Abstract
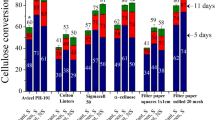
A new saccharification assay has been devised, in which a continuously buffer-swept membrane reactor is used to remove the solubilized saccharification products, thus allowing high extents of substrate conversion without significant inhibitory effects from the buildup of either cellobiose or glucose. This diafiltration saccharification assay (DSA) can, therefore, be used to obtain direct measurements of the performance of combinations of cellulase and substrate under simulated SSF conditions, without the saccharification results being complicated by factors that may influence the subsequent fermentation step. This assay has been used to compare the effectiveness of commercial and special in-house-producedTrichoderma reeSci. cellulase preparations in the saccharification of a standardized microcrystalline (Sigmacell) substrate and a dilute-acid pretreated lignocellulosic substrate. Initial results strongly suggest that enzyme preparations produced in the presence of the targeted lignocellulosic substrate will saccharify that substrate more effectively. These results call into question the widespread use of the “filter paper assay” as a reliable predictor of enzyme performance in the extensive hydrolysis of substrates that are quite different from filter paper in both physical properties and chemical composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghose, T. K. (1987),Pure Appl. Chem. 59, 257–268.
Ladisch, M. R., Lin, K. W., Voloch, M., and Tsao, G. T. (1983),Enz. Microb. Technol. 5, 82–102.
Lee, Y.-H. and Fan, L. T. (1983),Biotechnol. Bioeng. 25, 939–966.
Holtzapple, M., Cognata, M., Shu, Y., and Hendrickson, C. (1990),Biotechnol. Bioeng. 36, 275–287.
Gusakov, A. V. and Sinitsyn, A. P. (1992),Biotechnol. Bioeng. 40, 663–671.
Howell, J. A. and Stuck, J. D. (1975),Biotechnol. Bioeng. 17, 873–893.
Douglas, L. J. (1989),A Technical and Economic Evaluation of Wood Conversion Processes;Entropy Associates Report of Contract File 051SZ.23283-8-6091, Efficiency and Alternative Energy Technology Branch, Energy, Mines and Resources, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Mandels, M., Weber, J., and Parizek, R. (1971),Appl. Microbiol. 21, 152–154.
Vinzant, T. B., Ponfick, L., Nagle, N. J., Ehrman, C. I., Reynolds, J. B., and Himmel, M. E. (1994),Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 45/46, 611–626.
Esterbauer, J., Steiner, W., Labudova, I., Hermann, A., and Hayn, M. (1991),Bioresource Technol. 36, 51–65.
Pourquie, J. and Warzywoda, M. (1993), inBioconversion of Forest and Agricultural Plant Residues, Saddler, J. N., ed., CAB International, pp. 107–116.
Hayn, M, Steiner, W., Klinger, R., Steinmuller, H., Sinner, M., and Esterbauer, H. (1993), inBioconversion of Forest and Agricultural Plant Residues, Saddler, J. N., ed., CAB International, pp. 33–72.
Lynd, L. R., Cushman, J. H., Nichols, R. J., and Wyman, C. E. (1991),Science 251, 1318–1323.
Hinman, N. D., Schell, D. J., Riley, C. J., Bergeron, P. W., and Walter, P. J. (1992),Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 34/35, 639–649.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baker, J.O., Vinzant, T.B., Ehrman, C.I. et al. Use of a new membrane-reactor saccharification assay to evaluate the performance of celluloses under simulated ssf conditions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 63, 585–595 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920456
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920456