Abstract
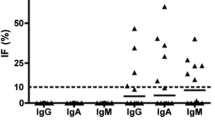
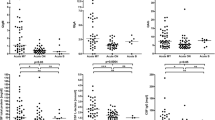
Levels of most of the examined proteins in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of 107 patients with neuroborreliosis were associated with cytological findings, the status of hematoencephalic barrier as evaluated byQ alb (cerebrospinal fluid to serum quotient) and the intrathecal synthesis of immunoglobulins. Cytological findings consisted of normal cytology, or both oligocytosis and pleocytosis of monocytes or lymphocytes. The lipophagic elements were present in 20 % of samples. Concentrations of apolipoproteins A-I and A-II in the CSF were correlated with the concentration of albumin without regard to the CSF cytology. The levels of apolipoprotein B were increased only in samples with lymphocytic pleocytosis andQ alb > 7.4. The presence of lipophages in the CSF was significantly associated with the CSF concentration of apolipoprotein A-II.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Apo:
-
apolipoproteins
- BBB:
-
blood-brain barrier
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- Ig:
-
immunoglobulins
- Ly-O:
-
lymphocytic oligocytosis
- Ly-P:
-
lymphocytic pleocytosis
- Mo-O:
-
monocytic oligocytosis
- Mo-P:
-
monocytic pleocytosis
- Q alb :
-
CSF albumin-to-serum albumin quotient
References
Adam P., Nekola P., Havrdova E.: Evaluation of CSF apolipoprotein A-I concentrations — a comparison with CSF cytological findings.Clin.Biochem.Metab.5, 8–12 (1997).
Adam P., Tichy J., Nekola P.: Biological role of apolipoprotein (Apo) A-II in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).Europ.J.Neurol.5, 219–222 (1998).
Adam P, Táborský L., Sobek O., Hildebrand T., Kelbich P., Průcha M., Hyánek J.: Cerebrospinal fluid.Adv.Clin.Chem.36, 1–62 (2001).
Araki H., Satoh K., Terajima M., Nakagawa T., Higuchi M., Kosaka Y., Zhu C., Sasaki H.: Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid — a potential marker of Alzheimer’s disease.Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi33, 669–675 (1996).
Bassett C.N., Montine K.S., Neely M.D., Swift L.L., Montine T.J.: Cerebrospinal fluid lipoproteins in Alzheimer’s disease.Microsci.Res.Techn.50, 282–286 (2000).
Blennow K., Hesse C., Fredman P.: Cerebrospinal fluid apolipoprotein E is reduced in Alzheimer’s disease.Neuroreport5, 2534–2536 (1994).
Carlsson J., Armstrong V.W., Reiber H., Felgenhauer K., Seidel D.: Clinical relevance of the quantification of apolipoprotein E in cerebrospinal fluid.Clin.Chim.Acta196, 167–176 (1991).
Castellani L.W., Lusis A.J.: ApoA-IIversus ApoA-I: two for one is not always a good deal.Arterioscler.Thromb.Vasc.Biol.21, 1870–1872 (1903).
Chiba H., Mitamura T., Fujisawa S., Ogata A., Aimoto Y., Tashiro K., Kobayashi K.: Apolipoproteins in rat CSF: a comparison with plasma lipoprotein metabolism and effect of aging.Neurosci.Lett.133, 207–210 (1991).
Dawson P.A., Schechter N., Williams D.L.: Induction of rat E and chicken A-I apolipoproteins and mRNAs during optic nerve degeneration.J.Biol.Chem.261, 5681–5684 (1986).
De Breedveld B., Kuiper J., Van Breimer D.D.: High-density lipoprotein and cerebral endothelial cellsin vitro: interactions and transport.Biochem.Pharmacol.50, 271–273 (1995).
Elshourbagy N.A., Bougski M.S., Liao W.S., Jefferson L.S., Gordon J.I., Taylor J.M.: Expression of rat apolipoprotein A-IV and A-I genes: mRNA induction during development and in response to glucocorticoids and insulin.Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA82, 8242–8246 (1985).
Escola G., Marzal C., Julve G., Ishida B.Y., Ordonez L., Chan L., Gonzalez S., Blanco V.: Human apolipoprotein A-II is a proatherogenic molecule when it is expressed in transgenic mice at a level similar to that in humans: evidence of a potentially relevant species-specific interaction with diet.J.Lipid Res.39, 457–462 (1998).
Felgenhauer K.: Laboratory diagnosis of neurological diseases, pp. 1308–1326 in L. Thomas (Ed.):Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics, Vol. 54. TH Books-Verlag Gesselschaft, Frankfurt/Main (Germany) 1998.
Gaillard O., Gervais A., Meillet D., Plassart E., Fontaine B., Lyon-Caen O., Delattre J., Schuller E.: Apolipoprotein E and multiple sclerosis: a biochemical and genetic investigation.J.Neurol.Sci.158, 180–186 (1998).
Hahne S., Nordstedt C., Ahlin A., Nyback H.: Levels of cerebrospinal fluid apolipoprotein E in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and healthy controls.Neurosci.Lett.224, 99–102 (1997).
Hančil J.: Lyme borreliosis, pp. 207–215 in M. Duniewicz, P. Adam,et al. (Eds):Neuroinfective Diseases. Maxdorf Jessenius, Prague 1999.
Harel A., Fainaru M., Shafer Z., Hernandez M., Cohen A., Schwartz M.: Optic nerve regeneration in adult fish and apolipoprotein A-I.J.Neurochem.52, 1218–1228 (1989).
Higuchi K., Naiki H., Kitagawa K., Kitado H., Kogishi K., Matsushita T., Takeda T.: Apolipoprotein A-II gene and development of amyloidosis and senescence in a congenic strain of mice carrying amyloidogenic ApoA-II.Lab.Invest.72, 75–82 (1995).
Kaiser R.: Variable CSF findings in early and late Lyme neuroborreliosis: a follow-up study in 47 patients.J.Neurol.242, 26–36 (1994).
Kane J.P., Havel R.J.: Disorders of the biogenesis and secretion of lipoproteins containing the B apolipoproteins, in C.R. Seriveret al. (Eds):The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 7th ed. Mc Graw-Hill, New York 1995.
Koch S., Donarski N., Goetze K., Kreckel M., Stuerenburg H.J., Buhmann C., Beisiegel U.: Characterization of four lipoprotein classes in human cerebrospinal fluid.J.Lipid Res.42, 1143–1151 (1992).
La Du M.J., Reardon C., Van Eldik L., Fagan A.M., Bu G., Holtzman D., Getz G.S.: Lipoproteins in the central nervous system.Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci.903, 167–175 (2000).
Lefranc D., Vermersch P., Dallongeville J., Daems-Monpeurt C., Petit H., Delacourte A.: Relevance of the quantification of apolipoprotein E in the CSF in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurosci.Lett.212, 91–94 (1996).
Linton M.F., Gish R., Hubl S.T., Butler E., Esquivel C., Bry W.I., Boyles J.K., Wardell M.R., Young S.G.: Phenotypes of apolipoprotein B and apolipoprotein E after liver transplantation.J.Clin.Invest.88, 270–281 (1991).
Meluzínová E., Adam P., Bojar M.: Findings in cerebrospinal fluid in the patients with neuroborreliosis.Clin.Biochem.Metab.5, 12–14 (1997).
Milne R., Theolis R., Maurice R., Pease R.J., Weech P.K., Rassart E., Fruchart J.C., Scott J., Marcel Y.L.: The use of monoclonal antibodies to localize the low density lipoprotein receptor-binding domain of apolipoprotein B.J.Biol. Chem.264, 19754–19760 (1989).
Möckel B., Zinke H., Flach R., Weiss B., Weiler G., Gassen H.G.: Expression of apolipoprotein A-I in porcine brain endotheliumin vitro.J.Neurochem.62, 788–798 (1994).
Osman I., Gaillard O., Meillet D., Bordas-Fonfrede M., Gervais A., Schuller E., Delattre J., Legrand A.: A sensitive time-resolved immunofluorometric assay for the measurement of apolipoprotein B in cerebrospinal fluid. Application to multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases.Eur.J.Clin.Chem.Clin.Biochem.33, 53–58 (1995).
Pachner A.R., Schaefer H., Amemiya K., Cadavid D., Zhang W.F., Reddy K., Neill T.: Pathogenesis of neuroborreliosis-lessons from a monkey model.Wien Klin.Wochenschr.110, 870–873 (1998).
Pitas R.E., Boyles J.K., Lee S.H., Hui D., Weisgraber K.H.: Lipoproteins and their receptors in the central nervous system. Characterization of the lipoproteins in cerebrospinal fluid and identification of apolipoprotein B,E(LDL) receptors in the brain.J.Biol.Chem.262, 14352–14360 (1987).
Rashid K.A., Hevi S., Chen Y., Le C., Chuck S.L.: A proteomic approach identifies proteins in hepatocytes that bind nascent apolipoprotein B.J.Biol.Chem.277, 22010–22017 (2002).
Razavi E., Fleury F., Gherardi R., Bernaudin J.F.: Cytologic features of cerebrospinal fluid in Lyme disease.Acta Cytol.31, 439–440 (1987).
Rebeck G.W., Alonzo N.C., Berezovska O., Harr S.D., Knowles R.B., Growdon J.H., Hyman B.T., Mendez A.J.: Structure and functions of human cerebrospinal fluid lipoproteins from individuals of different APOE genotypes.Exp.Neurol.149, 175–182 (1998).
Reiber H.: Flow rate of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) — a concept common to normal blood CSF barrier function and to dysfunction in neurological diseases.J.Neurol.Sci.122, 189–203 (1998).
Reiber H., Peter J.B.: Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: disease-related data patterns and evaluation programs.J.Neurol.Sci.184, 101–122 (2001).
Roheim P.S., Carey M., Forte T., Vega G.L.: Apolipoproteins in human CSF.Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA76, 4646–4649 (1979).
Saito K., Seishima M., Heyes M.P., Song H., Fujigaki S., Maeda S., Vickers J.H., Noma A.: Marked increases in concentrations of apolipoprotein in the cerebrospinal fluid of poliovirus-infected macaques: relations between apolipoprotein concentrations and severity of brain injury.Biochem.J.321, 145–149 (1997).
Salen G., Berginer V., Shore V., Horak I., Horak E., Tint G.S., Shefer S.: Increased concentrations of cholestanol and apolipoprotein B in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid.N.Engl.J.Med.316, 1233–1238 (1987).
Song H., Seishima M., Saito K., Maeda S., Takemura M., Noma A., Kondo A., Manabe M., Urakami K., Nakashima K.: Apo A-I and Apo E concentrations in CSF of patients with acute meningitis.Ann.Clin.Biochem.35, 408–414 (1998).
Tumani H., Nolker G., Reiber H.: Relevance of CSF variables for early diagnosis of neuroborreliosis.Neurology45, 1663–1670 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Táborský, L., Adam, P., Sobek, O. et al. Levels of apolipoprotein A-II in cerebrospinal fluid in patients with neuroborreliosis are associated with lipophagocytosis. Folia Microbiol 48, 849–855 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931523
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931523