Abstract
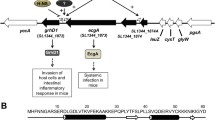
Using transcriptional promoter fusions, we investigated the expression of selected SPI-1 and SPI-2 genes ofSalmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium). Promoters of genes related to the invasion of the epithelial cell (hilA, hilC, hilD, invF, sicA, sopA, sopB andsopE2) were active in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium and LB with butyrate but were suppressed by bile salts and in glucose minimal (M9) medium. Genes related toS. Typhimurium intracellular survival (phoP, ssrA, ssaB, ssaG, sifA, sifB andpipB) were characterized by their expression in stationary phase in LB and M9 medium. Activity ofphoP andssrA promoters indicated that these might be expressed inside the gut. SPI-1 genes were expressed on the transition to stationary phase while SPI-2 genes were expressed in stationary phase. Among SPI-1 genes, those with regulatory functions preceded in expression the effector genes andsop genes were expressed in the order ofsopA, sopB andsopE2, showing hierarchy in the expression ofS. Typhimurium virulence genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LB:
-
Luria-Bertani (medium)
- M9:
-
glucose minimum medium
- RLU:
-
relative luminescence units
- S. Typhimurium:
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- SPI:
-
salmonella pathogenicity island
- TTSS:
-
type III secretion system
References
Bajaj V., Lucas R.L., Hwang C., Lee C.A.: Co-ordinate regulation ofSalmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control ofhilA expression.Mol.Microbiol. 22, 703–714 (1996).
Barrow P.A., Hassan J.O., Berchieri A. Jr.: Reduction in fecal excretion ofSalmonella typhimurium strain F98 in chickens vaccinated with live and killedS. typhimurium organisms.Epidemiol.Infect. 104, 413–426 (1990).
Behlau I., Miller S.I.: A PhoP-repressed gene promotesSalmonella typhimurium invasion of epithelial cells.J.Bacteriol. 175, 4475–4484 (1993).
Beuzon C.R., Meresse S., Unsworth K.E., Ruiz-Albert J., Garvis S., Waterman S.R., Ryder T.A., Boucrot E., Holden D.W.:Salmonella maintains the integrity of its intracellular vacuole through the action of SifA.EMBO J. 19, 3235–3249 (2000).
Bijlsma J.J., Groisman E.A.: The PhoP/PhoQ system controls the intramacrophage type three secretion system ofSalmonella enterica.Mol.Microbiol. 57, 85–96 (2005).
Blanc-Potard A.B., Solomon F., Kayser J., Groisman E.A.: The SPI-3 pathogenicity island ofSalmonella enterica.J.Bacteriol. 181, 998–1004 (1999).
Boddicker J.D., Jones B.D.: Lon proteinase activity causes down-regulation ofSalmonella pathogenicity island 1 invasion gene expression after infection of epithelial cells.Infect.Immun. 72, 2002–2013 (2004).
Brown N.F., Vallance B.A., Coombes B.K., Valdez Y., Coburn B.A., Finlay B.B.:Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 is expressed prior to penetrating the intestine.PLoS Pathog. 1, e32 (2005).
Cirillo D.M., Valdivia R.H., Monack D.M., Falkow S.: Macrophage-dependent induction of theSalmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system and its role in intracellular survival.Mol.Microbiol. 30, 175–188 (1998).
Darwin K.H., Miller V.L.: InvF is required for expression of genes encoding proteins secreted by the SPI1 type III secretion apparatus inSalmonella typhimurium.J.Bacteriol. 181, 4949–4954 (1999).
Darwin K.H., Miller V.L.: The putative invasion protein chaperone SicA acts together with InvF to activate the expression ofSalmonella typhimurium virulence genes.Mol.Microbiol. 35, 949–960 (2000).
Darwin K.H., Miller V.L.: Type III secretion chaperone-dependent regulation: activation of virulence genes by SicA and InvF inSalmonella typhimurium.EMBO J. 20, 1850–1862 (2001).
Doyle T.C., Burns S.M., Contag C.H.:In vivo bioluminescence imaging for integrated studies of infection.Cell.Microbiol. 6, 303–317 (2004).
Drecktrah D., Knodler L.A., Galbraith K., Steele-Mortimer O.: TheSalmonella SPI1 effector SopB stimulates nitric oxide production long after invasion.Cell.Microbiol. 7, 105–113 (2005).
Dukes J.D., Lee H., Hagen R., Reaves B.J., Layton A.N., Galyov E.E., Whitley P.: The secretedSalmonella dublin phosphoinositide phosphatase, SopB, localizes to PtdIns(3)P-containing endosomes and perturbs normal endosome to lysosome trafficking.Biochem.J. 395, 239–247 (2006).
Durant J.A., Corrier D.E., Ricke S.C.: Short-chain volatile fatty acids modulate the expression of thehilA andinvF genes ofSalmonella typhimurium.J.Food Prot. 63, 573–578 (2000).
Eichelberg K., Galan J.E.: Differential regulation ofSalmonella typhimurium type III secreted proteins by pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1)-encoded transcriptional activators InvF andhilA.Infect.Immun. 67, 4099–4105 (1999).
Eriksson S., Lucchini S., Thompson A., Rhen M., Hinton J.C.: Unravelling the biology of macrophage infection by gene expression profiling of intracellularSalmonella enterica.Mol.Microbiol. 47, 103–118 (2003).
Feng X., Oropeza R., Kenney L.J.: Dual regulation by phospho-OmpR ofssrA/B gene expression inSalmonella pathogenicity island 2.Mol.Microbiol. 48, 1131–1143 (2003).
Freeman J.A., Ohl M.E., Miller S.I.: TheSalmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium translocated effectors SseJ and SifB are targeted to theSalmonella-containing vacuole.Infect.Immun. 71, 418–427 (2003).
Hensel M., Shea J.E., Waterman S.R., Mundy R., Nikolaus T., Banks G., Vazquez-Torres A., Gleeson C., Fang F.C., Holden D.W.: Genes encoding putative effector proteins of the type III secretion system ofSalmonella pathogenicity island 2 are required for bacterial virulence and proliferation in macrophages.Mol.Microbiol. 30, 163–174 (1998).
Kalir S., McClure J., Pabbaraju K., Southward C., Ronen M., Leibler S., Surette M.G., Alon U.: Ordering genes in a flagella pathway by analysis of expression kinetics from living bacteria.Science 292, 2080–2083 (2001).
Kaniga K., Trollinger D., Galan J.E.: Identification of two targets of the type III protein secretion system encoded by theinv andspa loci ofSalmonella typhimurium that have homology to theShigella IpaD and IpaA proteins.J.Bacteriol. 177, 7078–7085 (1995).
Knodler L.A., Celli J., Hardt W.D., Vallance B.A., Yip C., Finlay B.B.:Salmonella effectors within a single pathogenicity island are differentially expressed and translocated by separate type III secretion systems.Mol.Microbiol. 43, 1089–1103 (2002).
Kubori T., Galan J.E.: Temporal regulation ofSalmonella virulence effector function by proteasome-dependent protein degradation.Cell 115, 333–342 (2003).
Layton A.N., Brown P.J., Galyov E.E.: TheSalmonella translocated effector SopA is targeted to the mitochondria of infected cells.J.Bacteriol. 187, 3565–3571 (2005).
Lostroh C.P., Bajaj V., Lee C.A.: The cis requirements for transcriptional activation by HilA, a virulence determinant encoded on SPI-1.Mol.Microbiol. 37, 300–315 (2000).
Miller S.I., Kukral A.M., Mekalanos J.J.: A two-component regulatory system (phoP phoQ) controlsSalmonella typhimurium virulence.Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA 86, 5054–5058 (1989).
Norris F.A., Wilson M.P., Wallis T.S., Galyov E.E., Majerus P.W.: SopB, a protein required for virulence ofSalmonella dublin is an inositol phosphate phosphatase.Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA 95, 14057–14059 (1998).
Olekhnovich I.N., Kadner R.J.: DNA-binding activities of the HilC and HilD virulence regulatory proteins ofSalmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J.Bacteriol. 184, 4148–4160 (2002).
Prouty A.M., Gunn J.S.:Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium invasion is repressed in the presence of bile.Infect.Immun. 68, 6763–6769 (2000).
Rakeman J.L., Bonifield H.R., Miller S.I.: A HilA-independent pathway toSalmonella typhimurium invasion gene transcription.J.Bacteriol. 181, 3096–3104 (1999).
Rychlik I., Barrow P.A.:Salmonella stress management and its relevance to behavior during intestinal colonization and infection.FEMS Microbiol.Rev. 29, 1021–1040 (2005).
Schechter L.M., Damrauer S.M., Lee C.A.: Two AraC/XylS family members can independently counteract the effect of repressing sequences upstream of thehilA promoter.Mol.Microbiol. 32, 629–642 (1999).
Schechter L.M., Lee C.A.: AraC/XylS family members, HilC and HilD, directly bind and derepress theSalmonella typhimurium hilA promoter.Mol.Microbiol. 40, 1289–1299 (2001).
Shea J.E., Hensel M., Gleeson C., Holden D.W.: Identification of a virulence locus encoding a second type III secretion system inSalmonella typhimurium.Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA 93, 2593–2597 (1996).
Shotland Y., Kramer H., Groisman E.A.: TheSalmonella SpiC protein targets the mammalian Hook3 protein function to alter cellular trafficking.Mol.Microbiol. 49, 1565–1576 (2003).
Stender S., Friebel A., Linder S., Rohde M., Mirold S., Hardt W.D.: Identification of SopE2 fromSalmonella typhimurium, a conserved guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Cdc42 of the host cell.Mol.Microbiol. 36, 1206–1221 (2000).
Tucker S.C., Galan J.E.: Complex function for SicA, aSalmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium type III secretion-associated chaperone.J.Bacteriol. 182, 2262–2268 (2000).
Uchiya K., Barbieri M.A., Funato K., Shah A.H., Stahl P.D., Groisman E.A.: ASalmonella virulence protein that inhibits cellular trafficking.EMBO J. 18, 3924–3933 (1999).
Ulitzur S., Matin A., Fraley C., Meighen E.: H-NS protein represses transcription of thelux systems ofVibrio fischeri and other luminous bacteria cloned intoEscherichia coli.Curr.Microbiol. 35, 336–342 (1997).
Van Immerseel F., De Buck J., Boyen F., Bohez L., Pasmans F., Volf J., Ševčík M., Rychlik I., Haesebrouck F., Ducatelle R.: Medium-chain fatty acids decrease colonization and invasion throughhilA suppression shortly after infection of chickens withSalmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis.Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 70, 3582–3587 (2004).
Wong K.K., McClelland M., Stillwell L.C., Sisk E.C., Thurston S.J., Saffer J.D.: Identification and sequence analysis of a 27-kilobase chromosomal fragment containing aSalmonella pathogenicity island located at 92 minutes on the chromosome map ofSalmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2.Infect.Immun. 66, 3365–3371 (1998).
Wood M.W., Jones M.A., Watson P.R., Hedges S., Wallis T.S., Galyov E.E.: Identification of a pathogenicity island required forSalmonella enteropathogenicity.Mol.Microbiol. 29, 883–891 (1998).
Wood M.W., Jones M.A., Watson P.R., Siber A.M., McCormick B.A., Hedges S., Rosqvist R., Wallis T.S., Galyov E.E.: The secreted effector protein ofSalmonella dublin, SopA, is translocated into eukaryotic cells and influences the induction of enteritis.Cell.Microbiol. 2, 293–303 (2000).
Zaslaver A., Mayo A.E., Rosenberg R., Bashkin P., Sberro H., Tsalyuk M., Surette M.G., Alon U.: Just-in-time transcription program in metabolic pathways.Nature Genet. 36, 486–491 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work has been supported by projects 1B44020 of theMinistry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic and EU project 505523.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papezova, K., Gregorova, D., Jonuschies, J. et al. Ordered expression of virulence genes inSalmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Folia Microbiol 52, 107–114 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932148
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932148