Abstract
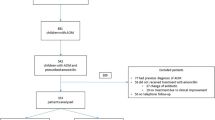
Acute Otitis Media (AOM) is the most frequent respiratory tract infection of infancy and childhood that is treated with antimicrobial agents. The most common causative pathogens includeStreptococcus pneumoniae, Hemophilus influenzae andMoxarella catarrhalis, and therefore antibacterial management should target against these isolates. Cefactor, a congener of cephalexin monohydrate, is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic. It is an orally active cephalosporin which has demonstrated activity against a wide range of organismsin vitro. Present study is designed as a multicentric prospective trial to study and compare the efficacy and safety of cefaclor versus amoxicillin+clav in children with acute otitis media. One hundred and sixty seven patients were evaluated for efficacy endpoints in the cefaclor arm comprised of 104 males and 63 females with a mean age of 5.74±2.80 years and 185 patients in the amoxy-clav group comprised of 118 males and 67 females with a mean age of 4.93±2.92 years. Both cefaclor and amoxy-clav caused a significant improvement in all the signs and symptoms after a 10-day treatment period. However, between-the-group comparisons showed that the reduction i nmost of the symptoms was significantly more in cefaclor arm as compared to amoxicillin-clav arm. The clinical success (clinical cure + improvement) at the end of therapy was significantly more in cefaclor arm: 98% with cefaclor versus 85% with amoxicillin+clav, p<0.05 (Table 3). Failure cases were prescribed other antibiotics according to the culture sensitivity reports, as rescue medication. Bacterial eradication rates were largely consistent with clinical responses. Bacteriological eradication was seen in 95% of patients in cefaclor group and 78% of patients in amoxicillin+clav group. In conclusion, cefaclor is a well tolerated and effective antibacterial option for acute otitis media in children and it is superior to the combination of amoxicillin+clav in efficacy and tolerability in acute AOM. Moreover, its expanded spectrum of activity, ability to achieve adequate concentrations in tissues, suitability for twicedaily dosing, and proven tolerability suggest that it is a good alternative to agents traditionally used in acute otitis media.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dagan R. Can the choice of antibiotics for acute AOM be logical?Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1998; 17:1–5.
Parsons DS, Wald ER. Otitis media and sinusitis: similar diseases.Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1996; 29:11–25.
Poole MD. Otitis media complications and treatment failures: implications of pneumococcal resistance.Pediatr Infect Dis J 1995; 14: S23–26.
Rodriguez WJ, Shwartz RH, Thorne MM. Increasing incidence of penicillin and ampicillin-resistant middle ear pathogens.Pediatr Inf Dis J 1995; 14: 1075–1078.
Pichichero ME, Pichichero CL. Persistent acute otitis media: causative pathogens.Pedaitr Inf Dis J 1995; 14: 178–183.
Derry JE. Evaluation of cefaclor.Am J Hosp Pharm 1981; 38(1): 54–58.
Bluestone CD, Klein JO, eds.Otitis Media in Infants and Children. WB Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1987.
Glebink GS. The microbiology of otitis media.Pedaitr Inf Dis 1989; 8: S18-S20.
Rodriguez AF. An open study to compare azithromycin with cefaclor in the treatment of children with acute otitis media.J Antimicrob Chemother 1996; 37 Suppl C: 63–69.
Turik MA, Johns D. Comparison of cefaclor and cefuroxime axetil in the treatment of acute AOM with effusion in children who failed amoxicillin therapy.J Chemother 1998; 10(4): 306–312.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aggarwal, M., Sinha, R., Murali, M.V. et al. Comparative efficacy and safety evaluation of cefaclor VS amoxycillin + calvulanate in children with Acute Otitis Media (AOM). Indian J Pediatr 72, 233–238 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02859264
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02859264