Abstract
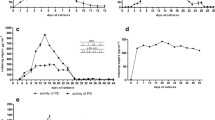
Biological conversion of the herbicide bromoxynil (3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzonitrile) was studied in a batch culture ofPseudomonas putida by using HPLC. The process had a cometabolic character and proceeded only in the presence of another, simultaneously metabolizable, carbon and energy source. The intensity of degradation correlated with the growth rate, the degradation stopping when the cosubstrate becomes exhausted or the pH value of the medium falls below 6.5. In a medium with glucose, no lag phase longer than one day was observed concerning growth, sugar and herbicide consumption and formation of metabolic herbicide derivatives (3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzamide and 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzoic acid). In a medium with ribose, the initial lag of the above processes took 2 d. No formation of other degradation products was detected. Growth inhibition was proportional to the concentration of bromoxynil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander M.: Microbial degradation and biological effect of pesticides in soil, pp. 209–240 inSoil Biology, Reviews of Research. UNESCO, Paris 1969.
Ashton F.M., Crafts A.S.:Mode of Action of Herbicides, pp. 236–255. John Wiley and Sons, New York 1973.
Bernfeld P.: Enzymes of starch degradation and synthesis.,Adv. Enzymol.12, 379–427 (1951).
Carpenter K., Cottrell H.J., De Silva W.H., Heywood B.J., Gleeds W., Rivet K.F., Soundy M.L.: Chemical and biological properties of two new herbicides—ioxynil and bromoxynil.Weed Res.4, 175–195 (1964).
Collins R.F.: Perfusion studies with bromoxynil octanoate in soil.Pestic. Sci.4, 181–192 (1973).
Cullimore D.H., Kohout M.: Isolation of bacterial degrader of the herbicide bromoxynil from a Saskatchewan soil.Can. J. Microbiol.20, 1449–1452 (1974).
Dalton H., Stirling D.I.:Co-metabolism.Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London, B297, 481–496 (1982).
Golovleva L.A., Vokounová M., Pertsova R.N., Baskunov B.P.: Degradation of herbicide bromoxynil in soil, its behaviour and effect on soil microflora. (In Russian)Agrokhimiya6, 80–86 (1987).
Golovleva L.A., Percova R.N., Kunc F., Vokounová M.: Degradation of herbicide bromoxynil in soil and in bacteria culture.Folia Microbiol.33, 491–499 (1988).
Krištůfek V., Beran M., Dufek P., Khan M.: Resistence ofStreptomyces felleus to the herbicide bromoxynil.Folia Microbiol.32, 297–304 (1987).
Krištůfek V.: Interactions between herbicides and soil streptomycetes. (In Czech)PhD Thesis, Czech. Acad. Sci., České Budějovice 1987.
Smith A.E.: Degradation of dromoxynil in Regina heavy clay.Weed. Res.11, 276–282 (1971).
Smith A.E., Cullimore D.R.: Thein vitro degradation of the herbicide bromoxynil.Can. J. Microbiol.20, 773–776 (1974).
Spiro R.G.: Analysis of sugars found in glycoproteins, pp. 3–26 inMethods in Enzymology, Vol. 8 (E.F. Neufeld, V. Ginsburg Eds.) Academic Press, New York 1966.
Torstensson L.: Role of microorganisms in decomposition, pp., 159–179 inInteractions between Herbicides and the Soil (R.J. Hance, Eds.) Academic Press, London 1980.
Večeřa M., Panchartek J.:Laboratory Handbook of Organic Chemistry 156–157. (In Czech) SNTL ALFA, Prague 1987.
Wells M.J.M., Michael J.L.: Reversed-phase solid-phase extraction for aqueous environmental sample preparation in herbicidal residue analysis.J. Chromatogr. Sci.25, 345–350 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated by Č. Novotný
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vokounová, M., Vacek, O. & Kunc, F. Degradation of the herbicide bromoxynil inPseudomonas putida . Folia Microbiol 37, 122–127 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836616
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836616