Abstract
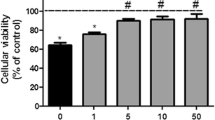
Administration of adenosine A1 receptor agonists in vivo is neuroprotective in various stroke models. Experiments using either mixed cultures of neurons and astrocytes or brain slices, in which several cell types are present, have demonstrated that activation of A1 receptors also is protective against hypoxia and/or hypoglycemia in vitro. In this study, we have examined the effect of the A1 agonist cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) on cellular damage, measured by efflux of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), in highly enriched primary cultures of either neurons or astrocytes exposed to different metabolic insults. CPA reduced neuronal LDH release induced by a combination of hypoxia and substrate deprivation (“simulated ischemia”; IC50=28 nM) or by hypoxia alone (IC50=170 nM). In contrast, CPA had no effect on neuronal damage induced by substrate deprivation alone, nor did it affect ischemic death to astrocytes. The neuroprotective effects of CPA during simulated ischemia and hypoxia were reversed by the A1 antagonist 1, 3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine (DPCPX). These data demonstrate that activation of an adenosine A1 receptor on neurons, but not astrocytes, is protective against cellular damage or death induced specifically by hypoxia as opposed to other metabolic insults such as hypoglycemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbracchio M. P., Saffrey M. J., Höpker V., and Burnstock G. (1994) Modulation of astroglial cell proliferation by analogues of adenosine and ATP in primary cultures of rat striatum.Neuroscience 59, 67–76.
Choi D. W. and Rothman S. M. (1990) The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxicischemic neuronal death.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 171–182.
Daval J-L. and Nicholas F. (1994) Opposite effects of cyclohexyladenosine and theophylline on hypoxic damage in cultured neurons.Neurosci. Lett. 175, 114–116.
Delumeau J. C., Petitet F., Cordier J., Glowinski J., and Premont J. (1991) Synergistic regulation of cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations in mouse astrocytes by NKI tachykinin and adenosine agonists.J. Neurochem. 57, 2026–2035.
Dolphin A. C. and Prestwich S. A. (1985) Pertussis toxin reverses adenosine inhibition of neuronal glutamate release.Nature 316, 148–150.
Driscoll B. F., Deibler G. E., Law M. J., and Crane A. M. (1993) Damage to neurons in culture following medium change: role of glutamine and extracellular generation of glutamate.J. Neurochem. 61, 1795–1800.
Fredholm B. B. (1995) Purinoceptors in the nervous system.Pharmacol. Toxicol. 76, 228–239.
Fredholm B. B., Abbrachio M. P., Burnstock G., Daly J. W., Harden T. K., Jacobson K. A., Leff P., and Williams M. (1994) Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors.Pharmacol. Rev. 46, 143–156.
Gallo V., Ciotti M. T., Coletti A., Aloisi F., and Levi G. (1982) Selective release of glutamate from cerebellar granue cells differentiating in culture.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 7919–7923.
Goldberg M. P., Monyer H., Weiss J. H., and Choi D. W. (1988) Adenosine reduces cortical neuronal injury induced by oxygen or glucose deprivation in vitro.Neurosci. Lett. 89, 323–327.
Greene R. W. and Haas H. L. (1991) The electrophysiology of adenosine in the mammalian central nervous system.Prog. Neurobiol. 36, 329–341.
Hrseron A., Lekieffre D., Le Peillet E., Lasbennes F., Seylaz J., Plotkine M., and Boulu R. G. (1994) Effects of an A1 adenosine receptor agonist on the neurochemical, behavioral and histochemical consequences of ischemia.Brain Res. 641, 217–224.
Hösli E. and Hösli L. (1988) Autoradiographic studies on the uptake of adenosine and on binding of adenosine analogues in neurons and astrocytes of cultured rat cerebellum and spinal cord.Neuroscience 24, 621–628.
Huang R. and Hertz L (1994) Effect of anoxia on glutamate formation from glutamine in cultured neurons: dependence on neuronal subtype.Brain Res. 660, 129–137.
Huang R. and Hertz L. (1995) Neuroprotective effect of phenylsuccinate, an inhibitor of cytosolic glutamate formation from glutamine, under anoxic conditions but not during exposure to exogenous glutamate.Neurosci. Lett. 183, 22–26.
Juurlink B. H. J. and Hertz L. (1993) Ischemia-induced death of astrocytes and neurons in primary culture: pitfalls in quantifying neuronal cell death.Devel. Brain Res. 71, 239–246.
Lobner D. and Choi D. W. (1994) Dipyridamole increases oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury in cortical cell culture.Stroke 25, 2085–2090.
Lowry O. H., Rosebrough N. J., Farr A. L., and Randall R. J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Marangos P. J. (1990) Adenosinergic approaches to stroke therapeutics.Med. Hypoth. 32, 45–49.
Mori M., Nishizaki T., and Okada Y. (1992) Protective effect of adenosine on the anoxic damage of hippocampal slice.Neuroscience 46, 301–307.
Ogata T., Nakamura Y., Tsuji K., Shibata T., Kataoka K., and Schubert P. (1994) Adenosine enhances intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in conjunction with metabotropic glutamate receptor activation by t-ACPD in cultured hippocampal astrocytes.Neurosci. Lett. 170, 5–8.
Phillis J. W., Smith-Barbour M., Perkins L. M., and O’Regan M. H. (1994) Characterization of glutamate, aspartate, and GABA release from ischemic rat cerebral cortex.Brain Res. Bull. 34, 457–466.
Roussel S., Pinard E., and Seylaz J. (1991) Focal cerebral ischemia in chronic hypertension: no protection by (R)-phenylisopropyladenosine.Brain Res. 545, 171–174.
Rudolphi K. A., Schubert P., Parkinson F. E., and Fredholm B. B. (1992) Neuroprotective role of adenosine in cerebral ischaemia.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 13, 439–445.
Salter M. W., DeKoninck Y., and Henry J. L. (1993) Physiological roles for adenosine and ATP in synaptic transmission in the spinal dorsal horn.Prog. Neurobiol. 41, 125–156.
Schubert P., Rudolphi K. A., Fredholm B. B., and Nakamura Y. (1994) Modulation of nerve and glial function by adenosine—role in the development of ischemic damage.Int. J. Biochem. 26, 1227–1236.
Simpson R. E., O’Regan M. H., Perkins L. M., and Phillis, J. W. (1992) Excitatory transmitter amino acid release from the ischemic rat cerebral cortex: effects of adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists.J. Neurochem. 58, 1683–1690.
Sweeney M. I. (1994) Activation of adenosine receptors protects neurons from ischemiainduced death.Soc. Neurosci. Abstracts 20, 1042.
Sweeney M. I. (1997) Neuroprotective effects of adenosine in cerebral ischemia: window of opportunity.Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21, 207–217.
Sweeney M. I. (1996) Adenosine release and uptake in cerebellar granule neurons both occurvia an inhibitor-sensitive equilibrative nucleoside carrier which is modulated by G-proteins.J. Neurochem. 67, 81–88.
Sweeney M. I. and Logan M. (1995) Endogenous adenosine protects neurons but not astrocytes from hypoxic cell death.Proc. Can. Fed. Biol. Soc. 38, 58.
Sweeney M. I., Yager J. Y., Walz W., and Juurlink B. H. J. (1995) Cellular mechanisms involved in brain ischemia.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 73, 1525–1535.
Von Lubitz D. K. E. G., Lin R. C.-S., Malman N., Ji X., Carter M. F., and Jacobson K. A. (1994) Chronic administration of selective adenosine A1 receptor agonist or antagonist in cerebral ischemia.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 256, 161–167.
Wahlefeld A. W. (1983) UV-method and L-lactate and NAD, inMethods of Enzymatic Analysis, vol. 3, Enzymes I: Oxireductases (Bergmeyer H. U., Bergmeyer J., and Graβ1 M., eds.), pp. 126–133, Verlag-Chemie, Deerfield Beach, FL.
Zhou J., Meno J. R., Hsu S. S.-F., and Winn H. R. (1994) Effects of theophylline and cyclohexyladenosine on brain injury following normo- and hyperglycemic ischemia: a histopathologic study in the rat.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 14, 166–173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Logan, M., Sweeney, M.I. Adenosine A1 receptor activation preferentially protects cultured cerebellar neurons versus astrocytes against hypoxia-induced death. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 31, 119–133 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815237
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815237