Summary
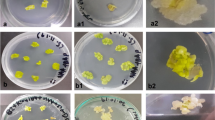
Apical and axillary buds ofGlycyrrhiza glabra commonly known as licorice, a plant of repute in the Indian system of medicine, were used for induction of adventitious shoots. For induction of multiple shoots, Murashige and Skoog’s (MS) medium with N6-benzyladenine (BA, 0.88–8.87 μM) was used. Reduction in major salts of MS medium enhanced the multiplication ratio up to 1∶10. Plants transferred to the greenhouse showed 90% survival. The present work describes a stepwise protocol for production ofGlycyrrhiza glabra plants on simple minimal media, where very high multiplication rates with healthy root systems were obtained. Roots being the organ of commercial importance, the protocol has tremendous potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Business India. Natural cancer drugs. January 31–February 13, 1994.
CIMAP Newsletter.In vitro propagation of licorice through multiple shoot formation, 21(4):4–5; 1995.
Fujita, Y.; Teranishi, K.; Furukawa, T. Glycyrrhizine: Patent Jpn. Kokai 78, 91, 188; 1978.
George, E. F.; Sherrington, P. D. Plant propagation by tissue culture: handbook and directory of commercial laboratories. London: Exegetics Ltd.; 1984.
Henry, M.; Edy, A. M.; Desmarest, P., et al.Glycyrrhiza glabra L. (licorice): cell culture, regeneration and the production of glycyrrhizine. In: Bajaj, Y. P. S., ed. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry, medicinal and aromatic plants III. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1991: 270–282.
Hyndman, S. E.; Hasegawa, P. M.; Bressan, R. A. Stimulation of root initiation from cultured rose shoots through the use of reduced concentrations of mineral salts. HortScience 17:82–83; 1982.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–479; 1962.
Shah, R. R.; Dalal, K. C. In vitro multiplication ofGlycyrrhiza. Curr. Sci. (Bangalore): 49:69–71; 1980.
Snedecor, G. W.; Cochran, W. G. Statistical Methods. India: Oxford and IBH Publishing Co.; 1967.
Syrtanova, G. A.; Mukhitdinova, Z. R. Clonal multiplication attempts ofGlycyrrhiza glabra L. and ofGlycyrrhiza uralensis on culture media. Rastit. Resur. 1:85–88; 1984.
Zalkov, L. H.; Hudson, C. C.; Powis, G. Mechanism based natural product anticancer drug discovery. ASOMPS VIII Malaysia. 1994:94 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thengane, S.R., Kulkarni, D.K. & Krishnamurthy, K.V. Micropropagation of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) through shoot tip and nodal cultures. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 34, 331–334 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02822743
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02822743