Abstract
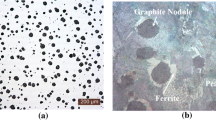
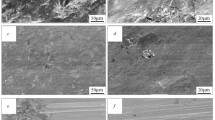
Several Alloys of Ductile Cast Iron containing various amounts of manganese, molybdenum, and nickel were austempered in the temperature range 316° to 427 °C. The rate and morphology of ferrite platelet formation (bainite reaction) were studied by optical metallography, x-ray diffraction, and hardness measurements. Austenitizing temperature, austempering temperature, and deformation by rolling were used as variables to control the kinetics of ferrite formation, stage I of the austempering reaction.
Vickers hardness, austenite carbon content, and volume fraction all change rapidly during the formation of the ferrite platelets, reaching a plateau when stage I is completed. The rate of this reaction is increased dramatically by deformation of the austenite prior to the reaction, is retarded somewhat by alloy additions, and increases with decreasing austenitization temperature. In addition, as the rate of the bainite reaction increases, with its higher ferrite plate density, a more uniform microstructure results, thus minimizing the incidence of martensite in the higher-alloy-content interdendritic volumes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. D. Matas and R. F. Hehemann: “The Structure of Bainite in Hypoeutectoid Steels,”AIME Trans., 1961, vol. 221, pp. 179–85.
R. LeHouillier, G. Begin, and A. Dube: “A Study of the Peculiarities of Austenite During the Formation of Bainite,”Met. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2645–53.
E. Dorazil, B. Barta, E. Munsterova, L. Stransky, and A. Huvar: “High Strength Bainitic Ductile Cast Iron,”AFS Int. Cast Met. J., June 1982, pp. 52–62.
T. Shiokawa: “On the Austempering of Ductile Cast Iron, Their Mechanical Properties and Some Practical Applications,” presented at 59th Japan Ductile Cast Iron Association’s License Conference, November 1978.
R. H. Edwards and N. F. Kennon: “The Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Bainite Formed from Deformed Austenite,”Met. Trans., 1978, vol. 9A, p. 1801.
W. J. Dubensky and K. B. Rundman: “An Electron Microscope Study of Carbide Formation in Austempered Ductile Iron,” submitted for publication in AFS Transactions, 1985.
D. Moore, T. Rouns, and K. Rundman: “On the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Austempered Ductile Iron,” accepted for publication in AFS Transactions, 1984.
H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia and D. V. Edmonds: “Bainite in Silicon Steels: New Composition-Property Approach—Part II,”Met. Sci., 1983, vol. 17, p. 420.
H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia and D.V. Edmonds: “The Bainite Transformation in a Silicon Steel,”Met. Trans., 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 895–907.
M. D. Jepson and F. C. Thomas:JISI, 1949, vol. 162, p. 49.
T. Rouns and K. Rundman: “On the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Austempered Ductile Iron,” to be presented at AFS Congress, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, D.J., Rouns, T.N. & Rundman, K.B. The effect of heat treatment, mechanical deformation, and alloying element additions on the rate of bainite formation in austempered ductile irons. J. Heat Treating 4, 7–24 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02835485
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02835485