Summary
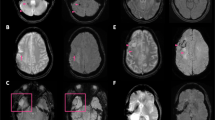
The utility of three-dimensional spoiled gradient recalled acquisition in steady state (3D-SPGR) imaging in the cerebral diseases was evaluated and 3D-SPGR after enhancement in depicting contrast enhancement of all lesions and 2D-SE T1WI comparatively analyzed. 117 patients were subjected to MRI by a GE 1. 5T MR system. After performance of axial T1WI and T2WI in all patients, MRA (3D-MOTSA) images were acquired in 6 cases (8 lesions) of aneurysms. After enhancement, 3D-SPGR images were obtained in all the remaining patients. Quality parameters (SNR, C and CNR) were calculated on enhanced 2D-SE T1WI and 3D-SPGR images. And a four-point scale was used to measure the signal intensity of the main lesions on both sequences, then statistical analysis of the average score was performed with “t” test. Except for aneurysms, 2D-SE T1WI detected 134 lesions and 3D-SPGR disclosed 147 lesions. It was found that there was no statistically significant difference between the two average scores as determined by the “t” test (t=1.894,P>0.05). The enhancement degree of the main lesion was equivalent on 3D-SPGR and 2D-SE T1WI. Quality parameters (SNR, C and CNR) on 2D-SE T1WI were much larger than that of 3D-SPGR, increasing by an average of 57%, 20% and 97% respectively. 3D-SPGR imaging with MPR could clearly depict vascularity related to neoplasms in 20 cases and demonstrate shifted, deformed and blocked vessels involved by tumors. Six cases of large aneurysms (8 lesions) were visualized more clearly on 3D-SPGR than MRA (3D-MOTSA): 3D-SPGR could display aneurysm necks and differentiate thrombosed portion from the patent lumen, and disclose relationship of aneurysm to surrounding structures. It was concluded that enhanced 3D-SPGR played an important role in the depiction of the cerebral lesions and was superior to 2D-SE T1WI in many aspects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prorok R J. Signal applications guide Vol2, 4th edition. Milwaukee, Wisconsin, U. S. A: GE Medical System, 1990, 12–14
MRI Diagnosis, Editor Gao Yuangui, Beijing Publisher, 1993, 48–49
Bomans M, Hohne K H, Laub Get al. Improvement of 3D acquisition and visualization in MRI. Magen Reson Imaging, 1991,9:597
Held P, Fellner C, Fellner Fet al. Three-dimensional MP-RAGE: an alternative to conventional three-dimensional flash sequences of the diagnosis of viscerocranial tumors. Br J Radiol, 1995,668:1316
Mirowitz S A. Intracranial lesion enhancement with Gadolinnium: T1-weighted spin-echo versus three-dimensional fourier transform gradient-echo MR imaging. Radiology, 1992,185:529
Zawadzki M B, Gillan G D, Nite W Ret al. MP-RAGE: a three-dimensional, T1-weighted, gradiented-echo sequence, initial experience in the brain. Radiology, 1992,182:769
Shogry M C, Elsteer A D. Cerebrovascular enhancement in spoiled GRASS (SPGR) images: comparison with spin-echo technique. JCAT, 1992,16:48
Atlas S W. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine. 2nd edition. Lippincott-Ravenn Publicshers, Philadelphia, 1996, 1481–1483
Kurihara N, Takahashi S, Higano Set al. Evaluation of large intracranial aneurysm with three-dimensional MRI. JCAT, 1995,19:707
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
ZHU Wenzhen, female, born in 1969, Doctor in Charge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wenzhen, Z., Jianpin, Q. & Chengyuan, W. Comparative study of 3D-SPGR vs 2D-SE T1WI after enhancement in the brain. Current Medical Science 23, 180–183 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02859951
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02859951