Abstract
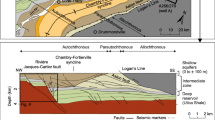
The conduit system of heat fluids in diapiric belt of Yinggehai basin is dominantly vertical faults and fractures. Detailed research on the formation mechanism and their occurrence features shows that the faults and fractures can be classified into three types: intrastratal dispersive hydrofracture, puncturing fault and upwarping-extensional fault. The development of the fault and fracture system not only resulted in the changes of the temperature and pressure fields in the basin, but also affected the hydrocarbon migration in the overpressured system. These faults and fractures constituted the main pathways for vertical hydrocarbon migration, and opening and closing intermittently led to episodic expulsion of overpressured fluid compartment. Thus there formed the pool-forming model of multi-source mixing and ploy-stage migration and accumulation for hydrocarbons in the Yinggehai basin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du Xu, Zheng Hongyin, Jiao Xiuqiong, Abnormal pressure and hydrocarbon accumulation,Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese), 1995, (2)3: 137.
Hunt, J., Generation and migration of petroleum from abnormally pressured fluid compartments,AAPC Bulletin, 1990, 74: 1.
Anderson, R. N., Sedimentary basins as thermochemical reactors, 1990 and 1991,Report of Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory, 1993, 65–76.
Roberts, S. J., Nunn, J. A., Episodic fluid expulsion from geopressured sediments,Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1995, 12(2): 195.
Wang, C. Y., Xie, X. N., Hydrofracturing and episodic fluid flow in shale-rich basins-a numerical study,AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(10): 1857.
Wang Chiyuen, Yang Jiaming, Zhu Weilin et al., Some problems in understanding basin evolution,Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese), 1995, 2(3–4): 29.
Xie Xinong, Wang Chiyuen, Li Sitian, Hydrofracture and episodic compaction in low permeable muddy rocks,Chinese Science Bulletin, 1997, 42(19): 2193.
du Rouchet, J., Stress field, a key to oil migration,AAPG Bulletin, 1991, 65: 74.
Bour, O., Lerche, I., Numerical modeling of abnormal fluid pressures in the Navarin basin, Bering Sea,Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1994, ll(4): 491.
Powers, M. C., Fluid release mechanisms in compacting marine mudstones and their importance in oil exploration,AAPG Bulletin, 1967, 51: 1240.
Dickey, P. A., Possible primary migration from source rock in oil phase,AAPG Bulletin, 1975, 59: 337.
Capuano, R. M., Evidence of fluid flow in microfractures in geopressured shales,AAPC Bulletin, 1993, 77: 1303.
Cartwright, J. A., Episodic basin-wide fluid expulsion from geopressured shale sequences in the North Sea Basin,Geology, 1994, 22: 447.
Li Sitian, Lin Changsong, Zhang Qiming, Dynamic process of episodic rifting in continental marginal basin and tectonic events since 10 Ma in South China Sea,Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(8): 797.
Zhang Qiming, Hu Zhongliang, High temperature and pressure environments and migrating regime of hydrocarbon in Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan basin,China Offihore Oil and Gas (Geology) (in Chinese). 1992, 6(1): 1.
Zhang Qiming, Liu Funing, Yang Jihai, Overpressure system and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Yinggehai basin,China offshore Oil and Gas (Geology) (in Chinese), 1996, 10(1): 65.
Chen Fajing, Tian Shicheng,Compaction and Hydrocarbon Migration (in Chinese), Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1989, 63–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project jointly supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No.95-Pre-39) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 49732005), and A Hundred Excellent Researchers Foundation from the Ministry of Land and Resources.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, X., Li, S., Hu, X. et al. Conduit system and formation mechanism of heat fluids in diapiric belt of Yinggehai basin, China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 42, 561–571 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877783
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877783