Abstract
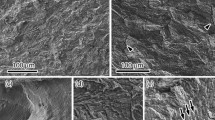
The cathodic charging of hydrogen into 4340 steel produces damage which ranges from reversible to irreversible, depending on the fugacity level of the charging. Fracture face morphology, (EDAX) and Auger spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were utilized to examine static fatigue, notch tensile, and ordinary tensile samples in various tempered and annealed conditions. The critical current densities for irreversible damage are between 0.1 and 0.5 mA/ cm2 and at about 10 mA/cm2 for As2O5 and thiourea-poisoned 1 N H2SO4 solutions, respectively, over a period of up to 3 hr. Fracture is intergranular for low fugacity charging but becomes transgranular for higher concentrations and fugacities of hydrogen. High fugacity hydrogen increased dislocation density and formed dislocation substructures. Cracks were nucleated at or just below external surfaces without external applied stress during charging and/or subsequent aging and baking treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.R. Troiano, Trans. ASM, 1960, vol. 52, p. 54.
R.A. Oriani,Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1978, vol. 8, p. 327.
J.P. Hirth,Met. Trans., 1980, vol. 11A, p. 861.
C.G. Iterrante, inCurrent Solutions to Hydrogen Problems in Steels, p. 3, ASM, Metals Park, Ohio, 1982.
B. Craig,Metals Handbook, 9th edition, vol. 13, p. 145, ASM, Metals Park, Ohio, 1987.
M. Smialowski,Hydrogen in Steel, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1962.
R. Speiser, inStress Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement in Iron Base Alloys, R.W. Staehl, J. Hochmann, R.D. McCright, and J.E. Slater, Eds., NACE-5, p. 226, NACE, 1977.
R.A. Oriani, inFundamental Aspects of Stress Corrosion Cracking, R.W. Staehl, A.J. Forty, and D. van Rooyen, Eds., NACE-1, p. 32, NACE, 1967.
M.J. Morgan and C.J. McMahon, Jr., inHydrogen Degradation of Ferrous Alloys, R.A. Oriani, J.P. Hirth, and M. Smialowski, Eds., p. 608, Noyes Publishers, Park Ridge, New Jersey, 1985.
In-Ok Shim, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utah, 1988.
A.H. Cottrell,An Introduction to Metallurgy, p. 352, Edward Arnold Ltd., London, 1967.
G.R. Speich,Metals Handbook, vol. 8, p. 202, ASM, 1973.
G.R. Speich,Met. Trans. AIME, vol. 245, p. 2553, 1969.
G.R. Speich and W.C. Leslie,Met. Trans., vol. 12A, p. 1197, 1981.
A. Seeger, inFrontiers in Materials Science, L.E. Murr and C. Stein, Eds., p. 177, Marcel Dekker Inc., 1976.
F. Alex, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utah, 1976.
K. Farrell,Corrosion, vol. 26, p. 105, 1970.
K. Farrell and A.G. Quarrell,J. Iron Steel Inst., vol. 202, p. 1002, 1964.
D.A. Vaughan and D.I. Phalen, inStress Corrosion Testing, ASTM STP 425, p. 209, 1967.
J. Clumm,Scripta Met., vol. 9, p. 51, 1975.
P.G. Shewmon, G. Meyrick, S. Mishra, and T. Parthsarathy,Scripta Met., vol. 17, p. 51, 1975.
J.C.M. Li, C.G. Park, and S.M. Ohr,Scripta Met., vol. 30, p. 371, 1986.
J.J. Kim and J.G. Byrne,Scripta Met., vol. 17, p. 773, 1983.
F. Alex, T.D. Hadnagy, K.G. Lynn, and J.G. Byrne, Intl. Conf. on the Effect of Hydrogen on the Behavior of Materials, TMS of AIME, p. 642, 1976.
Po-We Kao, R.W. Ure, Jr., and J.G. Byrne,Phil. Mag., vol. 39, No. 4, p. 517, 1979.
In-Ok Shim and J.G. Byrne, Materials Research Society, Symposium on Nondestructive Monitoring of Materials Properties, Boston, Dec. 1988.Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., vol. 142, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, IO., Byrne, J.G. Microstructural response of 4340 Steel to hydrogen charging. J. Materials Engineering 12, 235–244 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02834499
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02834499