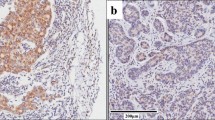
Abstract
Metallothioneins (MTs) are a family of metal binding proteins that play an important role in maintaining transition metal ion homoeostasis, redox balance in the cell and fundamental cellular processes such as proliferation and apoptosis. In humans, there are 4 groups of MT proteins which are encoded by 10 functional MT isoforms. In breast tissues, MT is primarily expressed in myoepithelial and malignant epithelial cells. Immunohistochemical studies have revealed that 26% to 100% of invasive ductal breast cancers express the MT protein. The MT-1F and MT-2A isoforms have been reported to be associated with higher histological grade in breast cancer, whereas higher MT-1E mRNA expression was found in estrogen receptor-negative tumors compared to their estrogen receptor-positive counterparts. A number of studies have shown that MT expression in breast cancer is associated with poorer prognosis. In addition, metallothionein expression may have a potential role in protecting the breast cancer cell from chemotherapeutic threats to survival.(Pathology Oncology Research Vol 10, No 2, 74–79)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima Y, Binz P-A, Kagi JHR: Nomenclature of metallothionein: proposal for a revision. In: Klaassen, C.D. eds. Metallothionein IV, Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, Switzerland. pp 3–6, 1999.
Pande J, Vasak M, Kagi JH: Interaction of lysine residues with the metal thiolate clusters in metallothionein. Biochemistry 24: 6717–6722, 1985.
Robbins AH, McRee DE, Williamson M, et al.: Refined crystal structure of Cd, Zn metallothionein at 2.0Å resolution. J Mol Biol 221: 1269–1293, 1991.
Binz P-A, Kagi JHR: Metallothionein: molecular evolution and classification. In: Klaassen, C.D. eds. Metallothionein IV, Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, Switzerland. pp 7–13, 1999.
West AK, Stallings R, Hildebrand CE, et al.: Human metallothionein genes: structure of the functional locus at 16q13. Genomics 8: 513–518, 1990.
Stennard FA, Holloway AF, Hamilton J, et al.: Characterisation of six additional human metallothionein genes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1218: 357–365, 1994.
Mididoddi S, McGuirt JP, Sens MA, et al.: Isoform-specific expression of metallothionein mRNA in the developing and adult human kidney. Toxicol Lett 85:17–27, 1996.
Palmiter RD, Findley SD, Whitmore TE, et al.: MT-III, a brainspecific member of the metallothionein gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 6333–6337, 1992.
Quaife CJ, Findley SD, Erickson JC, et al.: Induction of a new metallothionein isoform (MT-IV) occurs during differentiation of stratified squamous epithelia. Biochemistry 33: 7250–7259, 1994.
Kagi JH, Hunziker P. Mammalian metallothionein. Biol Trace Elem Res 21: 111–118, 1989.
Braun W, Wagner G, Worgotter E, et al.: Polypeptide fold in the two metal clusters of metallothionein-2 by nuclear magnetic resonance in solution. J Mol Biol 187: 125–129, 1986
Schultze P, Worgotter E, Braun W, et al.: Conformation of [Cd7]-metallothionein-2 from rat liver in aqueous solution determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol 203: 251–268, 1988
Braun W, Vasak M, Robbins AH et al.: Comparison of the NMR solution structure and the X-ray crystal structure of rat metallothionein-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 10124–10128, 1992.
Tapiero H, Tew KD: Trace elements in human physiology and pathology: zinc and metallothioneins. Biomed Pharmacother 57: 399–411, 2003.
Roesijadi G. Metal transfer as a mechanism for metallothioneinmediated metal detoxification. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-legrand) 46: 393–405, 2000.
Kagi JH, Kojima Y. Chemistry and biochemistry of metallothionein. Experientia 52: 25–61, 1987.
Kondoh M, Imada N, Kamada K, et al.: Property of metallothionein as a Zn pool differs depending on the induced condition of metallothionein. Toxicol Lett 142: 11–18, 2003.
Maret W: Metallothionein/disulfide interactions, oxidative stress, and mobilization of cellular zinc. Neurochem Int 27: 111–117, 1995.
Maret W, Vallee BL: Thiolate ligands in metallothionein confer redox activity on zinc clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3478–3482, 1998.
Miura T, Muraoka S, Ogiso T: Antioxidant activity of metallothionein compared with reduced glutathione. Life Sci 60: 301–309, 1997.
Hussain S, Slikken JW, Ali SF. Role of metallothionein and the antioxidants in scavenging superoxide radicals and their possible role in neuroprotection. Neurol Chem Int 29: 145–152, 1996.
Abel J, Ruiter N: Inhibition of hydroxy radical generated DNA degradation by metallothionein. Toxicol Lett 47: 191–196, 1989.
Cai L, Klein JB, Kang YJ: Metallothionein inhibits peroxynitriteinduced DNA and lipoprotein damage. J Biol Chem 275: 38957–38960, 2000.
Mendez-Armenta M, Villeda-Hernandez J, Barroso-Moguel R, et al.: Brain regional lipid peroxidation and metallothionein levels of developing rats exposed to cadmium and dexamethasone. Toxicol Lett 144: 151–157, 2003.
Garrett SH, Sens MA, Shukla D, et al.: Metallothionein isoform 1 and 2 gene expression in the human prostate: downregulation of MT-1X in advanced prostate cancer. Prostate 43: 125–135, 2000.
Tai SK, Tan OJ, Chow VT, et al.: Differential expression of metallothionein 1 and 2 isoforms in breast cancer lines with different invasive potential: identification of a novel nonsilent metallothionein-1H mutant variant. Am J Pathol 163: 2009–2019, 2003.
Haq F, Mahoney M, Koropatnick J: Signaling events for metallothionein induction. Mutat Res 533: 211–226, 2003.
Garrett SH, Somji S, Todd JH, et al.: Differential expression of human metallothionein isoform I mRNA in human proximal tubule cells exposed to metals. Environ Health Perspect 106: 825–832, 1998.
Garrett SH, Belcastro M, Sens MA, et al.: Acute exposure to arsenite induces metallothionein isoform-specific gene expression in human proximal tubule cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A 64: 343–355, 2001.
Jahroudi N, Foster R, Price-Haughey J, et al.: Cell-type specific and differential regulation of the human metallothionein genes. Correlation with DNA methylation and chromatin structure. J Biol Chem 265: 6506–6511, 1990.
Barnes NL, Ackland ML, Cornish EJ: Metallothionein isoform expression by breast cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32: 895–903, 2000.
Fresno M, Wu W, Rodriguez JM, et al.: Localization of metallothionein in breast carcinomas. An immunohistochemical study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 423: 215–219, 1993.
Jin R, Bay BH, Chow VT, et al.: Significance of metallothionein expression in breast myoepithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 303: 221–226, 2001.
Bier B, Douglas-Jones A, Totsch M, et al.: Immunohistochemical demonstration of metallothionein in normal human breast tissue and benign and malignant breast lesions. Breast Cancer Res Treat 30: 213–221, 1994.
Schmid KW, Ellis IO, Gee JM, et al.: Presence and possible significance of immunocytochemically demonstrable metallothionein over-expression in primary invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 422: 153–159, 1993.
Zhang R, Zhang H, Wei H, et al.: Expression of metallothionein in invasive ductal breast cancer in relation to prognosis. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 19: 95–97, 2000.
Vazquez-Ramirez FJ, Gonzalez-Campora JJ, Hevia-Alvarez E, et al.: P-glycoprotein, metallothionein and NM23 protein expressions in breast carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 196: 553–559, 2000.
Jin R, Chow VT, Tan PH, et al.: Metallothionein 2A expression is associated with cell proliferation in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 23: 81–86, 2002.
Ioachim E, Tsanou E, Briasoulis E, et al.: Clinicopathological study of the expression of hsp27, pS2, cathepsin D and metallothionein in primary invasive breast cancer. Breast 12: 111–119, 2003.
Jin R, Bay BH, Chow VTK, et al.: Metallothionein 1F mRNA expression correlates with histological grade in breast carcinoma. Breast Caner Res Treat 66: 265–272, 2001.
Sens MA, Somji S, Garrett SH, et al.: Metallothionein isoform 3 overexpression is associated with breast cancers having a poor prognosis. Am J Pathol 159: 21–26, 2001.
Nartey N, Cherian MG, Banerjee D: Immunohistochemical localization of metallothionein in human thyroid tumors. Am J Pathol 129: 177–182, 1987
Cherian MG, Huang PC, Klaassen CD, et al.: National Cancer Institute workshop on the possible roles of metallothionein in carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 53: 922–925, 1993
Cherian MG, Howell SB, Imura N, et al.: Role of metallothionein in carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 126: 1–5, 1994
Fan LZ, Cherian MG. Potential role of p53 on metallothionein induction in human epithelial breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 87: 1019–1026, 2002.
Kagi JH: Overview of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol. 205: 613–26, 1991.
Schwarz MA, Lazo JS, Yalowich JC, et al.: Metallothionein protects against the cytotoxic and DNA-damaging effects of nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 4452–4456, 1995.
Andrews GK, Adamson ED, Gedamu L: The ontogeny of expression of murine metallothionein: comparison with the alpha-fetoprotein gene. Dev Biol 1984; 103: 294–303.
Nagel WW, Vallee BL: Cell cycle regulation of metallothionein in human colonic cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:579–583, 1995.
Abdel-Mageed A, Agrawal KC: Antisense down-regulation of metallothionein induces growth arrest and apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther 4: 199–207, 1997.
Gurel V, Sens DA, Somji S, et al.: Stable transfection and overexpression of metallothionein isoform 3 inhibits the growth of MCF-7 and Hs578T cells but not that of T-47D or MDA-MB-231 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 80: 181–191, 2003.
Cai L, Wang GJ, Xu ZL, et al.: Metallothionein and apoptosis in primary human hepatocellular carcinoma from northern China. Anticancer Res 18: 4667–4672, 1998.
Jayasurya A, Bay BH, Yap WM, et al.: Correlation of metallothionein expression with apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer 82: 1198–1203, 2000.
Huang J, Tan PH, Thiyagarajan J, et al.: Prognostic significance of glutathione S-transferase-pi in invasive breast cancer. Mod Pathol 16: 558–565, 2003.
Abdel-Mageed A, Agrawal KC: Activation of nuclear factor kappaB: potential role in metallothionein-mediated mitogenic response. Cancer Res 58: 2335–2338, 1998.
Sakurai A, Hara S, Okano N, et al.: Regulatory role of metallothionein in NF-kappaB activation. FEBS Lett 455:55–58, 1999.
Butcher HL, Kennette WA, Collins O, et al.: Metallothionein mediates the level and activity of nuclear factor ppaB (NFkB) in murine fibroblasts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004 Mar 23 [Epub ahead of print]
Kim CH, Kim JH, Lee J, et al.: Zinc-induced NF-kappaB inhibition can be modulated by changes in the intracellular metallothionein level. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 190: 189–196, 2003.
Cui Y, Wang J, Zhang X, et al.: ECRG2, a novel candidate of tumor suppressor gene in the esophageal carcinoma, interacts directly with metallothionein 2A and links to apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:904–915, 2003.
Hainaut P, Mann K: Zinc binding and redox control of p53 structure and function. Antioxid Redox Signal 3: 611–623, 2001.
Meplan C, Richard MJ, Hainaut P: Metalloregulation of the tumor suppressor protein p53: zinc mediates the renaturation of p53 after exposure to metal chelators in vitro and in intact cells. Oncogene 19: 5227–5236, 2000.
Jacob C, Maret W, Vallee BL: Control of zinc transfer between thionein, metallothionein, and zinc proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3489–3494, 1998.
Haerslev T, Jacobsen GK, Zedeler K: The prognostic significance of immunohistochemically detectable metallothionein in primary breast carcinomas. APMIS 103: 279–285, 1995.
Oyama T, Take H, Hikino T, et al.: Immunohistochemical expression of metallothionein in invasive breast cancer in relation to proliferative activity, histology and prognosis. Oncology 53: 112–117, 1996.
Ioachim E, Kamina S, Demou A, et al.: Immunohistochemical localization of metallothionein in human breast cancer in comparison with cathepsin D, stromelysin-1, CD44, extracellular matrix components, P53, Rb, C-erbB-2, EGFR, steroid receptor content and proliferation. Anticancer Res 19: 2133–2139, 1999.
Goulding H, Jasani B, Pereira H, et al.: Metallothionein expression in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer 72: 968–972, 1995.
Douglas-Jones AG, Navabi H, Morgan JM, et al.: Immunoreactive p53 and metallothionein expression in duct carcinoma in situ of the breast. No correlation. Virchows Arch 430: 373–379, 1997.
Jin R, Bay BH, Chow VT, et al.: Metallothionein 1E mRNA is highly expressed in oestrogen receptor-negative human invasive ductal breast cancer. Br J Cancer 83: 319–323, 2000.
Cree IA, Knight L, Di Nicolantonio F, et al.: Chemosensitization of solid tumors by modulation of resistance mechanisms. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 3: 634–640, 2002.
Kishi K, Doki Y, Miyata H, et al.: Prediction of the response to chemoradiation and prognosis in oesophageal squamous cancer. Br J Surg 89:597–603, 2002.
Siu LL, Banerjee D, Khurana RJ, et al.: The prognostic role of p53, metallothionein, P-glycoprotein, and MIB-1 in muscleinvasive urothelial transitional cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 4: 559–565, 1998.
Joseph MG, Banerjee D, Kocha W, et al.: Metallothionein expression in patients with small cell carcinoma of the lung: correlation with other molecular markers and clinical outcome. Cancer 92: 836–842, 2001.
Andrews PA, Murphy MP, Howell SB. Metallothionein-mediated cisplatin resistance in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 19: 149–154, 1987.
Germain I, Tetu B, Brisson J, et al.: Markers of chemoresistance in ovarian carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study of 86 cases. Int J Gynecol Pathol 15: 54–62, 1996.
Wrigley E, Verspaget HW, Jayson GC, et al.: Metallothionein expression in epithelial ovarian cancer: effect of chemotherapy and prognostic significance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126: 717–721, 2000.
Shimoda R, Achanzar WE, Qu W, et al.: Metallothionein is a potential negative regulator of apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 73: 294–300, 2003.
Cherian MG, Jayasurya A, Bay BH: Metallothioneins in human tumors and potential roles in carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 533: 201–209, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, R., Huang, J., Tan, PH. et al. Clinicopathological significance of metallothioneins in breast cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 10, 74–79 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893459
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893459