Abstract
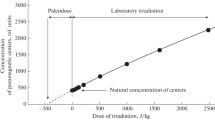
Average life of oxygen vacancies of quartz in sediments is estimated by using the ESR (electron spin resonance) signals of E’ centers from the thermal activation technique. The experimental results show that the second-order kinetics equation is more applicable to the life estimation compared with the first order equation. The average life of oxygen vacancies of quartz from 4895 to 4908 deep sediments in the Tarim Basin is about 1018 a at 27°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toyoda, S., Ikeya, M., Thermal stabilities of paramagnetic and defect and impurity centers in quartz: Basic for ESR dating of thermal history, Geochem. J., 1991, 25: 437–445.
Ye, Y. G., Diao, S. B., Wu, X. L. et al., Thermodynamic behavior of E’centers in quartz from deep sediments of the Tarim Basin, Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2001, 28 (5): 23–24.
Jin, S. Z., Peng, Z. C., Huang, P. H. et al., ESR research on loess in Luochuan, Chinese Sci. Bull., 1988, 33 (14): 1092–1095.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diao, S., Ye, Y. Average life of oxygen vacancies of quartz in sediments. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 45 (Suppl 1), 55–60 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932207
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932207