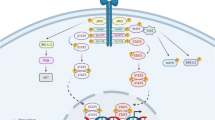
Abstract
Leptin restricts intake of calories as a satiety hormone. It probably stimulates neoplastic proliferation in breast cancer, too. Growth of malignant cells could be regulated by various leptininduced second messengers like STAT3 (signal transducers and activators of transcription 3), AP-1 (transcription activator protein 1), MAPK (mitogenactivated protein kinase) and ERKs (extracellular signalregulated kinases). They seem to be involved in aromatase expression, generation of estrogens and activation of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in malignant breast epithelium. Leptin may maintain resistance to antiestrogen therapy. Namely, it increased activation of estrogen receptors,therefore,it was suspected to reduce or even overcome the inhibitory effect of tamoxifen on breast cell proliferation. Although several valuable reviews have been focused on the role of leptin in breast cancer,the status of knowledge in this field changes quickly and our insight should be continuously revised. In this summary,we provide refreshed interpretation of intensively reported scientific queries of the topic.(Pathology Oncology Research Vol 12, No 2, 69–72)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, et al: Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372: 425–432, 1994.
Tartaglia LA: The leptin receptor. J Biol Chem 272: 6093–6096, 1997.
Gaja A andChury Z: The importance of leptin in oncologyhypothesis or facts? Vnitr Lek 47: 245–249, 2001.
Tessitore L, Vizio B, Pesola D, et al: Adipocyte expression and circulating levels of leptin increase in both gynaecological and breast cancer patients. Int J Oncol 24: 1529–1535, 2004.
O’Brien SN, Welter BH andPrice TM: Presence of leptin in breast cell lines and breast tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 259: 695–698, 1999.
Das UN: Is obesity an inflammatory condition? Nutrition 17: 953–966, 2001.
Cleary MP, Grande JP, Juneja SC andMaihle NJ: Dietinduced obesity and mammary tumor development in MMTVneu female mice. Nutr Cancer 50: 174–180, 2004.
Szymczak J, Milewicz A, Thijssen JH, et al: Concentration of sex steroids in adipose tissue after menopause. Steroids 63: 319–321, 1998.
Surmacz E andBartucci M: Role of estrogen receptor alpha in modulating IGF-I receptor signaling and function in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 23: 385–394, 2004.
Koda M, Sulkowski S, Kanczuga-Koda L, et al: Expression of ERalpha, ERbeta and Ki-67 in primary tumors and lymph node metastases in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 11: 753–759, 2004.
Stattin P, Soderberg S, Biessy C, et al: Plasma leptin and breast cancer risk: a prospective study in northern Sweden. Breast Cancer Res Treat 86: 191–196, 2004.
Somasundar P, Yu AK, Vona-Davis andMcFadden DW: Differential effects of leptin on cancer in vitro. J Surg Res 113: 50–55, 2003.
Caldefie-Chezet F, Damez M, de Latour M, et al: Leptin: Aproliferative factor for breast cancer? Study on human ductal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334: 737–741, 2005.
Markowska A, Malendowicz K andDrews K: The role of leptin in breast cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 25: 192–194, 2004.
Cleary MP, Phillips FC, Getzin SC, et al: Genetically obese MMTV-TGF-alpha/Lep(ob)Lep(ob) female mice do not develop mammary tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 77: 205–215, 2003.
Ishikawa M, Kitayama J andNagawa H: Enhanced expression of leptin and leptin receptor (OB-R) in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: 4325–4331, 2004.
Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Fantus IG, et al: Is leptin a mediator of adverse prognostic effects of obesity in breast cancer? J Clin Oncol 23: 6037–6042, 2005.
Miyoshi Y, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, et al: High expression of leptin receptor mRNA in breast cancer tissue predicts poor prognosis for patients with high, but not low, serum leptin levels. Int J Cancer 118: 1414–1419, 2006.
Mantzoros CS, Bolhke K, Moschos S andCramer DW: Leptin in relation to carcinoma in situ of the breast: a study of premenopausal cases and controls. Int J Cancer 80: 523–526, 1999.
Sauter ER, Garofalo C, Hewett J, et al: Leptin expression in breast nipple aspirate fluid (NAF) and serum is influenced by body mass index (BMI) but not by the presence of breast cancer. Horm Metab Res 36: 336–340, 2004.
Kumar S, Kishimoto H, Chua HL, et al: Interleukin-1 alpha promotes tumor growth and cachexia in MCF-7 xenograft model of breast cancer. Am J Pathol 163: 2531–2541, 2003.
Catalano S, Marsico S, Giordano C, et al: Leptin enhances, via AP-1, expression of aromatase in the MCF-7 cell line. J Biol Chem 278: 28668–28676, 2003.
Catalano S, Mauro L, Marsico S, et al: Leptin induces, via ERK1/ERK2 signal, functional activation of estrogen receptor alpha in MCF-7 cells. J Biol Chem 279: 19908–19915, 2004.
Masso-Welch PA, Zangani D, Ip C, et al: Isomers of conjugated linoleic acid differ in their effects on angiogenesis and survival of mouse mammary adipose vasculature. J Nutr 134: 299–307, 2004.
Yin N, Wang D, Zhang H, et al: Molecular mechanisms involved in the growth stimulation of breast cancer cells by leptin. Cancer Res 64: 5870–5875, 2004.
Hu X, Juneja SC, Maihle NJ andCleary MP: Leptin—a growth factor in normal and malignant breast cells and for normal mammary gland development. J Natl Cancer Inst 94: 1704–1711, 2002.
Laud K, Gourdou I, Pessemesse L, et al: Identification of leptin receptors in human breast cancer: functional activity in the T47-D breast cancer cell line. Mol Cell Endocrinol 188: 219–226, 2002.
Dieudonne MN, Machinal-Quelin F, Serazin-Leroy V, et al: Leptin mediates a proliferative response in human MCF7 breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293: 622–628, 2002.
Magoffin DA, Weitsman SR, Aagarwal SK andJakimiuk AJ: Leptin regulation of aromatase activity in adipose stromal cells from regularly cycling women. Ginekol Pol 70: 1–7, 1999.
Garofalo C, Sisci D andSurmacz E: Leptin interferes with the effects of the antiestrogen ICI 182,780 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 10: 6466–6475, 2004.
Nunez NP, Jelovac D, Macedo L, et al: Effects of the antiestrogen tamoxifen and the aromatase inhibitor letrozole on serum hormones and bone characteristics in a preclinical tumor model for breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: 5375–5380, 2004.
Cleary MP, Juneja SC, Phillips FC, et al: Leptin receptor-deficient MMTV-TGF-alpha/Lepr(db)Lepr(db) female mice do not develop oncogene-induced mammary tumors. Exp Biol Med 229: 182–193, 2004.
Coskun U, Gunel N, Toruner FB, et al. Serum leptin, prolactin and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in patients with breast cancer. Neoplasma 50: 41–46, 2003.
Ozet A, Arpaci F, Yilmaz MI, et al. Effects of tamoxifen on the serum leptin level in patients with breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 31: 424–427, 2001.
Marttunen MB, Andersson S, Hietanen P, et al. Antiestrogenic tamoxifen and toremifene increase serum leptin levels in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Maturitas 35: 175–179, 2000.
Gunel N, Coskun U, Toruner FB, et al: Serum leptin levels are associated with tamoxifen-induced hepatic steatosis. Curr Med Res Opin 19: 47–50, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sulkowska, M., Golaszewska, J., Wincewicz, A. et al. Leptin — From regulation of fat metabolism to stimulation of breast cancer growth. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 12, 69–72 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893446
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893446