Abstract
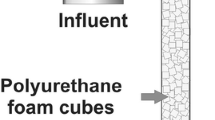
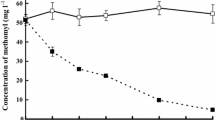
Ground-water contamination by chlorinated aliphatic compounds is a major cause for concern because of their toxicity. This study examined the biodegradation of trichloroethylene and aromatic compounds by microbial consortia enriched from contaminated subsurface sediments. The consortia were capable of utilizing methane and propane as sources of carbon and energy. Two continuously recycled expanded-bed bioreactors were inoculated with (1) the subsurface consortium, and (2)P. fluorescence, P. putida (strains pRB1401 and pWWO), andM. trichosporium OB3b. An uninoculated reactor containing 0.2% sodium azide and 0.5% formalin served as the control. Methane (5% v/v) and propane (3% v/v) were maintained by batch feeding through the course of the experiment. Greater than 97% degradation of trichloroethylene was observed over a period of 12 d. More than 99% of benzene, toluene, and xylene were degraded within the first 7 d. Dissolved oxygen levels were measured and found to be in the range 4.9–6.5 mg/L throughout the experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirschhorn, J. S. (1985),Superfund Strategy. OTA-ITE-252, Office of Technology Assessment, Washington, D.C.,
Fliermans, C. B., Phelps, T. J., Ringelberg, D., Mikell, A. T., and White, D. C. (1988),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 1709.
Phelps, T. J., Ringelberg, D., Hedrick, D., Davis, J., Fliermans, C. B., and White, D. C. (1988),Geomicrobiol. J. 6, 157.
U. S. DOE. Evaluation of mid-to-long term basic research for environmental restoration. DOE/ER-0419; US Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., September 1989.
Hirschhorn, J. S. (1986),Serious Reduction of Hazardous Waster—Summary. OTA-ITE-318. Office of Technology Assessment, Washington, D.C.
Little, C. D., Palumbo, A. V., Herbes, S. E., Lidstrom, M. E., Tyndall, R. L., and Gilmer, P. J. (1988),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 951.
Wilson, B. H. and Wilson, B. H. (1985),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49, 242.
Nelson, M. J. K., Montgomery, S. O., Mahaffey, W. R., and Pritchard, P. H. (1987),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53, 949.
Wackett, L. P. and Gibson, D. T. (1988),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 1703.
Henson, J. M., Yates, M. V., Cochran, J. W., and Shackleford, D. L. (1988),FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 53, 193.
Niedzielski, J. J., Schram, R. M., Phelps, T. J., Herbes, S. E., and White, D. C. (1989),J. Microbiol. Methods 10, 215.
Phelps, T. J., Niedzielski, J. J., Schram, R. M., Herbes, S. E., and White, D. C. (1990),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 1702.
Strandberg, G. W., Donaldson, T. L., and Farr, L. L. (1989),Environ. Sci. Technol. 23, 1422.
Phelps, T. J., Niedzielski, J. J., Malachowski, K. J., Schram, R. M., Herbes, S. E., and White, D. C. (1991),Environ. Sci. Technol. 25, 1461.
Atlas, R. M. and Bartha, R. (1987), inMicrobial Ecology, 2nd ed. Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Inc., New York, pp. 403–438.
Bartha, R. (1986),Microbial Ecol. 12, 155.
Dagley, S. (1971),Adv. Microb. Physiol. 6, 1.
Gibson, D. T., Koch, J. R., and Kallio, R. E. (1968),Biochemistry,7, 2653.
Gibson, D. T. and Subramanian, V. (1984), inMicrobial Degradation of Organic Compounds, Gibson, D. T., ed., Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp. 181–252.
Hou, C. T. (1982), inMicrobial Transformation, of Bioactive Compounds vol. 1, Rosazza, J. P., ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 81–107.
Marr, E. K. and Stone, R. W. (1961),Bacteriol. 81, 425.
Ribbons, D. W. and Eaton, R. W. (1982), inBiodegradation of Detoxification of Environmental Pollutants. Chakrabarty, A. M., ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 59–84.
Cornish, A., Nicholls, K. M., Scott, D., Hunter, B. K., Aston, W. J., Higgins, I. J., and Sanders, J. K. M. (1984),J. Gen. Microbiol. 130, 2565.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korde, V.M., Phelps, T.J., Bienkowski, P.R. et al. Biodegradation of chlorinated aliphatics and aromatic compounds in total-recycle expanded-bed biofilm reactors. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 39, 631–641 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919024
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919024