Abstract
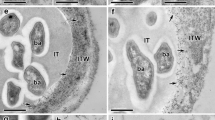
Bioassay based on thick and short root (Tsr) and hair deformation (Had) phenotypes were used to test the activity of Nod factors produced byRhizobium sp. (Cicer) strains HS-1, Rcd-301, IC-59, IC-76 and Ca-181 on chickpea (Cicer arietinum) cv. ‘C-235’. Nod− mutants ofRhizobium sp. (Cicer) did not produce Tsr+ and Had+ phenotypes on chickpea, indicating the requirement of nodulation genes for their appearance. The strain HS-1 treated with root exudates of pea (Pisum sativum), berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum) and lucerne (Medicago sativa) failed to produce the Tsr+ and Had+ phenotypes on chickpea. ConverselyR. leguminosarum bvs.viciae andtrifolii, R. meliloti, Rhizobium sp. (Sesbania), andRhizobium sp. (Cajanus) induced with chickpea root exudates did not show Tsr+ and Had+ phenotypes on chickpea. It appears that host specificity inRhizobium sp. (Cicer)-chickpea symbiosis is regulated by the production of host-specific factors which are not active on heterologous hosts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A.: Production of root hair deformation factors byRhizobium meliloti nodulation genes inEscherichia coli: HsnD (NodH) is involved in the plant host specific modification of the NodABC factor.Plant Mol. Biol.13, 1–12 (1989).
Bec-Ferte M.P., Krishnan H.B., Prome D., Savangnae A., Pueppke S.G., Prome J.C.: Structures of nodulation factors from the nitrogen fixing soybean symbiontRhizobium fredii USDA257.Biochemistry33, 11782–11788 (1994).
Cardenas L., Dominguez J., Quinto C., Lopez-Lara I.M., Lugtenberg B.J.J., Spaink H.P., Rademaker G.J., Haverkamp J., Thomas-Oates J.E.: Isolation, chemical structures and biological activity of the lipo-chitin oligosaccharide nodulation signals fromRhizobium etli.Plant Mol. Biol.29, 453–464 (1995).
Denarie J., Debelle F., Prome J.C.:Rhizobium lipo-chitooligosaccharide nodulation factors: signalling molecules mediating recognition and morphogenesis.Ann. Rev. Biochem.65, 503–535 (1996).
Fahraeus G.: The infection of clover root hairs by nodule bacteria studied by a simple glass techniqueJ. Gen. Microbiol.16, 374–381 (1957).
Faucher C., Camut S., Denarie J., Truchet G.: ThenodH andnodQ host range genes ofRhizobium meliloti behave as virulence genes inRhizobium leguminosarum bv.viciae and determine change in production of plant specific extracellular signals.Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact.2, 291–300 (1989).
Gaur Y.D., Sen A.N.: Cross inoculation group specificity inCicer-Rhizobium symbiosis.New Phytol.83, 745–754 (1979).
Hartwig U.A., Maxwell C.M., Joseph C.M., Phillips D.A.: Interaction among flavonoidnod gene inducers released from alfalfa seeds and roots.Plant Physiol.91, 1138–1142 (1989).
Heidstra R., Geurts R., Franssen H., Spaink H.P., Van Kammen A., Bisseling T.: Root hair deformation activity of nodulation factors and their fate onVicia sativa.Plant Physiol.105, 787–797 (1994).
Hungria M., Joseph C.M., Phillips D.A.: Anthocyanidins and flavonols, majornod gene inducers from seeds of a black seeded common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.).Plant Physiol.97, 751–758 (1991).
Kingsley M.T., Bohlool B.B.: Characterization ofRhizobium sp. (Cicer arietinum L.) by immunofluorescence, immunodiffusion, and intrinsic antibiotic resistance.Can. J. Microbiol.29, 518–526 (1983).
Long S.R.:Rhizobium symbiosis: Nod factors in perspective.Plant Cell8, 1885–1898 (1996).
Lopez-Lara I.M., Van der Drift, K.M.G.M., Van Brussel A.A.N., Haverkamp J., Lugtenberg B.J.J., Thomas-Oates J.E., Spaink H.P.: Induction of nodule primordia onPhaseolus andAcacia by lipo-chitin oligosaccharide nodulation signals from broad host rangeRhizobium strain GRH2.Plant. Mol. Biol.29, 465–477 (1995).
Mylona P., Pawlowski K., Bisseling T.: Symbiotic nitrogen fixation.Plant Cell7 869–885 (1995).
Price N.P.J., Relic B., Talmont F., Lewin A., Prome D., Pueppke S.G., Maillet F., Denarie J., Prome J.C., Broughton W.J.: Broad host rangeRhizobium sp. strain NGR234 secretes a family of carbamoylated, and fucosylated, nodulation signals that are O-acetylated or sulphated.Mol. Microbiol.6, 3575–3584 (1992).
Redmond J.W., Batley M., Djordjevic M.A., Innes R.W., Kuempel P.L., Rolfe B.G.: Flavones induce expression of nodulation genes inRhizobium.Nature323, 632–635 (1986).
Schlaman H.R.M., Lugtenberg B.J.J., Okker R.J.H.: The NodD protein does not bind to the promoter of inducible nodulation genes in bacteroids ofRhizobium leguminosarum bv.viciae.J. Bacteriol.174, 5177–5182 (1992).
Sharma P.K., Anand R.C., Lakshminarayana K.: Construction ofTn5 tagged mutants ofRhizobium sp. (Cicer) for ecological studies.Soil Biol. Biochem.23, 881–885 (1991).
Sharma P.K., Upadhyay K.K., Srivastava P.: Nodulation and nitrogen fixation ability of wild species ofCicer.Legume Res.17, 229–230 (1994).
Spaink H.P.: Rhizobial lipo-oligosaccharides: answers and questions.Plant Mol. Biol.20, 977–986 (1992).
Spaink H.P.: The molecular basis of infection and nodulation by rhizobia: The ins and outs of sympathogenesis.Ann. Rev. Phytopathol.33, 345–368 (1995).
Spaink H.P., Bloemberg G.V., Wijfjes A.H.M., Ritsema T., Geiger O., Lopez-Lara I.M., Harteveld M., Kafetzopoulos D., Van Brussel A.A.N., Kijne J.W., Lugtenberg B.J.J., Van der Drift K.M.G.M., Thomas-Oates J.E., Potrykus I., Sautter C.: The molecular basis of host specificity in theR. leguminosarum-plant infection, pp. 91–98 inAdvances in Molecular Genetics of Plant-Microbe Interactions (M. Daniels, J.A. Downie, A.E. Osbourn, Eds.), Vol. 3. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht 1994.
Spaink H.P., Okker R.J.H., Wijffelman C.A., Pees E., Lugtenberg B.J.J.: Promoters in the nodulation region of theRhizobium leguminosarum Sym plasmid pRL1JI.Plant Mol. Biol.9, 27–39 (1987).
Srivastava P.: Identification of nodulation genes and their inducers inRhizobium sp. (Cicer).PhD Thesis. Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar (India) 1995.
Van Brussel A.A.N., Tak T., Wetselaar A., Pees E., Wuffelman C.A.: Small leguminosae as test plants for nodulation ofRhizobium leguminosarum and other rhizobia and agrobacteria harbouringR. leguminosarum Sym-plasmid.Plant Sci. Lett.27, 317–325 (1982).
Van Brussel A.A.N., Zaat S.A.J., Canter-Cremers H.C.J., Wijffelman C.A., Pees E., Tak T., Lugtenberg B.J.J.: Role of plant root exudates and Sym-plasmid localized nodulation genes in synthesis byRhizobium leguminosarum of Tsr factor which causes thick and short root on common Vetch.J. Bacteriol.165, 517–522 (1986).
Van Rhijn P., Vanderleyden J.: TheRhizobium-plant symbiosis.Microbiol. Rev.59, 124–142 (1995).
Vincent J.M.: A mannual for the practical study of the root nodule bacteria, pp. 75–76 inI.B.P. Handbook no. 15. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford 1970.
Zaat S.A.J., Van Brussel A.A.N., Tak T., Pees E., Lugtenberg B.J.J.: Flavonoids induceRhizobium eguminosarum to producenodABC gene related factor that cause thick, short roots and root hair response on common Vetch.J. Bacteriol.169, 3388–3391 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Upadhyay, K.K., Kamboj, D.V. & Sharma, P.K. Host specificity of nodulation inRhizobium sp. (Cicer) as revealed by Tsr bioassay. Folia Microbiol 42, 381–384 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816953
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816953