Abstract
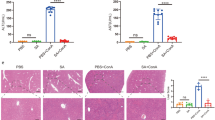
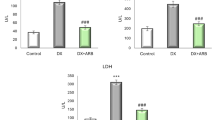
Objective: To study the effect of salvianolic acid B (SAB) and curcumin, the extracts ofSalvia Miltiorrhiza andCurcuma Longa, on the proliferation and activation of hepatic stellate cell (HSC), and the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) expression in it.Methods: Rat’s HSC-T6 were cultured and treated by SAB or curcumin. The inhibitory effect on cell proliferation was determined by 3-(4,5-dimthyl-2-2-thiazoly)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) colorimetry, and the expression levels of α smooth actin (α-SMA), collagen type I, and ERK were determined by Western blot.Results: SAB and curcumin inhibited the proliferation and activation of rat’s HSC-T6 in dose-dependent fashion and significantly reduced the expression level of a-SMA (P < 0.01). Curcumin significantly reduced the expression of collagen type I (P < 0.05). Both SAB and curcumin showed insignificant effect on the ERK expression level, but they could significantly reduce the level of phosphorylated-ERK expression, showing significant difference as compared with that in the control group (P < 0. 01 andP < 0. 05 respectively).Conclusion: SAB and curcumin could significantly inhibit the proliferation, activation of HSC, and the production of type I collagen in HSC, the mechanism may be associated with their inhibition on ERK phosphorylation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman SL. Mechanisms of disease: mechanisms of hepatic fibrosis and therapeutic implications. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;1(2): 98–105.
Xu LM, Liu C. Effect of lithospermate B on proliferation and shape of rat hepatic fat-storing cells and production of extracellular matrixin vitro. Chin J Hepatol 1996;4(2): 86–89.
Cheng Y, Ping J, Tan YZ, et al. Effect ofcurcuma longa Linn extraction on the proliferation and activation of rat hepatic stellate cell. World J of Infection 2006;6(1): 19–21.
Cheng Y, Ping J, Xu L, et al. Curcumin inhibits the gene expression of alpha smooth muscle actin and type I collagen in rat hepatic stellate cells by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma signal transduction pathway. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;21 (Suppl 2): A150.
Vogel S, Piantedosi R, Frank J, et al. An immortalized rat liver stellate cell line (HSC-T6): a new cell model for the study of retinoid metabolism in vitro. J Lipid Res 2000;41(6): 882–893.
Gu J, Hong JH, Xu LM, et al. Effects of “Fuzheng Huayu Capsule” on portal hemodynamics in patients with liver cirrhosis. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med 2005;39(11): 31 -32.
Cheng Y, Ping J. Salvianolic acid B and curcumin reduce the phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/ 2 expression level in rat hepatic stellate cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;21(S2): A145.
Liu YG, Chen HC, Jiang YP. Protective effect of curcumin on experimental liver injury in mice. Chin J Chin Mater Med 2003;28(8): 756–758.
Pinzani M, Marra F, Caligiuri A, et al. Inhibition by pentoxifylline of extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by platelet-derived growth factor in hepatic stellate cells. Br J Pharmacol 1996;119(6): 1117–1124.
Saxena NK, Titus MA, Ding X, et al. Leptin as a novel profibrogenic cytokine in hepatic stellate cells: mitogenesis and inhibition of apoptosis mediated by extracellular regulated kinase (Erk) and Akt phosphorylation. FASEB J 2004;18(13): 1612–1614.
Marra F, Arrighi MC, Fazi M, et al. Extracellular signalregulated kinase activation differentially regulates plateletderived growth factor’s actions in hepatic stellate cells, and is induced byin vivo liver injury in the rat. Hepatology 1999;30(4): 951–958.
Marra F, Delogu W, Petrai I, et al. Differential requirement of members of the MAPK family for CCL2 expression by hepatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2004;287(1): 18–26.
Friedman SL. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J Biol Chem 2000;275: 2247–2250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30300458)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Jian, P., Cheng, L. et al. Study on effects of extracts fromSalvia Miltiorrhiza andCurcuma Longa in inhibiting phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase expression in rat’s hepatic stellate cells. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 12, 207–211 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836524
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836524