Abstract
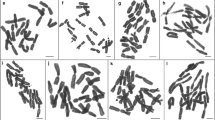
The cytological investigation of 12 taxa ofPanicum L. revealed that the vast majority of them have the basic number x=9 at different ploidy levels. The basic number x=8 was recorded only in the tetraploid speciesP. maximum with 2n=32. The diploid number 2n=18 was encountered inP. capillare, P. laevifolium, P. antidotale andP. coloratum (2) with 3B-chromosomes recorded in the latter species. The tetraploid chromosome number 2n=36 was found to exist inP. miliaceum, P. miliare, P. coloratum (1) andP. virgatum. The hexaploid number 2n=54 was recorded inP. bulbosum, P. dichotomiflorum andP. esculentum. The karyotypes of all accessions were mostly symmetrical and mainly comprised of meta- and submetacentric chromosomes with little variation in length among them within each karyotype. Investigation of chromosome association during metaphase I of meiosis revealed that the frequency of bivalents/cell was the highest among all investigated diploid, tetraploid and hexaploid accessions. Univalents were also frequently encountered in various accessions. These results may indicate that segmental alloploidy has been the major process by which polyploid species have originated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avdulov, N.P.: Systematic Karyology of the Family Gramineae.—Proc. All-Russ. bot. Kongr. Pp. 65–67. 1928.
Avdulov, N.P.: Karyo-systematische Untersuchung der Familie Gramineen.—Bull. appl. Bot. Plant. Breed.44 (Suppl.): 428, 1931.
Bolkhovskikh, Z., Grif, V., Matveeva, T., Zakharyeva, O.: Chromosome Number of a Flowering Plants.—Academy of Sciences of the USSR. V.L. Komarov Botanical Institute, Leningrad 1969.
Bouton, J.H., Brown, R.H., Bolton, I.K.: Photosynthesis of grass species differing in carbon dioxide fixation pathways.—Plant Physiol.67: 433–437, 1981.
Brown, W.L.: Cytological studies in Gramineae.—Amer. J. Bot.35: 382–396, 1948.
Brown, W.L.: Cytological studies of some Texas Gramineae.—Bull. Torrey bot. Club.77: 63–76, 1951.
Brown, W.L., Emery, W.H.P.: Apomixis in the Gramineae Panicoideae.—Amer. J. Bot.45: 253–263, 1958.
Burson, B.L., Bashaw, E.C.: Behaviour, transmission, and morphological effect of chromosomes inP. coloratum.—J. Crop. Sci.9: 176–179, 1969.
Burton, G.W.: A cytological study of some species in the tribe Paniceae.—Amer. J. Bot.29: 355–361, 1942.
Chandola, R.P.: Cytogenetics of millets.—Cytologia24: 115–137, 1959.
Chen, C., Huss, C.: Cytological studies on Taiwan grasses I. tribe Paniceae.—Bot. Bull. Acad. Chin. Sci.2: 101–110, 1961.
Christopher, I., Abraham A.: Studies on the cytology and phylogeny of south Indian grasses III. Subfamily 6. Panicoideae tribe I. The Paniceae.—Cytologia41: 621–634, 1976.
Church, G.L.: Meiotic phenomena in certain Gramineae II. Paniceae and Andropoganeae.—Bot. Gaz.88: 63–84, 1929.
Codd, L.E.W.: Seed setting and strain building in grasses with special reference to makarikari grass.— Forming S. Afr.14: 277–279, 1939.
Darlington, C.D., Wylie, A.B.: Chromosome Atlas of Flowering Plants. 3rd. Ed.—George Allen and Unwin, London 1955.
De Wet, J.M.J.: Chromosome numbers of a few South Africa grasses.—Cytologia19: 97–103, 1954.
Gould, F.W.: Chromosome number in southwestern grasses.—Amer. J. Bot.45: 757–768, 1958.
Gould, F.W.: Chromosome number in southwestern grasses II.—Amer. J. Bot.47: 873–877, 1960.
Hunter, A.W.S.: A karyosystematic investigation in the Gramineaee.—Can. J. Res.11: 213–224, 1934.
Hutchinson, D.G., Bashaw, E.C.: Cytology and reproduction ofP. coloratum and related species.— Crop Sci.4: 151–153, 1964.
Jauhar, P.P.: Occurrence of accessory chromosomes inP. maximum.—Curr. Sci.36: 244–245, 1967.
Jauhar, P.P., Joshi, A.B.: Cytological studies in some species ofPanicum.—Cytologia31: 153–159, 1965.
Jauhar, P.P., Joshi, A.B.: Accessory chromosomes in a new hexaploid species ofPanicum.— Cytologia21: 105–110, 1968.
Jauhar, P.P., Joshi, A.B.: Cytotaxonomic investigation in theP. maximum complex III.—Cytologia34: 222–233, 1969.
Joshi, A.B., Patil, B.D., Manchanda, P.L.: Chromosome numbers in some grasses.—Curr. Sci.,28: 454–455, 1959.
Krishnaswamy, N.: Untersuchungen zur Zytologie und Systematik der Gramineen.—Beih. bot. Centralbl.60: 1–50, 1940.
Kumatsu, T., Suzuki, S.: Chromosome numbers, behaviour and mode of reproduction in introduced strain ofPanicum species.—J. jap. Soc. Grassl. Sci.33: 56–61, 1987.
Moffett, A.A., Hurcombe, R.: Chromosome numbers of South African grasses.—Heredity3: 369–373, 1949.
Narayan, K.N.: Apomixis in some species ofPennisetum and inPanicum antidotale in plant embrology.—A Symposium. Council of Scientific and Industrial Research. Pp. 55–61. New Delhi 1962.
Nath, J., Swaminathan, M.S.: Chromosome numbers of some grasses.—Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed.17: 120, 1957.
Nielsen, E.L.: Analysis of variation inP. virgatum. L.—J. agr. Res.69: 327–353, 1944.
Pienaar, R.V.: The chromosome number of some indigenous South African and introduced Gramineae —In: Meredith, D. (ed.): The Grasses and Pastures of South Africa. Pp. 551–570. Central News Agency, 1955.
Pritchard, A.J., Delacy, I.H.: The cytology, breeding system and flowering behaviour ofP. coloratum.—Aust. J. Bot.22: 57–66, 1974.
Raman, V.S., Chandrasekharan, P., Krishnaswany, D.: Note on some chromosome numbers in Gramineae.—Curr. Sci.28: 127–128, 1959.
Rau, N.S.: Further contributions to the cytology of some crop plants of South India.—J. indian bot. Soc.8: 201–206, 1929.
Savidan, Y.: Chromosome and embryological analysis in sexual apomictic hybrids ofP. maximum.— Theor. appl. Genet57: 153–156, 1980.
Singh, D.N., Godward, M.B.E.: Cytological Studies in the Gramineae.—Heredity15: 139–199, 1960.
Sokolovskaya, A.P., Probatova, N.S.: [Karyological investigation of grasses (Poaceae) in the south part of the Soviet Far-East.]—Bot. Zh.62: 1143–1153, 1972. [In Russ.]
Tateoka, T.: Contributions to biosystematic interactions of East African grasses.—Bull. nat. Sci.8: 161–173, 1965.
Warmke, H.E.: Cytotaxonomic investigations of some varieties ofP. maximum andP. purpurascens in Puerto Rico.—Agron. J.43: 143–149, 1951.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by T. GICHNER
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamoud, M.A., Haroun, S.A., MacLeod, R.D. et al. Cytological relationships of selected species ofPanicum L.. Biol Plant 36, 37–45 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02921265
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02921265