–617.
Muckle, D. S. and R. J. Minns (1989) Biological response to woven carbon fibre pads in the knee: a clinical and experimental study.J. Bone Jt. Surg. (Br.) 71: 60–62.
Grande, D. A., C. Halberstadt, G. Naughton, R. Schwartz, and R. Manji (1997) Evaluation of matrix scaffolds for tissue engineering of articular cartilage grafts.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 34: 211–220.
Dasdia, T., S. Bazzaco, L. Bottero, R. Buffa, S. Ferrero, G. Campanelli, and E. Dolfini (1998) Organ culture in 3-Dimensional matrix:in vitro model for evaluating biological compliance of synthetic mashes for abdominal wall repair.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 43: 204–209.
Hasegawa, M., A. Sudo, Y. Shikinami, and A. Uchida (1999) Biological performance of a three-dimensional fabric as artificial cartilage in the repair of large osteochondral defects in rabbit.Biomaterials 20: 1969–1975.
Freed, L. E., G. Vunjak-Novakovic, R. J. Biron, D. B. Eagles, D. C. Lesnoy, S. K. Barlow, and R. Langer (1994) Biodegradable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering.Bio/Technology 12: 689–693.
Brown, A. N., B.-S. Kim, E. Alsberg, and D. J. Moony (2000) Combining chondrocytes and smooth muscle cells to engineer hybrid soft tissue constructs.Tissue Eng. 6: 297–305.
Perka, C., R.-S. Spitzer, K. Lindenhayn, M. Sittinger, and O. Schultz (2000) Matrix-mixed culture: New methodology for chondrocyte culture and preparation of cartilage transplants.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 49: 305–311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yang, ST. Effects of three-dimensional scaffolds on cell organization and tissue development. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 6, 311–325 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932999
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932999