Abstract
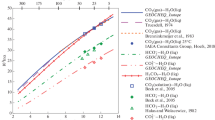
Oxygen isotope fractionation in TiO2 polymorphs has been calculated by the modified increment method. The results suggest that rutile is enriched in18O relative to brookite but depleted in18O relative to anatase. Due to the same crystal structure, oxygen isotope partitioning in the TiO2 polymorphs is determined by the cation-oxygen interatomic distances. The theoretical calibrations involving rutile are in fair agreement with known experimental measurements and empirical estimates. Application of the theoretical quartz-rutile calibration to geothermometry of natural eclogite assemblages indicates the preservation of isotopic equilibrium at high temperatures. The isotopic temperatures calculated are only slightly lower than the non-isotopic temperatures, indicating the slow rates of exchange for oxygen diffusion in rutile. The kinetics of exchange for oxygen diffusion in rutile is accordingly estimated by reconciling the differences between the isotopic and the non-isotopic temperatures. The rates of exchange for oxygen diffusion in rutile should be smaller than those for hornblende, but may be equal to or greater than those for diopside.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addy, S. K. and G. D. Garlick, 1974, Oxygen isotope fractionation between rutile and water: Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v. 45, p. 119–121.
Agrinier, P., 1991, The natural calibration of18O /16O geothermometers: application to the quartz-rutile mineral pair: Chem. Geol., v. 91, p. 49–64.
Agrinier, P., M. Javoy, D. C. Smith, and F. Pineau, 1985, Carbon and oxygen isotopes in eclogites, amphibolites, veins and marbles from the western Gneiss Region, Norway: Chem. Geol., v.52, p. 145–162.
Berry, L. G., B. Mason, and R. V. Dietrich, 1983, Mineralogy: Concepts, Descriptions and Determinations: San Francisco, W. H. Freeman and Co., 561p.
Bigeleisen, J., 1961, Statistical mechanics of isotope effects on the thermodynamic properties of condensed systems: J. Chem. Phys., v. 34, p. 1485–1593.
Bigeleisen, J. and M. G. Mayer, 1947, Calculation of equilibrium constants for isotopic exchange reactions: J. Chem. Phys., v. 15, p. 261–267.
Bird, M., F. J. Longstaffe, and W. S. Fyfe, 1993, Oxygen-isotope fractionation in titanium-oxide minerals at low temperature: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 57, p. 3083–3091.
Bottinga, Y. and M. Javoy, 1975, Oxygen isotope partitioning among the minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks: Rev. Geophys. Space Phys., v. 13, p. 401–418.
Chiba, H., T. Chacko, R. N. Clayton, and J. R. Goldsmith, 1989, Oxygen isotope fractionations involving diopside, forsterite, magnetite, and calcite: application to geothermometry: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 53, p. 2985–2995.
Cole, D. R., H. Ohmoto, and A. C. Lasaga, 1983, Isotopic exchange in mineral-fluid systems, I. Theoretical evaluation of oxygen isotopic exchange accompanying surface reaction and diffusion: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 47, p. 1681–1693.
Desmons, J. and J. R. O’Neil, 1978, Oxygen and hydrogen isotope composition of eclogites and associated rocks from the eastern Sesia Zone (western Alps, Italy): Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v. 67, p. 79–85.
Eiler, J. M., J. W. Valley, and L. P. Baumgartner, 1993, A new look at stable isotope thermometry: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 57, p. 2571–2583.
Elphick, S. C. and C. M. Graham. 1988, The effect of hydrogen on oxygen diffusion in quartz: evidence for fast proton transients: Nature, v. 335, p. 243–245.
Farver, J. R., 1989, Oxygen self-diffusion in diopside with application to cooling rate determination: Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v. 92, p. 386–396.
Farver, J. R. and B. J. Giletti, 1985, Oxygen diffusion in amphiboles: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 49, p. 1403–1411.
Farver, J. R. and R. A. Yund, 1990, The effect of hydrogen, oxygen, and water fugacity on oxygen diffusion in alkali feldspar: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 54, p. 2953–2964.
Fortier, S. M. and B. J. Giletti, 1991, Volume self-diffusion of oxygen in biotite, muscovite, and phlogopite micas: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 55, p. 1319–1330.
Freer, R. and P. F. Dennis, 1982, Oxygen diffusion studies, I. A preliminary ion microprobe investigation of oxygen diffusion in some rock-forming minerals: Mineral. Mag., v. 45, p. 179–192.
Garlick, G. D., 1966, Oxygen isotope fractionation in igneous rocks: Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v. 1, p. 361–368.
Giletti, B. J., 1985, The nature of oxygen transport within minerals in the presence of hydrothermal water and the role of diffusion: Chem. Geol. v. 53, p. 197–206.
Giletti, B. J., 1986, Diffusion effects on oxygen isotope temperatures of slowly cooled igneous and metamorphic rocks: Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v. 77, p. 218–228.
Giletti, B. J. and R. A. Yund, 1984, Oxygen diffusion in quartz: J. Geophys. Res., v. 89, p. 4039–4046.
Giletti, B. J. and K. C. Hess, 1988, Oxygen diffusion in magnetite: Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v. 89, p. 115–122.
Giletti, B.J., M. P. Semet, and R. A. Yund, 1978, Studies in diffusion, III. Oxygen in feldspars, and ion microprobe determination: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.42, p. 45–57.
Javoy, M, 1977, Stable isotopes and geothermometry: J. Geol. Soc. (London), v. 133, p. 609–636.
Jenkin, G. R. T., C. Link later, and A. E. Fallick, 1991, Modeling of mineral δ18O values in an igneous aureole: closed-system model predicts apparent open-system δ18O values: Geology, v. 19, p. 1185–1188.
Kawabe, I., 1978, Calculation of oxygen isotope fractionation in quartz-water system with special reference to the low temperature fractionation: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 42, p. 613–621.
Kieffer, S. W., 1982, Thermodynamics and lattice vibration of minerals: 5. application to phase equilibria, isotopic fractionation, and high pressure thermodynamic properties: Rev. Geophys. Space Phys., v. 20, p. 827–849.
Matthews, A. and M. Schliestedt, 1984, Evolution of the blueschist and greenschist facies rocks of Sifnos, Cyclades, Greece: a stable isotope study of subduction-related metamorphism: Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v. 88, p. 150–163.
Matthews, A., R. D. Beckinsale, and J. J. Durham, 1979, Oxygen isotope fractionation between rutile and water and geothermometry of metamorphic eclogites: Mineral. Mag., v. 43, p. 405–413.
Marthews, A., J. R. Goldsmith, and R. N. Clayton, 1983, On the mechanism and kinetics of oxygen isotope exchange in quartz and feldspars at elevated temperatures and pressures: Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., v. 94, p. 396–412.
O’Neil, J. R., 1986, Theoretical and experimental aspects of isotopic fractionation: Rev. Mineral., v. 16, p. 1–40.
O’Neil, J. R. and R. N. Clayton. 1964, Oxygen isotope geothermometry, in H. Craig, S. L. Miller and G. J. Wasserburg, eds., Isotopic and Cosmic Chemistry: Amsterdam, North-Holland Publ. Co., p. 157–168.
Richet, P., Y. Bottinga, and M. Javoy, 1977, A review of hydrogen, carbon nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur and chloride stable isotope fractionation among gaseous molecules: Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., v. 5, p. 65–110.
Richter, R. and S. Hoernes, 1988, The application of the increment method in comparison with experimentally derived and calculated 0-isotope fractionations: Chem. Erde, v. 48, p. 1–18.
RumbleIII D., 1982, Stable isotope fractionation during metamorphic volatilization reactions, in J. M. Ferry, ed., Characterization of Metamorphism through Mineral Equilibria: Reviews in Mineralogy, v. 10, p. 153–206.
Schütze, H., 1980, Der Isotopenindex—eine Inkrementenmethode zur näherungsweisen Berechnung von Isotopenaustauschgleichgewichten zwischen kristallinen substanzen: Chem. Erde, v. 39, p. 321–334.
Sharp, Z. D., J. R. O’Neil, and E. J. Essene, 1988, Oxygen isotope variation in granulite-grade iron formations: constraints on oxygen diffusion and retrograde isotope exchange: Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v. 98, p. 490–501.
Shieh, Y. -N., 1974, Mobility of oxygen isotopes during metamorphism, in A. W. Hofmann, B. J. Giletti, H. S. Yorder Jr. and R. A. Yund, eds., Geochemical Transport and Kinetics: Carnegie Inst. Washington Publication, v. 634, p. 325–335.
Smyth, J. R. and D. L. Bish, 1988, Crystal Structure and Cation Sites of the Rock-forming Minerals: Boston, Allen and Unwin, 332p.
Stern, M. J., W. Spindel, and E. U. Monse, 1968, Temperature dependence of isotope effects: J. Chem. Phys., v. 48, p. 2908–2919.
Taylor Jr., H. P. and S. Epstein, 1962, Relationship between18O /16O ratios in coexisting minerals of igneous and metamorphic rocks, Part 2, application to petrological problems: Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., v. 73, p. 675–694.
Urey, H. C., 1974, The thermodynamic properties of isotopic substances: J. Chem. Soc. (London), p. 562–581.
Valley, J. W., 1986, Stable isotope geochemistry of metamorphic rocks, in J. W. Valley, H. P. Taylor Jr. and J. R. O’Neil, eds., Stable Isotopes in High Temperature Geological Processes: Reviews in Mineralogy, v. 16, p. 445–490.
Vogel, D. E. and G. D. Garkick, 1970, Oxygen-isotope ratios in metamorphic eclogites: Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v. 28, p. 183–191.
Yund, R. A. and T. F. Anderson, 1978, Oxygen isotope exchange between feldspar and fluid as a function of fluid pressure: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 42, p. 235–239.
Zheng, Y. -F., 1992, Oxygen isotope fractionation in wolframite: Eur. J. Mineral., v. 4, p. 1331–1335.
Zheng Y. -F., 1993a, Oxygen isotope fractionation in SiO2 and Al2SiO5 polymorphs: effect of crystal structure: Eur. J. Mineral., v. 5, p. 651–658.
Zheng Y. -F., 1993b, Calculation of oxygen isotope fractionation in anhydrous silicate minerals: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 57, p. 1079–1091.
Zheng Y. -F., 1993b, Calculation of oxygen isotope fractionation in hydroxyl-bearing silicates: Earth Planet. Sci. lett., v. 120, p. 247–263.
Zheng Y. -F. and K. Simon, 1991, Oxygen isotope fractionation in hematite and magnetite: A theoretical calculation and application to geothermometry of metamorphic iron-formations: Eur. J. Mineral., v. 3, p. 877–886.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences within the framework of the project “Stable Isotope Geochemistry of the Earth’s Crust and Mantle”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yongfei, Z. Oxygen isotope fractionation in TiO2 polymorphs and application to geothermometry of eclogites. Chin. J. of Geochem. 14, 1–12 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840378
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840378