Abstract
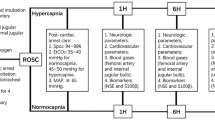
Anesthetic agent, arterial pCO2 level, and opioid peptides have all been implicated in the pathophysiology of experimental stroke models. The effects of halothane, α-chloralose, and differing concentrations of arterial pCO2 on injury volume and CSF β-endorphin levels were studied in a feline model of experimental focal cerebral ischemia. The type of anesthetic agent used had no effect on injury volume following 6 h of focal cerebral ischemia. Over a 6-h period, β-endorphin levels significantly increased from 10.1±5.0 fmol/mL at zero time to 14.4±7.2 fmol/mL at 6 h under halothane anesthesia (p<0.05), whereas they did not significantly change (10.1±6.7 to 7.8 ±4.7 fmol/mL) under α-chloralose anesthesia. In contrast, hypercapnia had no effect on β-endorphin levels, but significantly increased injury volume from 30.6±5.7% of the ipsilateral hemisphere under normocapnic conditions to 37.1±5.9% under hypercapnic conditions (p<0.05). These results suggest that hypercapnia increases injury volume in a feline model of focal cerebral ischemia, and pCO2 should be controlled in experimental focal cerebral ischemia models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams H. P., Brott T. G., Ctrowell R. M., Furlan A. J., Gomez C. R., Grotta J. Helgason C. M., Marler J. R., Woolson R. F., and Zivin J. A. (1994) AHA medical/scientific statement: Special report: Guidelines for the management of patients with acute ischemic stroke.Stroke 25, 1901–1914.
Alexander S. C. and Lassen N. A. (1970) Cerebral circulatory response to acute brain disease.Anesthesiology 32, 60–68.
Altman P. L. and Dittmer D. S. (eds.) (1972)Biology Data Book. Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, Washington, DC.
Andrews B. T., McIntosh T. K., Gonzales M. F., Weinstein P. R., and Faden A. I. (1988) Levels of endogenous opioids and effects of an opiate antagonist during regional cerebral ischemia in rats.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 247, 1248–1254.
Armstead W. M. (1995) Relationship between opioids and activation of phospholipase C and protein kinase C in brain injury induced pial artery vasoconstriction.Brain Res. 689, 183–188.
Avery W. F., Crockard H. A., and Russell R. W. R. (1983) Improved survival following severe cerebral ischemia using naloxone.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 3, S331-S332.
Baskin D. S. and Hosobuchi Y. (1981) Naloxone reversal of ischemic neurological deficits in man.Lancet 2, 272–275.
Baskin D. S. and Hosobuchi Y. (1986) Treatment of experimental stroke with the opiate antagonist WIN 44,441-3. Effects on neurologic function, infarct size, and survival, inNational Institute of Drug Abuse, Research Monograph, Series, Progress in Opioid Research, Proceedings of the International Narcotics Research Conference, US Department of Health, Rockville, MD, pp. 531–534.
Baskin D. S., Hosobuchi Y., Loh H., and Lee N. M. (1984) Dynorphin 1–13 improves survival from focal cerebral ischemia secondary to middle cerebral artery occlusion in baboons.Nature 312, 551–552.
Baskin D. S., Widmayer M. A., Browning J. L., Heizer M. L., and Schmidt W. K. (1994) Evaluation of delayed treatment of focal cerebral ischemia with three selective kappa opioid agonists in the cat.Stroke 25, 2047–2053.
Baughman V. L., Hoffman W. E., Miletich D. J., Albrecht R. F., and Thomas C. (1988) Neurologic outcome in rats following incomplete cerebral ischemia during halothane, isoflurane, or N2O.Anesthesiology 69, 192–198.
Birch P. J., Rogers H., Hayes A. G., Hayward N. J., Tyers M. B., Scopes D. I., Naylor A., and Judd D. B. (1991) Neuroprotective actions of GR89696, a highly potent and selective K-opioid receptor agonist.Br. J. Pharmacol. 103, 1819–1823.
Bose P. J., Jones S. C., Lorig R., Friel H. T., Weinstein M., and Little J. R. (1988) Evolving focal cerebral ischemia in cats: spatial correlation of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, cerrbral blood flow, tetrazolium staining and histopathology.Stroke 19, 28–37.
Browning J. L., Heizer M. L., and Baskin D. S. (1992) Variations in corticomotor and somatosensory evoked potentials: effects of temperature, halothane anesthesia, and arterial partial pressure of CO2.Anesth. Analg. 74, 643–648.
Busto R., Dietrich W., Globus M.-T., and Ginsberg M. (1989) The importance of brain temperature in cerebral ischemic injury.Stroke 20, 1113–1114.
Cahill C. A., Matthews J. D., and Akil H. (1983) Human plasma β-endorphin like peptides: A rapid, high recovery extraction technique and validation of radioimmunoassay.J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 56, 992–997.
Cahn R., Dupont J. M., Borzeix M. G., and Cahn J. (1990) Effect of halothane on ischemic brain edema.Adv. Neurol. 52, 93–96.
Clark S. C. and MacCannell K. L. (1975) Vascular responses to anesthetic agents.Can. Anaesth. Soc. J. 22, 20–33.
Faden A. I., Sacksen I., and Noble L. J. (1988) Opiate-receptor antagonist nalmefene improves neurological recovery after traumatic spinal cord injury in rats through a central mechanism.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 245, 742–748.
Garcia-Sanchez M. J., Polo A., and Peran F. (1993) Effects of halothane and isoflurane on beta-endorphin release in children.Anesthesia 48, 38–40.
Ghajar J., Hariri R. J., Narayan R. K., Iacono L. A., Firlink K., and Patterson R. H. (1995) Survey of critical care management of comatose, head-injured patients in the United States.Crit. Care Med. 23, 560–567.
Gibbs F. A., Lennox W. G., and Gibbs E. L. (1934) Cerebral blood flow preceding and accompanying epileptic seizures in man.Arch Neurol. Psychiatr. 32, 269–272.
Holzgrefe H. H., Everitt J. M., and Wright E. M. (1987) Alpha-chloralose as a canine anesthetic.Lab. Anim. Sci. 37, 587–595.
Hosobuchi Y., Baskin D. S., and Woo S. K. (1981) Reversal of induced neurologic deficit in gerbils by the opiate antagonist naloxone.Science 215, 69–71.
Hurn P. D., Koehler R. C., Norris S. E., Blizzard K. K., and Traystman S. E. (1991) Dependence of cerebral energy phosphate and evoked potential recovery on end-ischemic pH.Am. J. Physiol. 260, H532-H541.
Jakubowski J., Bell B. A., Symon L., Zawirski M. B., and Francis D. M. (1982) A primate model of subarachnoid hemorrhage: change in regional cerebral blood flow, autoregulation carbon dioxide reactivity and central conduction time.Stroke 13, 601–611.
Kagstrom E., Smith M.-L., and Siesjo B. K. (1983) Cerebral circulatory responses to hypercapnia and hypoxia in the recovery period following complete and incomplete cerebral ischemia in the rat.Acta Physiol. Scand. 118, 281–291.
Katsura K.-I., Kristián T., Smith M.-L., and Siesjö B. K. (1994) Acidosis induced by hypercapnia exaggerates ischemic brain damage.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 14, 243–250.
Kirsch J. R., Hanley D. F., Wilson D. A., and Traystman R. J. (1988) Effect of centrally administered encephalinamides on regional cerebral blood flow in the dog.J. Cereb. Blood. Flow Metab. 8, 385–394.
Kochs E. and Werner C. (1995) Neuroprotection: fact or fantasy.Eur. J. Anesthes. (Suppl.)10, 67–70.
Kobari M., Ishihara N., and Yunoki K. (1987) CSF beta-endorphin and leu-enkephalin levels in acute and chronic stages of cerebral infarction.J. Neurol. 234, 289–291.
Leffler C. W., Busija D. W., Armstead W. M., Mirro R., and Beasley D. G. (1989) Ischemia alters cerebral vascular responses to hypercapnia and acetylcholine in piglets.Pediatr. Res. 25, 180–183.
Levy R., Feustal P., Severinghaus J., and Hosobuchi Y. (1986) Focal cerebral ischemia in the cat: Effect of naloxone on cortical blood flow and neurological deficit following middle cerebral artery occlusion.Bull. Clin. Neurosci. 51, 94–101.
Marcoux F. W., Goodrich J. E., and Dominick M. A. (1988) Ketamine prevents ischemic neuronal injury.Brain Res. 452, 329–335.
Marmarou A., Bandoh K., Yoshihara M., and Tsuji O. (1993) Measurement of vascular reactivity in head injured patients. ActaNeurochir. Suppl. (Wien) 59 18–21.
McDowall D. G. (1967) The effects of clinical concentrations of halothane on the blood flow and oxygen uptake of the cerebral cortex.Br. J. Anaesth 39, 186–196.
Meyer J. S., Sawada T., Kitamura A., and Toyoda M. (1968) Cerebral oxygen, glucose, lactate, and pyruvate metabolism in stroke.Circulation 37, 1036–1048.
Miller C. L., Alexander K., Lampard D. G., Brown W. A., and Griffiths R. (1980) Local cerebral blood flow following transient cerebral ischemia II. Effect of arterial pCO2 on reperfusion following global ischemia.Stroke 11, 542–548.
Muizelaar J. P., Marmarou A., Ward J. D., Kontos H. A., Choi S. C., Becker D. P., Gruemer H., and Young H. F. (1991) Adverse affects of prolonged hyperventilation in patients with severe head injury: a randomized clinical trial.J Neurosurg. 75, 731–739.
Nakagawa Y., Othsuka K., Tsuru M., and Nakamura N. (1984) Effects of mild hypercapnia on somatosensory evoked potentials in experimental cerebral ischemia.Stroke 15, 275–278.
Nehls D. G., Todd M. M., Spetzler R. F., Drummond J. C., Thompson R. A., and Johnson P. C. (1987) A comparison of the cerebral protective effects of isoflurane and barbiturates during temporary focal ischemia in primates.Anesthesiology 66, 453–464.
O’Brien M. D. and Waltz A. G. (1973) Transorbital approach for occluding the middle cerebral artery without craniectomy.Stroke 4, 201–206.
Olsen T. S. (1986) Regional cerebral blood flow after occlusion of the middle cerebral artery.Acta Neurol. Scand. 73, 321–337.
Olsen T. S. and Lassen N. A. (1984) A dynamic concept of middle cerebral artery occlusion and cerebral infarction in the acute state based on interpreting severe hyperemia as a sign of embolic migration.Stroke 15, 458–468.
Olsen T. S., Larsen B., Skriver E. B., Herning M., Enevoldsen E., and Lassen N. A. (1981) Focal cerebral hyperemia in acute stroke.Stroke 12, 598–606.
Radulovacki M. (1973) 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid during wakefulness, sleep and after electrical stimulation of specific brain structures, in,Neurohumoral Coding of Brain Function (Myers R. D. and Drucker-Colin R. R. eds.), Plenum, New York, pp. 257–271.
Rothman K. J. (1990) No adjustments are needed for multiple comparisons.Epidemiology 1, 43–46.
Safar P. (1989) Resuscitation after brain ischemia, inBrain Failure and Resuscitation (Grenvik, A. and Safar, P., eds.), Churchill-Livingstone, New York, pp. 155–184.
Sandor P., Nyary I., Reivich M., and Kovach A. G. B. (1977) Comparative effects of chlorolose anesthesia and Sernylan analgesia on cerebral blood flow, CO2 responsiveness, and brain metabolism in the baboon.Stroke 8, 432–436.
Sandor P., DeJong W., and DeWied D. (1986a) Endorphinergic mechanisms in cerebral blood flow autoregulation.Brain Res. 386, 122–129.
Sandor P., Gotoh F., Tomita M., Tanahashi N., and Gogolak I. (1986b) Effects of a stable enkephalin analog (D-Met2, Pro5)-enkephalinamide, and naloxone on cortical blood flow and cerebral blood volume in experimental brain ischemia in anesthetized cats.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 6, 553–558.
Smith A. L., Larson C. P., and Hoff J. T. (1973) Effects of halothane on regional cerebral blood flow in experimental focal ischemia.Anesthesiology 39, 377–381.
Smith A. L., Hoff J. T., Nielsen S. L., and Larson C. P. (1974) Barbiturate protection in acute focal cerebral ischemia.Stroke 5, 1–7.
Spetzler R. F. and Hadley M. N. (1989) Protection against cerebral ischemia: the role of barbiturates.Cerebrovascular Brain Metab. Rev. 1, 212–229.
Strobel G. E. and Wollman H. (1969) Pharmacology of anesthetic agents.Fed. Proc. 28, 1386–1403.
Sundt T. M. and Waltz A. G. (1991) Cerebral ischemia and reactive hyperemia.Circ. Res. 28, 426–433.
Todd M. M., Tommasin C., and Shapiro H. M. (1985) Cerebrovascular effects of prolonged hypocarbia and hypercarbia after experimental global ischemia in cats.Crit. Care Med. 13, 720–724.
Trusk T. C. and Stein E. A. (1987) Effect of intravenous heroin and naloxone on regional cerebral blood flow in the conscious rat.Brain Res. 406, 238–245.
Vanicky I., Marsala M., Murár J., and Marsala J. (1992) Prolonged postischemic hyperventilation reduces acute neuronal damage after 15 min of cardiac arrest in the dog.Neurosci. Lett. 135, 167–170.
Warner D. S., Zhou J. G., Ramani R., and Todd M. M. (1991) Reversible focal ischemia in the rat: effects of halothane, isoflurane, and methohexital anesthesia.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 11, 794–802.
Warner D. S., McFarlane C., Todd M. M., Ludwig P., and McAllister A. M. (1993) Sevoflurane and halothane reduce focal cerebral ischemic brain damage in the rat.Anesthesiology 79, 985–992.
Widder B., Kleiser B., and Krapf H. (1994) Course of cerebrovascular reactivity in patients with carotid artery occlusions.Stroke 25, 1963–1967.
Wollman H., Alexander S. C., Cohen P. J., Chase P. E., Melman E., and Behar M. G. (1964) Cerebral circulation of man during halothane anesthesia.Anesthesiology 25, 180–184.
Youmans J. R. and Kindt G. W. (1968) Efficacy of carbon dioxide in the treatment of cerebral ischemia.Surg. Forum 19, 425–429.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Browning, J.L., Heizer, M.L., Widmayer, M.A. et al. Effects of halothane, α-chloralose, and pCO2 on injury volume and CSF β-endorphin levels in focal cerebral ischemia. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 31, 29–42 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815158
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815158