Abstract
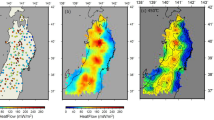
Based on the observed data, the average value of surface heat flow in the Yinggehai Basin is calculated and it turns out to be 84.1 mW/m2. The thermal evolution of the basin since the Cenozoic era has been attempted by tectono-thermal modeling. Three-phase extension made the basin become hotter and hotter, reaching its climax in paleo-temperature history since 5.2 Ma. And nowadays, the basin is in the heat flow decreasing period. During the Cenozoic era, the basement heat flow remained at 50–70 mW/m2 all the time. This is related to the degree of each extension phase, stretching rate mode and also the limited basin scale. Modeling results also show that, the surface heat flow is controlled mainly by the basement heat flow, and less than 20% comes from radiogenic heat production in the sediments of the basin
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Yuliang, Huang Zhongming, Thermal history about northern margin of South China Sea, China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology) (in Chinese), 1990, 4(6): 31.
Li Yuliang, Zhang Quanxing, Zhang Qiming, Thermal abnormality of Ya13-1 gas field, China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology) (in Chinese), 1992, 6(5): 33.
Gong Zaisheng, Li Sitian et al., Basin Analysis and Accumulation of Oil and Gas in Northern Margin of South China Sea (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1997.
He Lijuan, Xiong Liangping, Wang Jiyang et al., Calculation of stretching factors in the multi-phase modeling of sedimentary basins, Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1995, 40(24): 2261.
He Lijuan, Xiong Liangping, Wang Jiyang, Effects on the tectono-thermal modeling of extensional basins, Scientia Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1998, 33(2): 222.
Pitman, W. C., Andrews, J. A., Subsidence and thermal history of small pull-apart basins, in Strike-slip Deformation, Basin Formation and Sedimentation (eds. Kevin, T. B., Nicholas, C. B.), Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Special Publication, 1985.
Zhang Qiming, Hu Zhongliang, High-temperature and high-pressure conditions and migration of hydrocarbons in Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan basin, A Collection on Petroleum Geology of Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismology Press, 1993, 78–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Xiong, L., Wang, J. et al. Tectono-thermal modeling of the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 44, 7–13 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02906880
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02906880