Abstract
Background Benzodiazepines, which are commonly administered perioperatively, can depress immune function. Neutrophil apoptosis plays a central role in the regulation of inflammation. This is particularly important during and after surgery.
Aim To examine the effects of benzodiazepines (midazolam and diazepam) on neutrophil apoptosis.
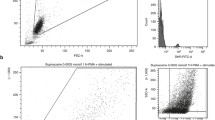
Methods Venous blood samples were withdrawn from patients scheduled to undergo elective surgery, (a) immediately prior to, and 10 minutes after administration of midazolam 0.2mg/kg intravenously (n=11) and (b) immediately prior to, and 60 minutes after administration of diazepam 10mg po (n=10). Neutrophil apoptosis was measured by Annexin VFITC after 1 and 12 hours in culture.
Results The percentage of apoptotic cells was significantly less after midazolam at 12% (11.9) hours in culture compared to pre-midazolam 29.7% (13.3) (p<0.05). After diazepam, the rates of neutrophil apoptosis were also significantly less after 12 hours in culture (p<0.05).
Conclusion Administration of benzodiazepines in clinically relevant doses inhibits neutrophil apoptosis. In the perioperative period, this may influence the inflammatory response to surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss M, Mirow N, Birkhahn A et al. Benzodiazepines and their solvents influence neutrophil granulocyte function.Br J Anaesth 1993; 70: 317–21.
Heine J, Leuwer M, Scheinichen D et al. Flow cytometry evaluation of the in vitro influence of four i.v. anaesthetics on respiratory burst of neut rophils.Br J Anaesth 1996; 77: 387–92.
Nishina K, Akamatsu H, Mikawa K et al. The inhibitory effects of thiopental, midazolam, and ketamine on human neutrophil function.Anaesth Analg 1998; 86: 159–65.
O’Donnell NG, McSharry CP, Wilkinson PC et al. Comparison of the inhibitory effect of propofol, thiopentone and midazolam on neut rophil polarization in vitro in the presence or absence of human serum albumin.Br J Anaesth 1992; 69: 70–4.
Galley HF, Dubbels AM, Webster NR. The effect of midazolam and propofol on interleukin-8 from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.Anesth Analg 1998; 86: 1289–93.
Davidson JAH, Boom FJ, Pearsall P et al. Comparison of the effects of four i.v. anaesthetic agents on polymorphonuclear leukocyte function.Br J Anaesth 1995; 74: 315–8.
Jimenez MF, Watson RWG, Parodo J et al. Dysregulated expression of neut rophil apoptosis in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome.Arch Surg 1997; 132: 1263–70.
Kasahara Y, Iwai K, Yachie A et al. Involvement of reactive oxygen inte rmediates in spontaneous and CS95 (Fas/APO-1) - mediated apoptosis of neutrophils.Blood 1997; 89: 1748–54.
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M et al. Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and generation of reactive oxygen species in early programmed cell death.J Exp Med 1995; 182: 367–77.
Canat X, Carayon P, Bouaboula M et al. Distribution profile and properties of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors on human hemopoietic cells.Life Sci 1993; 52: 107–18.
Kinnally KW, Zorov DB, Antonenko YN et al. Mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptor linked to inner membrane ion channels by nanomolar actions of ligands.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 1374–8.
Tatton WG, Chalmers RRM. Mitochondria in n€degenerative apoptosis: an opportunity for therapy?Ann Neur 1998; 44: S134–41.
Tanimoto Y, Sato Y, Kizaki H. Benzodiazepine receptor agonists modulate thymocyte apoptosis through reduction of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential.Jpn J Pharmacol 1999; 79: 177–83.
Carayon P, Portier M, Dussossoy D et al. Involvement of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in the protection of hematopoietic cells against oxygen radical damage.Blood 1996; 8: 3170–8.
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon AJ et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl.J Exp Med 1995; 182: 1545–56.
Homburg CH, de Hass M, von dem Borne AE et al. Human neut rophils lose their surface Fc gamma RIII and acquire annexin V binding sites during apoptosis in vitro.Blood 1995; 85: 532–40.
Chelli B, Falleni A, Salvett F, Gremigni V, Luccacchini A, Martini C. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor ligands: mitochondrial permeability transition induction in rat cardiac tissue.Biochem Pharmacol 2001; 61: 695–705.
Kroemer G, Zamzami N, Susin SA. Mitochondrial control of apoptosis.Immunol Today 1997; 18: 44–51.
Scorrano L, Petronilli V, Bernardi P. On the voltage dependence of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. A critical appraisal.J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 12295–9.
Zoratti M, Szabo I. The mitochondrial permeability transition.Biochim Biophys Acta 1995; 1241: 139–76.
Fanning NF, Porter J, Shorten GD et al. Inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis after elective surgery.Surgery 1999; 126: 527–34.
Hernandez LA, Grisham B, Twohig B, Arfors KE, Harlan JM, Granger DN. Role of neutrophils in ischemia-reperfusion-induced microvascular injury.Am J Physiol 1987; 253: H699–703.
Matute-Bello G, Liles WC, Radella FN et al. Neutrophil apoptosis in the acute respiratory distress syndrome.Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997; 156: 1969–77.
Davies MG, Hagen PO. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome.Br J Surg 1997; 84: 920–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goto, Y., O’Malley, C., Fanning, N. et al. Benzodiazepines inhibit the rate of neutrophil apoptosis. Ir J Med Sci 172, 191–194 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915288
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915288