Summary
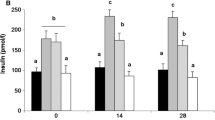
In order to confirm whether the mRNA levels of adiponectin in adipose tissue and mRNA levels of AdipoR1 in the skeletal muscles were correlated with the serum parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism and to clarify the regulation of adiponectin receptor gene expression in diabetic states, serum adiponectin, mRNA levels of adiponectin in adipose tissue and mRNA levels of AdipoR1 in the skeletal muscles were examined in type 2 diabetic rats. The model of type 2 diabetes was prepared by feeding high fat diet and injecting low dosage of streptozotocin (STZ). The diabetic rats were screened out by oral glucose tolerance test. One group of type 2 diabetic rats received rosiglitazone. The serum adiponectin concentration was detected by using ELISA and mRNA levels were examined by RT-PCR. The serum adiponectin levels and mRNA levels of adiponectin in adipose tissue of type 2 diabetic rats were significantly decreased as compared with the normal control rats (P<0.05,P<0.01 respectively). No siglificant changes were observed in the expression of adiponectin receptor 1 in the skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats. The mRNA levels of adiponectin in adipose tissue were reversely correlated with serum insulin (r=−0.66,P<0.05), triglyceride (r=−0.58,P<0.05), cholesterol (r=−0.49,P<0.05), interleukin-6 (r=−0.49,P<0.05) and tumor necrosis factor (r=−0.43,P<0.05). The expression of adiponectin receptors was not altered in the skeletal muscle of Type 2 diabetic rats. The decreased serum adiponectin was caused by the decreased expression of adiponectin mRNA in adipose tissue rather than the adiponectin receptors in the skeletal muscle, which could be improved by rosiglitazone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Yet al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature, 2003,423(6941):762
Pascoe W S, Storlien L H, Inducement by fat feeding of basal hyperglycemia in rats with abnormal beta-cell function. Model for study of etiology and pathogenesis of NIDDM. Diabetes, 1990,39:226
Frühbeck G, Gósmez-Ambrosi J, Muruzábal F Jet al. The adipocyte: a model for integration of endocrine and metabolic signaling in energy metabolism regulation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2001,280:E827
Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman B M. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem, 1996,271(18):10–697
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki Het al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med, 2001,7(8):941
Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Yamauchi Tet al. Disruption of adiponectin causes insulin resistance and neointimal formation. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(29):25–863
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Yet al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase, Nat Med, 2002,8(11):1288
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki Het al. Globular adiponectin protected ob/ob mice from diabetes and ApoE-deficient mice from atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem, 2003,278(4):2461
Hoffstedt J, Arvidsson E, Sjolin Eet al. Adipose tissue adiponectin production and adiponectin serum concentration in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004, 89(3):1391
Debard C, Laville M, Berbe Vet al. Expression of key genes of fatty acid oxidation, including adiponectin receptors, in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia, 2004,47(5):917
Tsuchida A, Yamauchi T, Ito Yet al. Insulin/Foxol pathway regulates expression levels of adiponectin receptors and adiponectin sensitivity. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(29):30–817
Staiger H, Kaltenbach S, Staiger Ket al. Expression of adiponectin receptor mRNA in human skeletal muscle cells is related to in vivo parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes, 2004,53(9):2195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
YAO Hui, female, born in 1965, Associate Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, Y., Hanhua, L., Hongwei, W. et al. Gene expression of adiponectin and adiponectin receptor 1 in type 2 diabetic rats and the relationship with the parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism. Current Medical Science 25, 285–288 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828144
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828144