Abstract
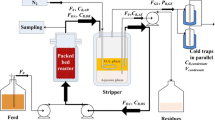
ImmobilizedClostridium acetobutylicum was used to ferment glucose into acetone and butanol in a fluidized-bed bioreactor. A nontoxic immiscible solvent, oleyl alcohol, was added to, and removed directly from, the fermenting columnar reactor and extracted the majority of the inhibitory butanol from the aqueous broth. The extracting solvent had a distribution coefficient of near 3 for butanol. Nonfermenting system tests indicated that equilibrium between the phases could be reached in one pass through the column. Steady-state results are presented for the fermentation with and without the extractive solvent addition. One run, with a continuous aqueous feedstream containing 40 g/L glucose, was operated for 23 d. A steady state was established with just the aqueous feedstream. Approximately half of the glucose was consumed, and the pH fell to 4.5 from 6.5. Then, during multiple intervals, the flow of organic extractive solvent (oleyl alcohol) was begun into the fermenting columnar reactor. A new apparent steady state was reached in about 4 h. The final aqueous butanol concentration was lowered by more than half. The total butanol production rate increased by 50–90% during the solvent extraction, as the organic-to-aqueous ratio increased from 1 to 4, respectively. There was an observed maximum volumetric productivity of 1.8 g butanol h−1L−1 in this nonoptimized system. The butanol yield apparently improved because of the removal of the inhibition. More substrate is going to the desired product, butanol, and less to maintenance or acid production, resulting in 10–20% increases in the ratio of butanol relative to all products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones, D. T. and Woods, D. R. (1986),Microbiol. Rev. 50, 484–524.
Linden, J. C., Moreira, A. R., and Lenz, T. G. (1986), inComprehensive Biotechnology, Moo-Young, M., ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp. 915–931.
Ladisch, M. R. (1991),Enzyme Microb. Technol. 13, 280–283.
Roffler, S. R., Blanch, H. W., and Wilke, C. R. (1987),Biotechnol. Prog. 3, 131–140.
Friedl, A. Qureshi, N., and Maddox, I. S. (1991),Biotechnol. Bioeng. 38, 518–527.
Shukla, R., Kang, W., and Sirkar, K. K. (1989),Biotech. Bioeng. 34, 1158–1166.
Kang, W., Shukla, R., and Sirkar, K. K. (1990),Biotach. Bioeng. 36, 826–833.
Ennis, B. M., Qureshi, N., and Maddox, I. S. (1987),Enzyme Microb. Technol. 9, 672–675.
Davison, B. H. and Thompson, J. E. (1992),Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 34/35, 431–435.
Gaillot, F. P., Gleason, C., Wilson, J. J., and Zwarick, J. (1990),Biotechnol. Prog. 6, 370–375.
Wang, H. Y. and Sobnosky, K. (1985),ACS Symp. Ser. 271, 123–131.
Roffler, S. R., Randolph, T. W., Miller, D. A. Blanch, H. W., and Prausnitz, J. M. (1991), inExtractive Bioconversions, Mattiasson, B. and Holst, O., eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 133–172.
Groot, W. J., van der Lans, R. G. J. M., and Luyben, K. Ch. A. M. (1992),Process Biochem. 27, 61–75.
Bruce, L. J. and Daugulis, A. J. (1991),Biotechnol. Prog. 7, 116–124.
Ishii, S., Masahito, T., and Kobayashi, T. (1985),J. Chem. Eng. Japan 18, 125–130.
Evans, P. J. and Wang, H. Y. (1988),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 1662–1667.
Wayman, M. and Parekh, R. (1987),J. Ferment. Technol. 65, 295–300.
Evans, P. J. and Wang, H. Y. (1990),Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 393–397.
Roffler, S. R., Blanch, H. W., and Wilke, C. R. (1988),Biotech. Bioeng. 31, 135–143.
Eckert, G. and Schugerl, K. (1987),Appl. Microbiol Biotechnol. 27, 221–228.
Godia, F., Casas, C., and Sola, C. (1987),Process Biochem. 22, 43–48.
Davison, B. H. and Scott, C. D. (1988),Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 18, 19–34.
Busche, R. M. and Allen, B. R. (1989),Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 20/21, 357–374.
Adler, H. I. and Crow, W. (1987),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53, 2496–2499.
Scott, C. D. (1987),Ann. NY Acad. 501, 487–493.
Roffler, S. R., Blanch, H. W., and Wilke, C. R. (1987),Bioproc. Engr. 2, 181.
Leung, J. C. Y. and Wang, D. I. C. (1981),Proc. 2nd World Congr. Chem. Eng. 1, 348–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
“The submitted manuscript has been authored by a contractor of the U.S. Government under contract DE-AC05-84OR21400. Accordingly, the U.S. Government retains a nonexclusive, royalty-free license to publish or reproduce the published form of this contribution, or allow others to do so, for U.S. Government purposes.”
Managed by Martin Marietta Energy Systems. Inc., under contract DE-AC05-84OR21400 with the US Department of Energy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davison, B.H., Thompson, J.E. Continuous direct solvent extraction of butanol in a fermenting fluidized-bed bioreactor with immobilizedClostridium acetobutylicum . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 39, 415–426 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919007
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919007