Abstract
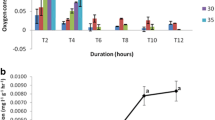
Temperature and the dissolved oxygen content affect the oxygen consumption of juveniles of Chinese prawn (Penaeus chinensis), giant tiger prawn (P. monodon) and giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). There is good correlation between the oxygen consumption rate (V, mg/g·h) of the above three prawn species and the water temperature, and dissolved oxygen. In the range of test temperature,V increased with water temperature and dissolved oxygen content. TheV of the above three prawn species increased 0.085 mg/g·h, 0.093 mg/g·h and 0.08 mg/g·h respectively with each °C of rising temperature. The comatose point and stifling point of the juveniles rose obviously at unsuitable temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guan Yunling, 1988. Studies of consumed oxygen of gill tissue taken from oyster.Oceanologia et Limnologia sinica 19(3): 210–214. (in Chinese).
Li Zengchong, Gao Tiyou, 1981, Giant Freshwater Prawn. Guangxi People Press, Nanning, p. 55–96. (in Chinese)
Pan Jiamo, Sun Zurong, Wang Zhiqiang, 1994. Giant Freshwater Prawn Latest Culturing Technique. Shanghai Science and Technique Press, Shanghai, p. 24–25, 113–114. (in Chinese).
Wang Jun, 1986. The Collecting Data Means for Culturing Shrimp. Mu Wentang Printing Limited Company, p. 221–238. (in Chinese).
Wang Liangchen, Liu Xiuye, 1991. Culturing Prawn. Nan Kai University Press, Tianjin, p. 39–47, 141–142. (in Chinese)
Wei Liping, 1989. Studies of respiration & abnormal respiration of Farrer'scallop.Oceanologia et Limnologia sinica 20(3): 209–216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu Guirong, Zang Weiling, Dai Xilin et al., 1997. The Influence of Salinity on Giant Freshwater Prawn Juvenile Growth.J. Shanghai fisheries Univ. 6(2): 89–91. (in Chinese)
Zang Weiling, 1991. Water Quality Analysis for Culturing Fish. Agricultural Press, Beijing, p. 44–51. (in Chinese)
Zang Weiling, Dai Xilin, Zhu Zhengguo et al., 1993. Hydrochemistry in Estuary Pond for intermediate Stage Culture ofPenaeus chinensis juvenile.J. of Shanghai Fisheries University 2(2–3): 101–112. (in Chinese)
Zang Weiling, Zhu Zhengguo, Dai Xilin et al., 1992. Studies on the Correlation between the Instantaneous Oxygen Consumption Rate of Chinese Prawn and the Aquatic Environment.Fisheries Science & Technology Information 19(4): 100–103. (in Chinese)
Zhang Hongjie, Li Mingde, 1993. Prawn Culture and Processing. Agricultural Scientific and Technological Press, Beijing, p. 77–78. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was a major program of the Agriculture Commission of Shanghai.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi-lin, D., Wei-ling, Z., Wei-dong, W. et al. Effects of temperature and dissolved oxygen content on oxygen consumption rate of Chinese prawn, giant tiger prawn and giant freshwater prawn. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 17, 119–124 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842709
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842709