Abstract
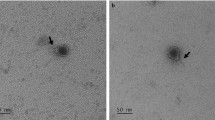
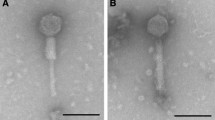
Rumen bacteriophage-lyzed bacterial strains of the genusPrevotella were isolated and preliminarily characterized. The strain TC1-1 the speciesP. bryantii was the only prevotella strain successfully infected with filter sterilized rumen fluid from a black-and-white Holstein cow. Two types of plaques were observed, both rather small and turbid. Preliminary electron microscopy observation showed that several morphologically different bacteriophages were present in these plaques. The plaque eluates were further used for the infection of other prevotella strains. The plaques produced by the bacteriophages were observed with two strains,i.e. P. bryantii B14 andP. brevis GA33. The bacteriophages from both strains were examined by transmission electron microscopy and several morphologically different bacteriophages were observed, among others also a large virion with an icosahedral head with the diameter of approximately 120 nm. The bacteriophage was identified in plaques of bacterial cells of the strain GA33 and has an approximately 800 nm long helical tail, which places it among the largest ruminal bacteriophages described to date. Other bacteriophages from the same indicator strain as well as fromP. bryantii B14 strain were smaller and tail structures were not observed in all of them.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accetto T., Avguštin G.: Non-specific DNAases from the rumen bacteriumPrevotella bryantii.Folia Microbiol..46, 33–35 (2001).
Avguštin G.: Analysis of the role of bacteriumPrevotella (Bacteroides) ruminicola in the rumen ecosystem using molecular genetic techniques.PhD Thesis. Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana (Slovenia) 1992.
Avguštin G., Ramšak A., Peterka M.: Systematics and evolution of ruminal species of the genusPrevotella.Folia Microbiol..46, 40–44 (2001).
Avguštin G., Wallace J.R., Flint H.J.: Phenotypic diversity among ruminal isolates ofPrevotella ruminicola: proposal ofPrevotella brevis sp.nov.,Prevotella bryantii sp.nov., andPrevotella albensis sp.nov. and redefinition ofPrevotella ruminicola.Internat. J. Syst. Bacteriol.47, 284–288 (1997).
Bryant M.P.: Commentary on Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria.Am. J. Clin. Nutr.25, 1324–1328 (1972).
Cheong J.P., Brooker J.D.: Lysogenic bacteriophage M1 fromSelenomonas ruminantium: isolation, characterization and DNA sequence analysis of the integration site.Microbiology144, 2195–2202 (1998).
Cotta M.A.: Interaction of ruminal bacteria in the production and utilization of maltooligosaccharides from starch.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.58, 48–54 (1992).
Dehority B.A.: Pectin-fermenting bacteria isolated from bovine rumen.J. Bacteriol.99, 196–198 (1969).
Ferme D., Ambrožič J., Grabnar M., Ravnikar M., Avguštin G.: Isolation and characterisation of bacteriophages of rumen bacteriumPrevotella bryantii TC1-1.Res. Rep. Biotech. Fac. Univ. Ljubljana (Agric. Issue. Zootech.), in press (2001).
Flint H.J., Thomson A.M.: Deoxyribonuclease activity in rumen bacteria.Lett. Appl. Microbiol.11, 18–21 (1990).
Flint H.J., Thomson A.M., Bisset J.: Plasmid-associated transfer of tetracycline resistance inBacteroides ruminicola.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.54, 855–860 (1988).
van Gylswyk N.O.: Enumeration and presumptive identification of some functional groups of bacteria in the rumen of dairy cows fed grass-silage based diets.FEMS Microbiol. Ecol.73, 243–254 (1990).
Gasparič A., Martin J., Daniel A.S., Flint H.J.: A xylan hydrolase gene cluster inPrevotella ruminicola B14: sequence relationships, synergistic interactions, and oxygen sensitivity of novel enzyme with exoxylanase and β-(1,4)-xylosidase, β-d-xylosidase activities.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.61, 2958–2964 (1995a).
Gasparič A., Marinšek-Logar R., Martin J., Wallace R.J., Nekrep F.V., Flint H.J.: Isolation of genes encoding β-d-xylanase, β-d-xylosidase and α-l-arabinofuranosidase activites from the rumen bacterium.FEMS Microbiol. Lett.125, 135–141 (1995b).
Gregg K., Kennedy B.G., Klieve A.V.: Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of the region containingattpP of the temperate phage ϕAR29 ofPrevotella ruminicola AR29.Microbiology140, 2109–2114 (1994).
Hobson P.N.: Rumen bacteria, pp. 133–149 in J.R. Noriss, D.W. Ribbons (Eds):Methods in Microbiology. Academic Press, New York 1969.
Klieve A.V., Hudman J.F., Bauchop T.: Inducible bacteriophages from ruminal bacteria.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.55, 1630–1634 (1989).
Klieve A.V., Bauchop T.: Phage resistance and altered growth habit in a strain ofStreptococcus bovis.FEMS Microbiol. Lett.64, 155–159 (1991).
Klieve A.V., Gregg K., Bauchop T.: Isolation and characterisation of lytic phages fromBacteroides ruminicola spp.brevis.Curr. Microbiol.23, 183–187 (1991).
Klieve A.V., Swain R.A.: Estimation of ruminal bacteriophage numbers by pulse-field gel electrophoresis and laser densitometry.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.59, 2299–2303 (1993).
Ogata K., Aminov R.I., Nagamine T., Benno Y., Sekizaki T., Mitsumori M., Minato H., Itabashi H.: Structural organization of pRAM4, a cryptic plasmid fromPrevotella ruminicola.Plasmid35, 91–97 (1996).
Ramšak A., Peterka M., Tajima K., Martin J.C., Wood J., Johnston M.E.A., Aminov R.I., Flint H.J., Avguštin G.: Unravelling the genetic diversity of ruminal bacteria belonging to the CFB phylum.FEMS Microbiol. Ecol.33, 69–79 (2000).
Ritchie A.E., Robinson I.M., Allison M.J.: Rumen bacteriophage: survey of morphological types, pp. 333–334 in P. Favard (Ed.):Microscopie Electronique. Societé Française de Microscopie electronique, Paris 1970.
Salyers A.A., Shoemaker N.B.: Genetics of human colonicBacteroides, pp. 299–320 in R.I. Mackie, B.A. White, R.I. Isaacson (Eds):Gastrointestinal Microbiology. Chapman and Hall, New York 1997.
Salyers A.A., Bonheyo G., Shoemaker N.B.: Starting a new genetic system: lessons from bacteroides.Methods20, 35–46 (2000).
Štyriak I., Kmeť V., Španová A.: Isolation and characterization of two rumenStreptococcus bovis bacteriophages.Microbiologica12, 317–322 (1989).
Swain R.A., Nolan J.V., Klieve A.V.: Natural variability and diurnal fluctuations within the bacteriophage population of the rumen.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.62, 994–997 (1996).
Wallace R.J., Brammall M.L.: The role of different species of bacteria in the hydrolysis of protein in the rumen.J. Gen. Microbiol.131, 821–832 (1985).
Wallace R.J., McKain N.: A survey of peptidase activity in rumen bacteria.J. Gen. Microbiol.137, 2259–2264 (1991).
Wells J.E., Russell J.B.: Why do many ruminal bacteria die and lyse so quickly?J. Dairy Sci.79, 1487–1495 (1996).
Wood J., Scott K.P., Avguštin G., Newbold C.J., Flint H.J.: Estimation of the relative abundance of differentBacteroides andPrevotella ribotypes in gut samples by restriction enzyme profiling of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene sequences.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.64, 3683–3689 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ambrožič, J., Ferme, D., Grabnar, M. et al. The bacteriophages of ruminal prevotellas. Folia Microbiol 46, 37–39 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02825881
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02825881