Abstract
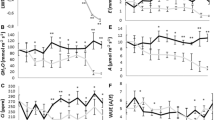
An improved system of plant cultivation at stable and specific levels of polyethyleneglycol (PEG, mol. mass 1400–1600) — induced water stress has been described. To set up this system a perforated tubular glass vessel containing soil to support seedling growth was wrapped externally first with a layer of macroporous silica gel-G and then with three layers of a dialysis membrane of a lower exclusion limit (2000 mol. mass). Effects of 8 days of PEG — induced stress have been studied on uptake and translocation of N and P and growth of barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv. KN 16) seedlings. Some of the noteworthy improvements of the system were exelusion of PEG from the plant consequent upon use of silica gel-membrane combination, shorter time (2 days) for the soil-plant-air continuum to attain steady state, and stability of the plant water potential over a period of a few days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon, D. I., Hoagland, D. R.: Composition of the tomato plants as influenced by the nutrient supply in relation to fruiting. - Bot. Gaz.104: 576–590, 1943.
Cox, L. M., Boersma, L.: Transpiration as a function of soil temperature and soil water stress. - Plant Physiol.42: 550–556, 1967.
Graham-Bryce, I. J.: Method of supplying water to soil at osmotically controlled potentials. - Chem. Ind.9: 353–354, 1967.
Haintes, J. R., Alexander, M.: Microbial degradation of polyethylene glycols. - Appl. Microbiol.29: 621–625, 1975.
Janes, B. E.: The effect of molecular size, concentration in nutrient solution and exposure time on the amount and distribution of polyethylene glycol in pepper plants. - Plant Physiol.54: 226–230, 1974.
Jensen, S.: A morphological and biochemical analysis of the early phases of cellular growth in the root tip ofVicia faba. -Exp. Cell Res.8: 506–522, 1955.
King, E. R., Wooton, T. D. P.: Microanalysis in Medical Biochemistry. - Churchill, London 1959.
Lawlor, D. W.: Absorption of polyethylene glycols by plants and their effects on plant growth. - New Phytol.69: 501–513, 1970.
Mexal, J., Fisher, J. T., Osteryoung, J., Reid, C. P.: Oxygen availability in polyethylene glycol solutions and its implications in plant water relations. - Plant Physiol.55: 20–24, 1975.
Parmar, M. T., Moore, R. P.: Carbowax-6000, mannitol and sodium chloride for stimulating drought conditions in germination studies of corn (Zea mays L.) of strong and weak vigour. - Agron. J.60: 192–196, 1968.
Resnik, M. E.: Effect of mannitol and polyethylene glycol on phosphorus uptake by maize plants. - Ann. Bot.24: 297–304, 1970.
Shardakov, V. S.: New field method for the determination of suction pressure in plants. - Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR60: 169–172, 1948.
Tingey, D. T., Stockwell, C.: Semipermeable membrane system for subjecting plants to water stress. - Plant Physiol.60: 58–60, 1977.
Zur, B.: Osmotic control of the matric soil-water potential. II. Soil-plant system. - Soil Sci.102: 130–138, 1967
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P.N., Prasad, R., Salim, M. et al. An improved system of subjecting plants to water stress. Biol Plant 26, 16–21 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02880419
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02880419