Abstract
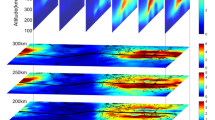
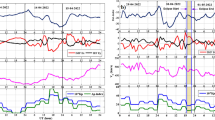
Simultaneous observations at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica, during May 1–7, 1998 are presented to show the responses of the polar ionosphere to the April/May 1998 solar events. One of the main geo-effects of the solar events resulted in the major magnetic storm on May 4. At the storm onset on May 2 the ionosphere F2 layer abruptly increased in altitude, the geomagnetic H-component started negative deviation and the spectral amplitude of the ULF wave intensified. Both large isolated riometer absorption and large negative deviation of the geomagnetic H-component occurred at about 0639UT. There was a time lag of about one hour and ten minutes between the storm onset and the IMF southward turning, as measured by the WIND satellite. The polar ionosphere was highly disturbed, as shown by frequent large deviations of the geomagnetic H-component, large riometer absorption events and strong ULF waves in all the courses of the storm. The absorption increased greatly causing the digisonde to be blackout most of the time. However, the data still showed a substantial decrease in the F2 electron density and oscillation of the F2 layer peak height with an amplitude exceeding 200 km.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knipp, D. J. et al., An overview of the early November 1993 geomagnetic storm, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, 103: 26197.
Fox, N. J., Perodo, M., Thompson, B. J., Cradle-to-grave traking of the January 6–11, 1997, Sun-Earth connection event, Geophys. Res. Letts., 1998, 24,14, 2461–2464.
Baker, D. N., Allen, J. H., Kanekal, S. G. et al. Disturbed space environment may have been related to pager satellite failure, EOS Trans. AGU, 1998, 79(40): 477.
Liu R. Y., Present and future research program in solar—terrestrial physics at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica, in Magnetospheric Research with Advanced Technique (eds. Xu, R. L., Lui, A. T. Y.), Dordrecht: Elsevier Science, 1998.
National Geophysical Data Center, Solar-Geophysical Data (prompt reports), Number 647-Part 1, July, 1998.
Akasofu, S.-I., Energy coupling between the solar wind and magnetosphere, Space Sci. Rev., 1981, 28: 121.
Huang, C. Y., Burke, W. J., Gussenhoven, M. S. et al., Ionospheric response to magnetic forcing: magnetic cloud passage of October 18–20, 1995, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1998, 25(14): 2581.
He Longsong, Nishino, M., Zhang Beichen et al., Absorption events associated with solar flares, Chinese Sci. Bull., 2000, 46(5): 369–372.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Hu, H., He, L. et al. Multiple ground-based observations at Zhongshan Station during the april/may 1998 solar events. Sci. China Ser. A-Math. 45 (Suppl 1), 120–131 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889693
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889693