Abstract
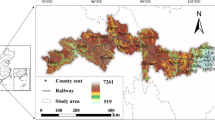
With the aid of the Remote Sensing (RS) and Geographic Information System (GIS) technology, the ecosystem pattern and fragility distribution maps of the 50-km-wide zone along the Qinghai-Tibet Railway were compiled and by using the superimposition method, range, area and indexes of the impact of various engineering activities on the ecosystems alongside the railway were studied. By making reference to the ecosystem recovery process of the Qinghai-Tibet Highway, mechanisms of recovery of the alpine ecosystems alongside the Qinghai-Tibet Railway were studied and extents and rates of the recovery were predicted. The results indicate that the impact of the railway engineering on the Alpine ecosystem depends mainly on how much the original surface soil in the zone has been disturbed and how fragile of the ecosystemper se. Restoration of vegetation coverage and species abundance shows a significantly reverse relationship with disturbance of the original surface soil but an extremely positive one with the length of the restoration period and mean annual precipitation and annual mean relative humidity in the period and no obvious bearings with altitude and temperature. In sections with an annual precipitation over 200 mm, as long as a certain percentage of original soil is leftin situ, it takes only 30 years or so for biodiversity to get basically restored to the original level after the construction is completed but at least 45–60 years or more for vegetation coverage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Scot, T. F., Josée, B., Response time of wetland biodiversity to road construction on adjacent lands, Conservation Biology, 2000, 14(1): 86–91.
Stephen, C. T., Christopher, A. F., Review of ecological effects of roads on terrestrial and aquatic communities, Conservation Biology, 2000, 14(1): 18–21.
Kenneth, R. Y., Roads and environmental degradation of tropical montane forests, Conservation Biology, 1994, 8(4): 972–776.
Radley, Z. W., Jiquan, Chen, Jim Pickens et al., Effects of forest roads on understory plants in a managed hardwood landscape, Conservation Biology, 2003, 17(2): 411–415.
Rebecca, A. R., Julia Johnson-Barnard, William, L. B., Contribution of roads to forest fragmentation in the Rocky Mountains, Conservation Biology, 1996, 10(4): 1098–1010.
P Klungboonkrong, M. A. P Taylor. An integrated planning tool for evaluating road environmental impacts, Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 1999, 14(5): 335–337.
Jia, Ch. Q., Yang, G. D., Study on remediation and ecological restoration for temporary landuse in highway construcion, J. Environmental Protection in Transportation, 2000, 21(6): 23–26.
Huang, J. H., Li, Q., Liu, X. L., Environmental impact of Zhoukou province boundary super highway in Henan Province, J. Journal of Ecology (in Chinese), 2002, 21(1): 74–79.
Sun, X. J., Chen, F. X., Environmental impact assessment and prediction of Huang-Huang expressway in operation in Hubei, J. Geological Reconnaissance and Safety (in Chinese), 2000, 4: 36–38.
Jiang, Ch., Ma, D. Z., Wen, F. L., Earth extraction sites for construction of highways in Ningxia and restoration of vegetation, J. Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology (in Chinese), 2002, 6: 39–40.
Li, L. J., Guo, W. J., Yang, Ch. Y., On comprehensive model for environmental impact assessment of railway construction projects, J, Environmental Protection in Transportation (in Chinese), 2002, 22(4): 17–20.
Gao, P. L., Lai, W. H., Zhao, X. J., Approaches to prediction and assessment of eco-environmental impact of railway construction projects in Northwest China, J, Environmental Science (in Chinese), 1998, 19(4): 35–37.
Zhang, H., Shen, W. Sh., Zou, Ch. X., Study on landscape visual management system of the qinghai-Tibet railway, J, Natural Resources (in Chinese), 2003, 18(6): 719–725.
Zou, Ch. X., Shen, W. Sh., Zhang, H., Soil erosin prediction for construction of the Qinghai-Tibet railway, Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation (in Chinese), 2003, 23(6): 15–18.
Zhang, H., Shen, W. Sh., Jiang, L. Sh. et al., approach of evaluation on landscape protection along the Qinghai-bibet railway, Acta Ecologica Sinica (in Chinese), 2004, 24(3): 574–582.
Zhao, Y. L., Distribution of Fragile Types of Eco-environment and Their Comprehensive Management in China (in Chinese), Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1999, 99–100.
Manuel, C. M., Jr., Ecology: Concepts and Applications, New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 1999, 383–394.
Su, D. X., Xue, Sh. M., Zhou, R. Y., Grassland Resources in Tibet (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1994, 189–190.
Wang, Q. J., Zhou, X. M., Shen, Zh. X. et al., Structure of the alpine Kobresia pusilla swampy meadow phytocommunity and its utilization(ed. Haibei Long-term Station on Alpine Meadow Eco-system), Alpine Meadow Ecosystems (in Chinese), Vol. 4, Beijing: Science Press, 1995, 91–100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, W., Zhang, H., Zou, C. et al. Approaches to prediction of impact of Qinghai-Tibet Railway construction on alpine ecosystems alongside and its recovery. Chin. Sci. Bull. 49, 834–841 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889757
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889757