Abstract
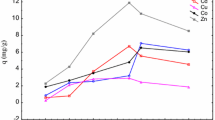
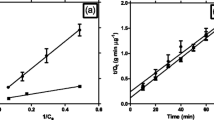
The ability of growing yeastCandida utilis to accumulate cadmium ions from the cultivation broth depends on the carbon source used; xylose and glucose were tested here. For the two substrates, the course of cadmium bioaccumulation and total uptake were quite different. With glucose the maximum of bioaccumulation was about ten times higher than with xylose. The data were consistent with a simple mathematical model of process dynamics which assumes a Freudlich isotherm to describe the biosorption equilibrium and first-order dynamics to simulated the transient state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
cadmium ion concentration in the solution, mg/L
- k F :
-
proportionality constant in Freudlich sorption isotherm, L/g dry matter
- K s :
-
constant characterizing the substrate limitation, g/L
- n :
-
exponent in Freundlich sorption isotherm
- q :
-
cadmium content in the biomass, mg Cd per g dry matter
- S :
-
substrate concentration, g/L
- t :
-
current time, h
- X :
-
biomass concentration, g dry matter per L
- Y x/s :
-
yield coefficient
- μ:
-
specific growth rate, 1/h
- τ:
-
time constant of bioaccumulation, h
- Indices :
-
e equilibrium, 0 initial, max maximum
References
Babich H., Devanas M.A., Stotzky G.: The mediation of mutagenecity and clastogenicity of heavy metals by physico-chemical factors.Environ. Res.37, 253–286 (1985).
Failla M.L., Benedict C.D., Weinberg E.D.: Accumulation and storage of Zn2+ byCandida utillis.J. Gen. Microbiol.94, 23–36 (1976).
Failla M.L., Weinberg E.D.: Cyclic accumulation of zinc byCandida utilis during growth in batch culture.J. Gen. Microbiol.99, 85–97 (1977).
Gadd G.M., Griffith A.J.: Microorganisms and heavy metal toxicity.Microbial Ecol.4, 303–317 (1978).
Gadd G.M.: The uptake of heavy metals by fungi and yeasts: The chemistry and physiology of the process and applications for biotechnology, pp. 135–147 in H. Eccles, S. Hunt (Eds)Immobilization of Ions by Biosorption. Ellis Horwood, Chichester 1986.
Gadd G.M.: Accumulation of metals by microorganisms and algae, pp. 402–433 in H.J. Rehm, G. Reed (Eds.):Biotechnology, Vol. 6b Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1988.
Grafl H.J., Schwantes H.O.: The effects of cadmium, zinc, lead and mercury on the growth and accumulating ability ofSaccharomyces cerevisiœ, Saccharomycopsis lipolytica, Candida tropicalis, andCandida utilis.Zbl. Bacteriol. Hyg. Ser. B177, 57–74 (1983).
Itoh M., Yuasa M., Kobayashi T.: Adsorption of metal ions on yeast cells at varied cell concentrations.Plant Cell Physiol.16, 1167–1169 (1975).
Minney S.F., Quirk A.V.: Growth and adaptation ofSaccharomyces cerevisiœ at different cadmium concentration.Microbios42, 37–44 (1985).
Mowll J.L., Gadd G.M.: Zinc uptake and toxicity in the yeastsSporobolomyces roseus andSaccharomyces cerevisiœ.J. Gen. Microbiol.129, 3421–3425 (1983).
Mowll J.L., Gadd G.M.: Cadmium uptake byAureobasidium pullulans.J. Gen. Microbiol.130, 279–284 (1984).
Norris P.R., Kelly D.P.: Accumulation of cadmium and cobalt bySaccharomyces cerevisiœ J. Gen. Microbiol.20, 299–308 (1977).
Olson B.H., Panigrahi A.K.: Bacteria fungi, and blue-green algœ pp. 419–448 in E. Merian (Ed.):Metals and Their Compounds in the Environment. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1991.
Perkin M.J., Ross I.S.: The specific uptake of managese in the yeastCandida utilis.J. Gen. Microbiol.132, 2155–2160 (1986).
Somogyi M.: Notes on sugar determination.J. Biol. Chem.195, 19–23 (1952).
Trevors J.T., Stratton G.W., Gadd G.M.: Cadmium transport, resistence, and toxicity in bacteria, algœ and fungi.Can. J. Microbiol.32, 447–464 (1986).
Varian Publ. (Anonymous) 85-100009-00 (1979).
Voleský B.: Biosorption by fungal biomass. pp. 139–172 in B. Voleský (Ed.):Biosorption of Heavy Metals. CRC Press, Boca Raton 1990.
Voleský B., Votruba J.:Modeling and Optimization of Fermentation Processes. Elsevier, Amsterdam 1992.
Voleský B., May H., Holan Z.R.: Cadmium biosorption bySaccharomyces cerevisiœ.Biotechnol. Bioeng.41, 826–829 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kujan, P., Votruba, J. & Kameník, V. Substrate dependent bioaccumulation of cadmium by growing yeastCandida utilis . Folia Microbiol 40, 288–292 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814210
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814210