Abstract
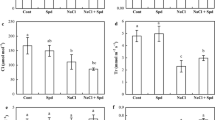
To cast light upon the role of Ca1+ and calmodulin on photosynthetic rate (Pn), dark respiration (RD) and amino acid and protein contents in salinity stressed and non-stressedChlorella cultures, the Ca2+ chelator EGTA [ethylene glycol-bis-(2-aminoethyl ether)-N,N- tetraacetate] and the calmodulin antagonist TFP (trifluperazine) were used. TFP markedly inhibited PN while EGTA exerted a slight, if any, effect on PN. NaCl tolerance, on the other side, was markedly abolished by TFP that inhibited PN and lowered rate of proline accumulation. Calmodulin might be involved in osmoregulation and salt tolerance ofChlorella. RD, however, was markedly enhanced by EGTA and Ca2+-free medium and hence the Ca2+ deprivation increased stress severity exerted by NaCl. Combinations of Na+ and Ca2+ enhanced PN, decreased RD and proline content in comparison with an osmotically equivalent reference culture containing only NaCl. Addition of Ca2+ to TFP treated cultures failed to reactivate calmodulin for proline synthesis. However, when Ca2+ was added to EGTA-treated cultures, only relatively reduced proline contents were recorded.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Basset, R.: Photosynthesis and some related metabolic processes as influenced by salinization treatments. - Ph.D. Thesis, Fac. Sci., Assiut Univ., Assiut 1986.
Bangerth, F., Dilley, D.R., Dewely, D.H.: Effect of postharvest calcium treatment on internal breakdown and respiration of apple fruit. - J. amer. Soc. hort. Sci.97: 679–682, 1972.
Barber, J.: Ionic regulation in intact chloroplasts and its effect on primary photosynthetic processes. - In: Barber, J. (ed.): The Intact Chloroplast. Pp. 89–134. Elsevier, Amsterdam 1976.
Barnett, N.M., Naylor, A.W.: Amino acid and protein metabolism in Bermuda grass during water stress. - Plant Physiol.41: 1222–1230, 1966.
Barr, R., Troxel, K.S., Grane, F.L.: Calmodulin antagonists inhibit electron transport in photosystem II of spinach chloroplasts. - Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.104: 1182–1188, 1982.
Bates, L.S., Waldren, R.P., Teare, I.D.: Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. -Plant Soil39: 205–207, 1973.
Burns, J.E., Clanton, C, Black, J.R.: Inhibition of coral and algal photosynthesis by Ca antagonist phenothiazine drugs. - Plant Physiol.71: 712–715, 1983.
Cheung, W.Y.: Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. - Science207: 19–27, 1980.
Dreier, W.: Verification and utilization of a preselection test system for the salt tolerance of plants based on proline content. -Biol. Plant.25: 88–94, 1983.
Ferguson, IB.: Calcium in plant senescence and fruit ripening. - Plant Cell Environ.7: 477–489, 1984.
Gale, J.: Water balance and gas exchange of plants under saline conditions. - In: Poljakoff-Mayber, A., Gale, J. (ed.): Plants in Saline Environment. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg - Berlin 1975.
Greenway, H., Munns, R.: Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. - Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.31: 149–190, 1980.
Gross, F.L., Zimmermann, R.J., Hormate, G.F.: The effects of mono- and divalent cations on the quantum yields for electron transport in chloroplasts. - Biochim. biophys. Acta440: 59–67, 1976.
Henkel, P.A.: Physiology of plants under drought. - Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.15: 363–369, 1964.
Imamul-Huq, S.M., Lahrer, F.: Osmoregulation in higher plants: Effects of maintaining a constant Na:Ca ratio on the growth, ion balance and organic solute of NaCl stressed cowpea (Vigna sinensis L). -Z. Pflanzenphysiol.113: 163–176, 1984.
Jarett, H.W., Brown, C.J., Black, C.C., Cormeir, M.J.: Evidence that calmodulin is in the chloroplast of peas and serves a regulatory role in photosynthesis. - J. biol. Chem.257: 13795–13804, 1982.
Jones, R.L., Jacobsen, J.V.: Calcium regulation of the secretion of a amylase isoenzymes and other proteins from barley aleurone layers. - Planta158: 1–9, 1983.
Kent, L, Läuchli, A.: Germination and seedling growth of cotton: salinity-calcium interactions. - Plant Cell Environ.8: 155–159, 1985.
Lahaye, P.A., Epstein, E.: Calcium and salt toleration by bean plants. - Physiol. Plant.25: 213–218, 1971.
Lambers, H., Szaniawski, R.K., De Visser, R.: Respiration for growth, maintenance and ion uptake. An evaluation of concepts, methods, values and their significance. - Physiol. Plant.58: 556–563, 1983.
Lee, Y.P., Takahanshi, T.: An improved colorimetric determination of amino acids with the use of ninhydrin. -Anal. Biochem.14: 71–77, 1966.
Leopold, A.C., Willing, R.P.: Evidence for toxicity effects of salt on membranes. - In: Staples, R.C., Toennissen, G.H. (ed.): Salinity Tolerance in Plants, Strategies for Crop Improvement. Pp. 67–91. John Wiley & Sons, New York1984.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. - J. biol. Chem.193: 265–275, 1951.
Lynch, J., Läuchli, A.: Salinity affects intracelluar calcium in com protoplasts. - Plant Physiol.87: 351–356, 1988.
Metzner, H., Rau, H., Senger, H.: Untersuchungen von Synchronisierbarkeit einzelner Pigmentmangel-Mutanten vonChlorella. - Planta65: 186–194, 1965.
Muto, S., Izawa, S., Miyachi, S.: Light induced Ca uptake by intact chloroplasts. - FEBS Lett.139: 250–254, 1982.
Pickard, B.G.: Comparison of calcium and lanthanum ions in theAvena coleoptile growth test. - Planta91: 314–320, 1970.
Schwarz, M., Gale, J.: Maintenance respiration and carbon balance of plant at low levels of sodium chloride salinity. -J. exp. Bot.32: 933–941, 1981.
Stein, J.R.: Growth and mating ofGonium pectorale (Volvocales) in defined media. - J. Phycol.2: 23–28,
Stewart, C.R., Hanson, A.D.: Proline accumulation as a metabolic response to water stress. - In: Turner, M.C., Kramer, P.J. (ed.): Adaptation of Plants to Water and High Temperature Stress Pp. 173–189. Wiley and Sons, New York 1980.
Thompson, J.F., Stewart, C.R., Morris, C.J.: Changes in amino acid content of exised leaves during incubation. 1. The effect of water content of leaves and atmospheric oxygen level. - Plant Physiol.41: 1578–1582, 1966.
Woodrow, I.E., Rowan, K.S.: Changes of flux of orthophosphate between cellular compartments in ripening tomato fruit in relation to the climacteric rise in respiration. - Aust. J. Plant Physiol.6: 39–46, 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Basset, R. Role of calcium and calmodulin antagonist in photosynthesis and salinity tolerance inChlorella vulgaris . Biol Plant 35, 237–244 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02925946
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02925946