Abstract
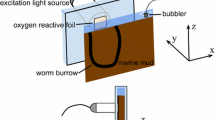
Diffusive boundary layers (DBL), sediment oxygen flux, and natural passive flow through model macrofauna burrows were compared in two benthic chambers: one with a conventional rotational stirrer and the other with a two-dimensional flow diffuser system. Oxygen microprobe profiles showed that at similar velocities the mean diffusive boundary layer (DBL) thickness induced by a conventional rotor stirrer (453±118 μm) was not significantly different to that produced by the diffuser system (403±53 μm). The rotor produced twice as much DBL spatial variability (coefficient of variation 27%) as the diffuser (CV 11%). Variability between the rotor system’s DBL transect replicates was also two times greater (average CV of 22%) compared to the diffuser (CV 14%). At equivalent stirring speeds over experimental sediments, mean O2 consumption rates were also not significantly different between the two systems. The diffuser induced consistently greater (16–37%) passive Bernoullian flow through model macrofauna borrows irrespective of the position of inhalant-exhalent openings. The rotor stimulated anomalous burrow flow regimes over a greater area of the chamber floor (36%) compared to the diffuser (23%). Depending on vent orientation the rotor was shown to reverse (exhalent to inhalant) burrow flow regimes in the central 9% of the chamber floor. This artifact of radial pressure and velocity differentials may have severe implications for tube dwelling infauna that rely on unidirectional flow. The diffuser system more closely mimicked natural two-dimensional water flow over the sediment surface and structures therein and is likely to give more representative results when measuring benthic processes within incubation devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Allanson, B. R., D. Skinner, andJ. Imberger. 1992. Flow in prawn burrows.Estuarine, Coast and Shelf Science 35:253–266.
Aller, R. C. 1984. The importance of relict burrow structures and burrow irrigation in controlling sedimentary solute distributions.Geochemica et Cosmochimica Acta 48:1929–1934.
Aller, R. C. 1988. Benthic fauna and biogeochemical processes in marine sediments: The role of burrow structures, p. 300–338.In T. H. Blackburn and J. Sorensen (eds.), Nitrogen Cycling in Coastal Marine Environments. John Wiley and Sons Ltd., Denmark.
Berelson, W. M. andD. E. Hammond. 1986. The calibration of a new free-vehicle benthic flux chamber for use in the deep sea.Deep Sea Research 33:1439–1454.
Buchholtz-Ten Brink, M. R., G. Gust, andD. Chavis. 1989. Calibration and performance of a stirred benthic chamber.Deep Sea Research 36:1083–1101.
Crawford, S. M. andL. P. Sanford. 2001. Comparison of carbon production and decomposition, benthic nutrient fluxes and denitrification in seagrass, phytoplankton, benthic microalgal and macroalgal dominated warm temperate Australian lagoons.Marine Ecology Progress Series 229:43–59.
Glud, R. H., S. Forster, andM. Huettel. 1996. Influence of radial pressure gradients on solute exchange in stirred benthic chambers.Marine Ecology Progress Series 141:303–311.
Glud, R. N., J. K. Gundersen, B. B. Jørgensen, N. P. Revsbech, andH. D. Schulz. 1994a. Diffusive and total oxygen uptake of deep-sea sediments in the South Atlantic Ocean: In situ and laboratory measurements.Deep Sea Research 41:1767–1788.
Glud, R. N., J. K. Gundersen, N. P. Revsbech, andB. B. Jorgensen. 1994b. Effects on the benthic diffusive boundary layer imposed by microelectrodes.Limnology and Oceanography 39:462–467.
Glud, R. N., J. K. Gundersen, N. P. Revsbech, B. B. Jorgensen, andM. Huttel. 1995. Calibration and performance of the stirred flux chamber from the benthic lander.Elinor. Deep Sea Research 42:1029–1042.
Glud, R. N., O. Holby, F. Hoffmann, andD. E. Canfield. 1998. Benthic mineralization and exchange in Arctic sediments (Svalbard, Norway).Marine Ecology Progress Series 173:237–251.
Glud, R. H., N. B. Ramsing, andJ. K. Gundersen. 2000. Electrochemical and optical oxygen microsensors for in situ measurement, p. 20–73.In J. Buffle and G. Horvai (eds.), In Situ Monitoring of Aquatic Systems: Chemical Analysis and Speciation. John Wiley and Sons Ltd., Denmark.
Gundersen, J. K. andB. B. Jørgensen. 1990. Microstructure of diffusive boundary layers and the oxygen uptake of the sea floor.Nature 345:604–607.
Huettel, M. andG. Gust. 1992. Solute release mechanisms from confined sediment cores in stirred benthic chambers and flume flows.Marine Ecology Progress Series 82:187–197.
Jørgensen, B. B. andN. P. Revsbech. 1985. Diffusive boundary layers and the oxygen uptake of sediments and detritus.Limnology and Ocanography 30:111–122.
Kenway, M. J. 1981. Biological studies ofCallianassa australiensis (Dana). James Cook University, North Queensland, Australia.
Kerr, G. A. 2001. The sedimentological and geochemical effects ofTrypaea australiensis (Decapoda: Thalassinidea) activity in the Richmond River estuary, NSW Australia. Centre for Coastal Management, Southern Cross University, Lismore, Australia.
Kristensen, E., M. H. Jensen, andR. C. Aller. 1991. Direct measurement of dissolved inorganic nitrogen exchange and denitrification in individual polychaete (Nereis virens) burrows.Journal of Marine Research 49:355–377.
Libelo, L. E., W. G. MacIntyre, R. D. Seitz, andL. F. Libelo. 1994. Cycling of water through the sediment—Water interface by passive ventilation of relict biological structures.Marine Geology 120:1–12.
Munksby, N., M. Benthien, andR. N. Glud. 2002. Flow-induced flushing of relict tube structures in the central Skagerrak (Norway).Marine Biology 141:939–945.
Poore, G. C. B. andD. J. G. Griffin. 1979. The thalassinidea (Crustacea: Decapoda) of Australia.Records of the Australian Museum 32:217–321.
Ray, A. J. andR. C. Aller. 1985. Physical irrigation of relict burrows: Implications for sediment chemistry.Marine Geology 62:371–379.
Revsbech, N. P. andB. B. Jørgensen. 1986. Microelectrodes and their use in microbial ecology, p. 263–352.In K. C. Marshall (ed.), Advances in Microbial Ecology, Volume 9. Plenum Press, New York.
Tengberg, A., F. De Bovee, P. Hall, W. Berelson, D. Chadwick, G. Ciceri, P. Crassous, A. Devol, S. Emerson, J. Gage, R. Glud, F. Graziottini, J. Gundersen, andD. Hammond. 1995. Benthic chamber and profile landers in oceanography—A review of design, technical solutions and functioning.Progressive Oceanography 35:253–294.
Vogel, S. 1974. Current induced flow through the sponge,Halichondria.Biological Bulletin 147:443–456.
Vogel, S. 1978. Organisms that capture currents.Scientific American 229:128–139.
Webb, A. P. 2001. The effect of natural populations of epi and infaunal animals on the biogeochemistry of shallow and intertidal estuarine setuarine sediments in subtropical eastern Australia. School of Environmental Science and Management. Ph.D. thesis, Southern Cross University, Lismore, New South Wales, Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Webb, A.P., Eyre, B.D. The effects of two benthic chamber stirring systems on the diffusive boundary layer, oxygen flux, and passive flow through model macrofauna burrows. Estuaries 27, 352–361 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02803391
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02803391