Abstract
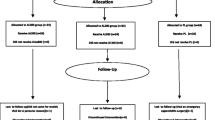
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of Taizhi’an (TZA) capsule combined with Simvastatin (Sim) in treating hyperlipidemia in diabetes mellitus (DM) patients.Methods: Eighty cases of type 2 DM patients with hyperlipidemia were randomized into two groups, 40 in each group. The patients in the treated group took orally TZA capsules at the dose of 0.9 g 3 times a day and Sim 10 mg at bedtime. And the patients in the control group were treated with Sim 20 mg alone at bedtime. Both regimens lasted for 12 weeks. Before and after the study the changes of blood lipid levels and adverse reaction were investigated.Results: The serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG) and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) were decreased respectively by 28.8%, 18.2% and 26.3% in the treated group; and by 29.4%, 19.4% and 24.6% in the control group. On the contrary, high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) was increased by 23.5% in the treated group and by 29.4% in the control group. All these changes were statistically significant before and after treatment (allP<0.05), but they did not differ statistically between the two groups (P>0.05). There was no significant changes in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). Patients in the treated group did not develop any adverse reactions. However, ALT was found to be higher above the normal range in 5% of the patients in the control group.Conclusion: In treating hyperlipidemia in DM patients, combination of TZA with Sim 10 mg taken daily achieved satisfactory efficacy which was similar to Sim 20 mg daily alone. But the combination therapy conducted in the treated group proved to be better in safety, and could overcome adverse reactions resulting from Sim that was seen in the control group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong YH, Qian RU editors. Contemporary treatment of diabetes and its complications. Jinan: Shandong Scientific and Technologic Publishing House, 1994: 121–122.
Mukamal KJ, Nesto RW, Cohen MC, et al. Impact of diabetes on long-term survival after acute myocardial infarction: comparability of risk with prior myocardial infarction. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 1422–1427.
Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486–2497.
Qian RL. New criteria for the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Chin J Diabetes 2000; 8(1): 5–6.
Fagan TC, Sowers J. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: greater cardiovascular risks and greater benefits of therapy (Editorial). Arc Intern Med 1999; 159: 1033–1034.
Steven AG, Louis C, Hanna Z, et al. Cost-effectiveness of treating hyperlipidemia in the presence of diabetes. Circulation 2000; 102: 722–727.
American Diabetes Association. Dyslipidemia management in adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: S68-S71.
He H, Liu QN, Wang HF, et al. Effect of Atorvastatin on hyperlipidemia in senile type 2 diabetics. Chin Hosp Pharm J 2004; 24(4): 232–233.
Qi BL. Cheng B, Zhang QH. Comparison of effects of Taizhian capsule and pravastatin on vascular endothelial function in senile patients with coronary heart disease. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med 2004; 24(5): 404–407.
Miao YD, Liu J. Evaluation for the efficacy of Taizhian in the treatment of primary hyperlipidemia in aged patients. Chin Pharm Health J 2003; 24(1): 32–34.
Li QL, Zhang YF. Clinical observation on effect of Taizhian capsule in treating 150 patients with hyperlipidemia. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med 2003; 23(5): 335–337.
Pedersen TR, Tobert JA. Simvastatin: a review. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2004;5(12): 2583–2596.
Ovesna Z, Vachalkova A, Horvathova K, et al. Pentacyclic triterpenoic acids: new chemoprotective compounds. Minireview. Neoplasma 2004; 51(5): 327–333.
Li GH, Yang ZN. Experimental studies on antihyperlipidemia effects of two compositions from hawthorn in mice. Chin Tradit Herbal Drugs 2002; 33(1): 50–52.
Yin XD, Zhao HR. Progress in ursolic acid research. Chin Pract J Tradit West Med 2004; 17(24): 3830–3832.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, G., Xiu-fen, H. Effect of Taizhi’an capsule combined with Simvastatin on hyperlipidemia in diabetic patients. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 12, 24–28 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857425
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857425