Abstract
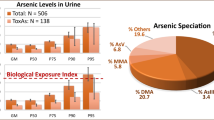
Extensive epidemiological study implicates that high arsenic content in artesian well water is the causal factor responsible for Blackfoot disease. We determine the arsenic concentration in urine samples of patients with Blackfoot and Bowen’s diseases and examine whether there exists any discrepancy of urinary arsenic concentrations among patients and the normal population. The analyses were made by hydride atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS) and the analytical reliability of the method was checked with a standard urine sample (ORTHO Bi-Level Urine Metal Control). The results show that the mean urinary arsenic concentration in 100 healthy adults is 63.4±29.7 μg/L, and those means for 23 and 11 patients with Blackfoot disease and Bowen’s disease are 75.7±39.1 μg/L (P vs controls >0.05) and 201±58 μg/L (P vs controls <0.001), respectively. From the analytical results obtained, we cannot conclude that urinary arsenic is associated with Blackfoot disease, as was disclosed from the epidemiological studies. However, urinary arsenic concentrations are possibly very closely associated with Bowen’s disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. J. Underwood,Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, 4th ed., Academic Press, New York, 1977, pp. 424–429.
L. Friberg, G. F. Nordberg, and V. B. Vouk,Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, 1979, pp. 293–319.
A. Astolfi et al.,Biol. Trace Element Res. 3, 133 (1981).
W. P. Tseng et al.,Mem. Coll. Med. Natl. Taiwan Univ. 7, 1–18.
F. J. Lu,Natl. Sci. Council Monthly (Taiwan, ROC),6, 388 (1978).
F. J. Lu et al.,J. Formosan Med. Assoc. 81, 1087 (1982).
R. Q. Blackwell et al.,J. Formosan Med. Assoc. 59, 1351 (1960).
R. Q. Blackwell,J. Formosan Med. Assoc. 60, 460 (1961).
K. Heydorn,Anal. Chim. Acta 28, 349 (1970).
J. T. Bowen,J. Cutan. Dis. 30, 241 (1912).
H. Z. Lund, Tumors of the Skin, inAtlas of Tumor Pathology, Sec. 1, fasc, 2, Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington DC, 1957, pp. 192–200, 258–264.
O. Neubauer,Brit. J. Cancer 1, 192 (1947).
S. Yeh, S. W. How, and C. S. Lin,Cancer 21, 312 (1968).
A. N. Currie,Brit. Med. Bull. 4, 402 (1947).
E. B. Helwing and J. H. Graham, inTumors of the Skin, Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, 1964, pp. 131–148.
J. H. Graham and E. B. Helwing,Arch. Dermatol. 80, 133 (1959).
R. C. Chu, G. P. Barron, and A. W. Baumgarner,Anal. Chem. 44, 1476 (1972).
J. A. Fiorino, J. W. Jones, and S. G. Capar,Anal. Chem. 48, 120 (1976).
B. Welz and M. Melcher,Atom. Absorp. Newsl. 18, 121 (1979).
J. M. Lo et al.,J. Radioanal. Chem. 72, 571 (1982).
B. L. Vallee, D. D. Ulmner, and W. E. C. Wacker,Arch. Ind. Health 21, 131 (1982).
R. S. Braman and C. C. Foreback,Science 182, 1247 (1973).
C. W. Dunnett,J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 50, 1096 (1955).
T. H. Yang, R. Q. Blackwell, and T. Yu,J. Formosan Med. 59, 1345 (1960).
D. C. Doong,Blackfoot Dis Res. 4, 18 (1976).
S. S. Pinto et al.,J. Occup. Med. 18, 677 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S.M., Chiang, C.H. & Yang, M.H. Arsenic concentration in the urine of patients with Blackfoot disease and Bowen’s disease. Biol Trace Elem Res 8, 11–18 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02917599
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02917599
Index Entries
- Blackfoot disease, and urinary arsenic concentrations
- Bowen’s disease, and urinary arsenic concentrations
- fluorescent compounds in urinary arsenic determinations
- chronic arsenicism
- hydride atomic absorption spectrophotometry, in urinary arsenic concentrations
- arsenic, concentrations in urine of patients with Blackfoot and Bowen’s diseases
- urinary arsenic, in Blackfoot and Bowen’s diseases