Abstract
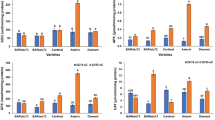
Carbohydrate changea in drought resistant and susceptible cultivars ofZea mays L. were studied at two different stages under imposed water stress in water culture experiments. The gradual decline in total carbohydrates with increasing stress levels was observed. At the 1st leaf stage starch content of the resistant cv. Agati-76 was lower than that of susceptible cv. Vijay but the reducing and non-reducing sugar content was much higher. At the 3rd leaf stage starch content was similar in two cultivars but sugar content was higher in the resistant cv. Agati-76. Differential changes in root and shoot carbohydrates as affected by increasing levels of stress were noticed. Carbohydrate changes have been discussed in relation to drought resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon, D. I., Hoagland, D. R.: Crop production in artificial solutions and soils with special reference to factors influencing yields and absorption of inorganic nutrients. — Soil Sci.50: 463–484, 1940.
Boyer, J. S.: Effects of osmotio water stress on metabolic rates of cotton plants with open stomata. — Plant Physiol.40: 229–234, 1965.
Brix, H.: The effect of water stress on the rates of photosynthesis and respiration in tomato plants and loblolly pine seedlings. — Physiol. Plant.15: 10–20, 1962.
Charles, C. A., Todd, G. W.: Ribonucleotide compositional changes in wheat leaves by water stress. — Crop. Sci.8: 319–321, 1968.
Eaton, F. M., Ergle, D. R.: Carbohydrate accumulation in the cotton plants at low moisture levels. — Plant Physiol.23: 169–187, 1948.
Hanson, A. D., Nelson, C. E., Everson, E. H.: Evaluation of free proline accumulation as an index of drought resistance using two contrasting barley cultivars. — Crop. Sci.17: 720 to 726, 1977.
Henckel, P. A.: Role of protein in drought resistance. — Can. J. Bot.48: 1235–1241, 1970.
Iljin, W. S.: Drought resistance in plants and physiological processes. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.8: 257–272, 1957.
Mali, P. C., Mehta, S. L.: Effect of drought on enzymes and free proline in rice varieties. — Phytochemistry16: 1355–1358, 1977.
Marnville, J. W., Paulsen, G. M.: Alterations of carbohydrate composition of corn (Zea mays L.) seedlings during moisture stress. — Agron. J.62: 605–608, 1970.
O’Toole, J. C., Ozbun, J. L., Wallace, D. H.: Photosynthetic responses to water stress inPhaseolus vulgaris. — Physiol. Plant.40: 111–114, 1977.
Pasternak, D., Wilson, G. L.: Photosynthesis and transpiration in the heads of droughted grain sorghum. — Aust. J. exp. Agr. anim. Husb.16: 72–75, 1976.
Smith, L. D.: Removing and analysing total non-structural cyrbohydrate from plant tissue. — Wisconsin agr. exp. Res. Rep. No.41, 1969.
Somogyi, M.: A new reagent for the determination of sugars. — J. biol. Chem.160: 61–68, 1945.
Spoehr, H. A., Milner, H. W.: Starch dissolution and amylolytic activity of leaves. — Proc. Amer. Phil. Soc.81: 37–38, 1939.
Stewart, C. R.: Effect of wilting on carbohydrates during incubation of excised bean leaves in the dark. — Plant Physiol.48: 792–794, 1971.
Stewart, C. R., Morris, C. J., Thomson, J. F.: Changes in amino aoid content of excised leaves during incubation. II Role of sugar in the accumulation of proline in wilted leaves. — Plant Physiol.41: 1585–1590, 1966.
Thakur, P. S.: Studies on basic growth behaviour and protein metabolism under water stress inZea mays L. — Thesis, Himachal Pradesh University, Simla1978.
Vaadia, Y., Raney, R. C., Hagan, R. M.: Plant water deficits and physiological processes. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.8: 257–272, 1961.
Wadleigh, C. H., Ayers, A. D.: Growth and biochemical composition of bean plants as conditioned by soil moisture tension and salt concentration. — Plant Physiol.20: 106–132, 1945.
Wager, H. G.: The effect of artificial wilting on the sugar content and respiration rate of maturing green peas. — New Phytol.53: 354–363, 1954.
Wardlaw, I. F.: The effect of water stress on translocation in relation to photosynthesis and growth: 1. Effect during grain development in wheat. — Aust. J. biol. Sci.20: 25–39, 1967.
Wiggans, S. C., Gardner, F. C.: Effectiveness of various solutions for simulating drought conditions as measured by germination and seedling growth. — Agron. J.51: 315–318, 1959.
William, G. C., Cox, G. M.: Experimental Designs. — John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York 1957.
Woodhams, D. H., Kozlowski, T. T.: Effect of soil moisture on carbohydrate development and growth in plant. — Amer. J. Bot.41: 316–320, 1954.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, P.S., Rai, V.K. Water stress effects on maize: Carbohydrate metabolism of resistant and susceptible cultivars ofZea mays L.. Biol Plant 22, 50–56 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878127
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878127