Abstract
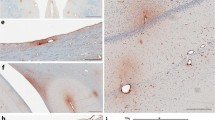
Disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and neuronal cytoskeletal damage were evaluated in two commonly used rat models of traumatic brain injury. Adult rats received a lateral cortical impact (CI) or lateral fluid percussion (FP) injury of mild or moderate severity or a sham procedure. Six hours after trauma, the brains were removed and analyzed with immunocytochemical techniques for alterations in the serum protein, IgG, and the cytoskeletal protein, microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2). Both models induced profound alterations in these proteins in the ipsilateral cortex and hippocampus compared to sham-injured controls. Following an injury of moderate severity, the CI injury resulted in greater IgG extravasation in the cortex and hippocampus than the FP injury. Conversely, after a mild injury, IgG extravasation in the hippocampus was greater for FP than CI. All of the animals in the CI group and most of the FP group showed a loss of MAP2 in the hippocampus. The specific subregions within the cortex and hippocampus that were affected by the injury varied between models, despite having identical impact sites. These data demonstrate that there are both similarities and differences between a CI and FP injury on vascular and neuronal cystoskeletal integrity, which should be considered when utilizing these animal models to study selected features of human head injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J. H. (1992) Head injury, inGreenfield's Neuropathology (Adams J. H. and Duchen L. W., eds.), Oxford University, New York, pp. 106–129.
Aihara N., Tanno H., Hall J. J., Pitts L. H., and Noble L. J. (1994) Immunocytochemical localization of immunoglobulins in the rat brain: relationship to the blood-brain barrier.J. Comp. Neurol. 342, 481–496.
Amaral D. G. and Witter M. P. (1989) The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: A review of anatomical data.Neuroscience 31, 571–591.
Baldwin S. A., Fugaccia I., Brown D. R., Brown L. V., and Scheff S. W. (1996a) Blood-brain barrier breach following cortical contusion in the rat.J. Neurosurg. 85, 476–481.
Baldwin S. A. and Scheff S. W. (1996b) Intermediate filament change in astrocytes following mild cortical contusion.Glia 16, 266–275.
Black M. M. and Bass P. W. (1989) The basis of polarity of neurons.Trends Neurosci. 12, 211–215.
Boobis A. R., Fawthrop D. J., and Davies D. S. (1989) Mechanisms of cell death.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 10, 275–280.
Bothe H. W., Bodsch W., and Hossmann K. A. (1984) Relationship between specific gravity, water content and serum protein extravasation in various types of vasogenic edema.Acta. Neuropathol. 64, 37–42.
Bralet J., Schreiber L., and Bouvier C. (1992) Effect of acidosis and anoxia on iron delocalization from brain homogenates.Biochem. Pharmacol. 43, 979–983.
Clark R. S. B., Schiding J. K., Kaczorowski S. L., Marion D. W., and Kochanek P. M. (1996) Neutrophil accumulation after traumatic brain injury in rats: comparison of weight drop and controlled cortical impact models.J. Neurotrauma 11, 499–506.
Cortez S., McIntosh T., and Noble L. (1989) Experimental fluid percussion brain injury: vascular disruption and neuronal and glial alterations.Brain Res. 482, 271–282.
Czurko A. and Nishino H. (1994) Appearance of immunoglobulin G and complement factor C3 in the striatum after transient focal ischemia in the rat.Neurosci. Lett. 166, 51–54.
Dhillon H. S., Donaldson D., Dempsey R. J., and Prasad M. R. (1994) Regional levels of free fatty acids and evans blue extravasation after experimental brain injury.J. Neurotrauma 11, 405–415.
Dietrich W. D., Alonso A., Busto R., Globus M. Y.-T., and Ginsberg M. D. (1994) Post-traumatic brain hypothermia reduces histopathological damage following concussive brain injury in the rat.Acta Neuropathol. 87, 250–258.
Dixon C., Clifton G., Lighthall J., Yaghmai A., and Hayes R. (1991) A controlled cortical impact model of traumatic brain injury in the rat.J. Neurosci. Methods 39, 253–262.
Dixon C. E. and Hayes R. L. (1995) Rodent models of traumatic brain injury and motor function assessment: controlled cortical impact and fluid percussion models of traumatic brain injury, inCentral Nervous System Trauma (Ohnishi S. T. and Ohnishi T., eds.), CRC, New York. pp. 255–265.
Dixon C. E., Lyeth B. G., Povlishock J. T., Findling R. L., Hamm R. J., Marmora A., Young H., and Hayes R. L. (1987) A fluid percussion models of experimental brain injury in the rat.J. Neurosurg. 67, 110–119.
Friedrich P. and Aszodi A. (1991) MAP2: A sensitive cross-linker and adjustable spacer in dendritic architecture.FEBS Lett. 295, 5–9.
Garner C. C., Tucker R. P., and Matus A. (1988) Selective localization of messenger RNA for cytoskeletal protein MAP2 in dendrites.Nature 336, 674–677.
Gennarelli T. A. (1994) Animate models of human head injury.J. Neurotrauma 11, 357–368.
Goodman J. C., Cherian L., Bryan R. M., Jr. and Robertson C. S. (1994) Lateral cortical impact injury in rats: pathologic effects of varying cortical compression and impact velocity.J. Neurotrauma 11, 587–597.
Hatateyama T., Matsumoto M., Brengman J. M. and Yanagihara T. (1988) Immunohistochemical investigation of ischemic and postichemic damage after bilateral carotid occlusion in gerbils.Stroke 19, 1526–1534.
Hicks R. R., Smith D. H., Lowenstein D. H., Saint Marie R., and McIntosh T. K. (1993) Mild experimental brain injury in the rat induces cognitive deficits associated with regional neuronal loss in the hippocampus.J. Neurotrauma 10, 405–414.
Hicks R. R., Smith D. H., and McIntosh T. K. (1995) Temporal response and effects of excitatory amino acid antagonism on microtubule-associated protein 2 immunoreactivity following experimental brain injury in rats.Brain Res. 678, 151–160.
Hicks R. R., Soares H. D., Smith D. H., and McIntosh T. K. (1996) Temporal and spatial characterization of neuronal injury following lateral fluid-percussion brain injury in the rat.Acta Neuropathol. 91, 236–246.
Hoshino S., Kobayashi S., and Nakazawa S. (1996) Prolonged and extensive IgG immunoreactivity after severe fluid-percussion injury in rat brain.Brain Res. 711, 73–83.
Hsu S.-M., Raine L. and Fanger H. (1981) Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques; a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 577–580.
Ishige N., Pitts L. H., Hashimoto T., Nishimura M. C., and Barkowski H. M. (1987) Effect of hypoxia on traumatic brain injury in rats: Part 1. Changes in neurological function, electroencephalograms, and histopathology.Neurosurgery 20, 848–853.
Jane J. A., Rimel R. W., Poberskin L. H., Tyson G. W., Steward O., and Gennarelli T. A. (1982) Outcome and pathology of head injury, inHead Injury: Basic and Clinical Aspects (Brossman R. G. and Gildenberg P. L., eds.), Raven, New York, pp. 229–237.
Jensen M. B., Finsen B., and Zimmer J. (1997) Morphological and immunophenotypic microglial changes in the denervated fascia dentata of adult rats: correlation with blood-brain barrier damage and astroglial reactions.Exp. Neurol. 143, 103–116.
Kitigawa K., Matsumoto M., Ninobe M., Mikoshiba K., Hata R., Ueda H., Handa N., Fukunaga R., Isaks Y., Kimura K., and Kamada T. (1989) Microtubule-association protein 2 as a sensitive marker for cerebral ischemic damage-immunohistochemical investigation of dendritic damage.Neuroscience 31, 401–411.
Kontos H. (1989) Oxygen radicals in central nervous system damage.Chem. Biol. Interact. 72, 229–255.
Kruger L. (1995)Photographic Atlas of the Rat Brain: The Cell and Fiber Architecture Illustrated in Three Planes with Stereotaxic Coordinates (Kruger L., Saporta S., and Swanson L., eds.), Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Lewen A., Li G. L., Olsson Y., and Hillered L. (1996) Changes in microtubule-associated protein 2 and amyloid precursor protein immunoreactivity following traumatic brain injury in rat: influence of MK-801 treatment.Brain Res. 719, 161–171.
Lighthall J., Goshgarian H., and Pinderski C. (1990) Characterization of anoxal injury produced by controlled cortical impact.J. Neurotrauma 7, 65–76.
Lowenstein D. H., Thomas M. J., Smith D. H., and McIntosh T. K. (1992) Selective vulnerability of dentate hilar neurons following traumatic brain injury: a potential mechanistic link between head trauma and disorders of the hippocampus.J. Neurosci. 12, 4846–4853.
McIntosh T. K., Vink R., Noble L., Yamakami I., Fernyak S., Soares H., and Faden A. I. (1989) Traumatic brain injury in the rat: characterization of a lateral fluid-percussion model.Neuroscience 28, 233–244.
Moos T. and Hoyer P. E. (1996) Detection of plasma proteins in CNS neurons: conspicuous influence of tissue-processing parameters and the utilization of serum for blocking nonspecific reactions.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 44, 591–603.
Moser E., Moser M.-B., and Andersen P. (1993) Spatial learning impairment parallels the magnitude of dorsal hippocampal lesions, but is hardly present following ventral lesions.J. Neurosci. 13, 3916–3925.
Nilsson P., Hillered L., Ponten V., and Ungerstedt V. (1990) Changes in cortical extracellular levels of energy-related metabolites and amino acids following concussive brain injury in rats.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 10, 631–637.
Paxinos G. and Watson C. (1986) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic, New York.
Posmantur R. M., Kampfl A., Liu S. J., Heck K., Taft W. C., Clifton G. L., and Hayes R. L. (1996a) Cytoskeletal derangements of cortical neuronal processes three hours after traumatic brain injury in rats: immunofluorescence study.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55, 68–80.
Posmantur R. M., Kampfl A., Taft W. C., Bhattacharjee M., Dixon C. E., Bao J., and Hayes R. L. (1996b) Diminished microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) immunoreactivity following cortical impact brain injury.J. Neurotrauma 13, 125–137.
Povlishock J. T., Becker D. P., Sullivan H. G., and Miller J. D. (1978) Vascular permeability alterations to horseradish peroxidase in experimental brain injury.Brain Res. 153, 223–239.
Povlishock J. T., Becker D. P., Miller J. D., Jenkins L. W., and Dietrich W. D. (1979) The morphopathologic substrates of concussion.Acta Neuropathol. 47, 1–11.
Povlishock J. T., Hayes R. L., Michel M. E., and McIntosh T. K. (1994) Workshop on animal models of traumatic brain injury.J. Neurotrauma 11, 723–732.
Scheff S. W., Baldwin S. A., Brown R. W., and Kraemer P. J. (1997) The Morris Water Maze deficits in rats following traumatic brain injury: lateral controlled cortical impact.J. Neurotrauma 14, 615–627.
Schmidt R. H. and Grady M. S. (1993) Regional patterns of blood-brain barrier break-down following central and lateral fluid percussion injury in rodents.J. Neurotrauma 10, 415–430.
Seisjo B. K. (1988) Mechanisms of ischemic brain damaga.Crit. Care Med. 16, 954–963.
Smith D. H., Okiyama K., Thomas M. J., Claussen B., and McIntosh T. K. (1991) Evaluation of memory dysfunction following experimental brain injury using the Morris water maze.J. Neurotrauma 8, 259–269.
Soares H. D., Hicks R. R., Smith D. H., and McIntosh T. K. (1995) Inflammatory leukocytic recruitment and diffuse neuronal degeneration are separate pathological processes resulting from traumatic brain injury.J. Neurosci. 15, 8223–8233.
Stubley-Weatherly L. A., Harding J. W., and Wright J. W. (1996) Effects of discrete kainic acid-induced hippocampal lesions on spatial and contextual learning and memory in rats.Brain Res. 716, 29–38.
Sutton R. L., Lescaudron L., and Stein D. G. (1993) Unilateral cortical contusion injury in the rat: Vascular disruption and temporal development of cortical necrosis.J. Neurotrauma 10, 135–149.
Szentistvanyi I., Patlak C. S., Ellis R. A., and Cserr H. F. (1984) Drainage of interstitial fluid from different regions of the rat brain.Am. J. Physiol. 246, F835–44.
Taft W. C., Yang K., Dixon C. E., and Hayes R. L. (1992) Microtubule-associated protein 2 levels decrease in hippocampus following traumatic brain injury.J. Neurotrauma 9, 281–290.
Taft W. C., Yang K., Dixon C. E., Clifton G. L., and Hayes R. L. (1993) Hypothermia attenuates the loss of hippocampal microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) following traumatic brain injury.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 13, 796–802.
Tanno H., Nockels R. P., Pitts L. H., and Noble L. J. (1992) Breakdown of the blood-brain barrier after fluid percussive brain injury in the rat. Part 1: Distribution and time course of protein extravasation.J. Neurotrauma 9, 21–32.
van den Brink W. A., Santos B. O., Marmarou A., and Avezaat C. J. J. (1994) Quantitative analysis of blood-brain barrier damage in two models of experimental head injury in the rat.Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 60, 456–458.
Williams D. H., Levin H. S., and Eisenberg H. M. (1990) Mild head injury classification.Neurosurgery 27, 422–428.
Yoshimi K., Takeda M., Nishimura T., Kudo T., Nadamura Y., Tada K., and Iwata N. (1991) An immunohistochemical study of MAP2 and clathrin in gerbil hippocampus after cerebral ischemia.Brain Res. 560, 149–158.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hicks, R.R., Baldwin, S.A. & Scheff, S.W. Serum extravasation and cytoskeletal alterations following traumatic brain injury in rats. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 32, 1–16 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815164
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815164