Summary
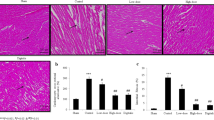
The effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on cardiomyocyte apotosis after ischemia (30 min) and reperfusion (6 h) in rats was observed. The ischemia/reperfusion heart model was established by ligating left anterior descending branch of coronary artery in Wistar rats. The apoptotic cardiomyocytes were examined under transmission electron microscopy and counted byin situ nick end labeling (TUNEL) method and light microscopy. Results showed that (1) The apoptotic cardiomyocytes were found in ischemic regions in the ischemia/reperfusion group, but not in the sham-operating group under transmission electron microscopy; (2) The number of apoptotic cells were 134.45±45.61/field in the ischemia/reperfusion group, 0/field in the sham-operating group and 51.65±13.71/field in the ginsenoside Rb1-treated group. The differences were significant among the three groups (P<0.01). It was concluded that myocardial ischemia-reperfusion could induce cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and ginsenoside Rb1 could significantly inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats, indicating that ginsenoside Rb1 could inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion, thus alleviating ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gottlieb R A, Engler R L. Apoptosis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1999, 874: 412
Maulik N, Yoshida T, Engelman R Met al. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates apoptotic cell death associated with ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Cell Biochem, 1998, 186(1–2): 139
Maulik N, Yoshida T, Das D K. Oxidative stress developed during the reperfusion of ischemic myocardium induces apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med, 1998, 24(5): 869
Maxwell S R, Lip G Y. Reperfusion injury: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and therapeutic options. Intern J Cardil, 1997, 58(2): 95
Harada-Shiba M, Kinoshita M, Kamido Het al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein induces apoptosis in cultured human umbilical vein endothelical cell by common and unique mechanisms. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273: 9681
Maffei Facino R, Carini M, Aldini Get al. Panax ginseng administration in the rate prevents myocardial ischemia-reperfusion damage induced by hyperbaric oxygen: evidence for an antioxidant intervention. Planta Med, 1999, 65(7): 614
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
GUAN Li, female, born in 1967, Doctor in Charge
This project was supported by a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Serial No. 2000J050).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Weizhen, L. & Zhengxiang, L. Effect of ginsenoside-Rb1 on cardiomyocyte apoptosis after ischemia and reperfusion in rats. Current Medical Science 22, 212–215 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828182
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828182