Abstract
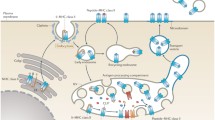
The MHC class II antigen processing pathway provides a mechanism to selectively present peptides generated in the endosomal compartments of antigen presenting cells to CD4+ T cells. Transport of newly synthesized class II molecules to the endosomal pathway requires the function of an accessory protein, invariant chain, which contains a region that interacts directly with the class II peptide binding site. Release of invariant chain and peptide loading by class II molecules are facilitated by a second accessory protein, HLA-DM. This MHC-encoded membrane protein catalyzes peptide exchange reactions, influencing the repertoire of peptides that are available for recognition by T cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buus S, Sette A, Colon SM, Jenis DM, Grey HM: Isolation and characterization of antigen-Ia complexes involved in T cell recognition. Cell 1986;47:1071–1077.
Babbitt BP, Allen PM, Matsueda, G, Haber E, Unanue ER: Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. Nature 1985;317:359–361.
Sadegh-Nasseri S, McConnell HM: A kinetic intermediate in the reaction of an antigenic peptide and IEk. Nature 1989;337:274–276.
Jensen PE: Regulation of antigen presentation by acidic pH. J Exp Med 1990;171:1779–1789.
Jensen PE: Enhanced binding of peptide antigen to purified class II major histocompatibility glycoproteins at acidic pH. J Exp Med 1991;174:1111–1120.
Jensen PE: Long-lived complexes between peptide and class II MHC are formed at low pH with no requirement for pH neutralization. J Exp Med 1992;176:793–798.
Jensen PE: Acidification and disulfide reduction can be sufficient to allow intact proteins to bind class II MHC. J Immunol 1993; 150:3347–3356.
Sherman MA, Runnels HA, Moore JC, Stern LJ, Jensen PE: Membrane interactions influence the peptide binding behavior of DR1. J Exp Med 1994;179:229–234.
Sadegh-Nasseri S, Germain RN: A role for peptide in determining MHC class II structure. Nature 1991;353:167–170.
Boniface JJ, Lyons DS, Wettstein DA, Allbritton NL, Davis MM: Evidence for a conformational change in a class II MHC molecule occurring in the same pH range that enhances antigen binding. J Exp MEd 1996;183:119–126.
Runnels HA, Moore JC, Jensen PE: A structural transition in class II MHC proteins at mildly acidic pH. J Exp Med 1996;183:127–136.
Germain RN, Hendrix LR: MHC class II structure, occupancy and surface expression determined by post-endoplasmic reticulum antigen binding. Nature 1991;353: 134–139.
Jensen PE: Stable assocuation of processed antigen with antigenpresenting cell membranes. J Immunol 1989;143:420–425.
Lanzavecchia A, Reid PA, Watts C: Irreversible association of peptides with class II MHC molecules in living cells. Nature 1992;357: 249–252.
Stern LJ, Wiley DC: The Human Class II MHC Protein HLA-DR1 Assembles as Empty αΒ Heterodimers in the Absence of Antigenic Peptide. Cell 1992;68: 465–477.
Reay PA, Wettstein DA, Davis MM: pH dependence and exchange of high and low responder peptides binding to a class II MHC molecule. EMBO J 1992;11:2829–2839.
Sherman MA, Weber DA, Jensen PE: DM enhances peptide binding to class II MHC by release of invariant chain-derived peptide. Immunity 1995;3:197–205.
Mellins E, Smith L, Arp B, Cotner T, Celis E, Pious D: Defective processing and presentation of exogenous antigens in mutants with normal HLA class II genes. Nature 1990;343:71–74.
Mellins E, Kempin S, Smith L, Monji T, Pious D: A gene required for class II-restricted antigen presentation maps to the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med 1991;174:1607–1615.
Riberdy JM, Newcomb JR, Surman MJ, Barbosa JA, Cresswell P: HLA-DR molecules from an antigenprocessing mutant cell line are associated with invariant chain peptides. Nature 1992;360:474–477.
Sette A, Ceman S, Kubo RT, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Hunt DF, et al.: Invariant chain peptides in most HLA-DR molecules of anantigen-processing mutant. Science 1992;258:1801–1804.
Fling Sp, Arp B, Pious: HLA-DMA and DMB genes are both required for MHC class II/peptide complex formation in antigenpresenting cells. Nature 1994; 368:554–558.
Morris P, Shaman J, Attaya M, Amaya M, Goodman S, Bergman C, et al.: An essential role for HLA-DM in antigen presentation by class II major histocompatibility molecules. Nature 1994;368:551–554.
Cho SG, Attaya M, Monaco JJ: New class Il-like genes in the murine MHC. Nature 1991;353: 573–576.
Kelly AP, Monaco JJ, Cho SG, Trowsdale J: A new human HLA class Il-related locus, DM. Nature 1991;353:571–573.
Mosyak L, Zaller DM, Wiley DC: The structure of HLA-DM, the peptide exchange catalyst that loads antigen onto class II MHC molecules during antigen presentation. Immunity 1998;9:377–383.
Fremont DH, Crawford F, Marrack P, Hendrickson WA, Kappler J: Crystal structure of mouse H2-M. Immunity 1998;9:385–393.
Sloan VS, Cameron P, Porter G, Gammon M, Amaya M, Mellins E, et al.: Mediation by HLA-DM of dissociation of peptides from HLA-DR. Nature 1995;375:802–806.
Denzin LK, Cresswell P: HLA-DM induces CLIP dissociation from MHC class II ab dimers and facilitates peptide loading. Cell 1995;82:155–165.
Weber DA, Evavold BD, Jensen PE: Enhanced dissociation of HLA-DR-bound peptides in the presence of HLA-DM. Science 1996; 274:618–620.
Kropshofer H, Vogt AB, Stern LJ, Hammerling GJ: Self-release of CLIP in peptide loading of HLA-DR molecules. Science 1995;270: 1357–1359.
Ghosh P, Amaya M, Mellins E, Wiley DC: The structure of an intermediate in class II MHC maturation: CLIP bound to HLA-DR3. Nature 1995;378:457–462.
Sette A, Southwood S, Miller J, Appella E: Binding of major histocompatibilty complex class II to the invariant chain-derived peptide, CLIP, is regulated by allelic polymorphism in class II. J Exp Med 1995;181:677–683.
Bangia N, Watts TH: Evidence for invariant chain 85–101 (CLIP) binding in the antigen binding site of MHC class II molecules. Int Immunol 1995;7:1585–1591.
vanHamSM, Gruneberg U, Malcherek G, Broker I, Melms A, Trowsdale J: Human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DM edits peptides presented by HLA-DR according to their ligand binding motifs. J Exp Med 1996; 184:2019–2024.
Kropshofer H, Vogt AB, Moldenhauer G, Hammer J, Blum JS, Hammerling GJ: Editing of the HLA-DR-peptide repertoire by HLA-DM. EMBO J 1996;15: 6144–6154.
Stern LJ, Brown JH, Jardetzky TS, Gorga JC, Urban RG, Strominger JL, et al.: Crystal structure of the human class II MHC protein HLA-DR1 complexed with an influenza virus peptide. Nature 1994;368: 215–221.
Garrett TPJ, Saper MA, Bjorkman PJ, Strominger JL, Wiley DC: Specificity pockets for the side chains of peptide antigens in HLA-Aw68. Nature 1989;342:692–696.
Fahnestock ML, Tamir I, Narhi L, Bjorkman PJ: Thermal stability comparison of purified empty and peptide-filled forms of a class I MHC molecule. Science 1992; 258:1658–1662.
Miyazaki T, Wolf P, Tourne S, Waltzinger C, Dierich A, Barois N, et al.: Mice lacking H@-M complexes, engimatic elements of the MHC class II peptide-loading pathway. Cell 1996;84:531–541.
Freisewinkel IM, Schenck K, Koch N: The segment of invariant chain that is critical for association with major histocompatibility complex class II molecules contains the sequence of a peptide eluted from class II polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90:9703–9706.
Bijlmakers MJ, Benaroch P, Ploegh HL: Mapping functional regions in the lumenal domain of the class II-associated invariant chain. J Exp Med 1994;180:623–629.
Romagnoli P, Germain RN: The CLIP region of invariant chain plays a critical role in regulating major histocompatibility complex class II folding, transport, and peptide occupancy. J Exp Med 1994;180:1107–1113.
Liang MN, Beeson C, Mason K, McConnell HM: kinetics of the reaction between the invariant chain (85-99) peptide and proteins of the murine class II MHC. Int Immunol 1995;7:1397–1404.
Thayer WP, Ignatowicz L, Weber DA, Jensen PE: Class II-associated invariant chain peptide-independent binding of inavariant chain to class II MHC molecules. J Immunol 1999;162:1502–1509.
Kropshofer H, Vogt AB, Hammerling GJ: Structural features of the invariant chain fragment CLIP controlling rapid release from HLA-DR molecules and inhibition of peptide binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995;92:8313–8317.
Stumptner P, Benaroch P: Interaction of MHC class II molecules with the invariant chain: role of the invariant chain (81-90) region. EMBO J 1997;16:5807–5818.
Siebenkotten IM, Carstens C, Koch N: Identification of a sequence that mediates promiscuous binding of invariant chain to MHC class II allotypes. J Immunol 1998; 160:3355–3362.
Zhong G, Castellino F, Romagnoli P, Germain RN: Evidence that binding site occupancy is necessary and sufficient for effective major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II transport through the secretory pathway redefines the primary function of class II-associated invariant chain peptides (CLIP). J Exp Med 1996; 184:2061–2066.
Fung-Leung WP, Surch CD, Li-lijedahl M, Pang J, Leturcq D, Peterson PA, et al.: Antigen presentation and T cell development in H2-M-deficient mice. Science 1996;271:1278–1281.
Martin WD, Hicks GG, Mendiratta SK, Leva HI Ruley HE, VanKaer L: H2-M mutant mice are defective in the peptide loading of class II molecules, antigen presentation, and T cell repertoire selection. Cell 1996;84:543–550.
Kropshofer H, Vogt AN, Moldenhauer G, Hammer J, Blum JS, Hammerling GJ: Editing of the HLA-DR-peptide repertoire by HLA-DM. EMBO J 1996;15: 6144–6154.
Katz JF, Stebbins C, Appella E, Sant AJ: Invariant chain and DM edit self-peptide presentation by Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) class II moloecules. J Exp Med 196;184:1747–1753.
Lavoie PM, Thibodeau J, Cloutier I, Busch R, Sekaly RP: Selective binding of bacterial toxins to major histocompatibility complex class II-expressing cells is controlled by invariant chain and HLA-DM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:6892–6897.
Lightstone L, Hargreaves R, Bobek G, Peterson M, Aichinger G, Lombardi G, et al.: In the absence of the invariant chain, HLA-DR molecules display a distinct array of peptides which influenced by the presence or absence of HLA-DM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:5772–5777.
Tourne S, Miyazaki T, Wolf P, Ploegh H, Benoist C, Mathis D: Functionality of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules in mice doubly deficient for invariant chain and H-2M complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:9255–9260.
Swier K, Brown DR, Bird JJ, Martin WD, VanKaer L, Reiner SL: A critical, invariant chain-independent role for H2-M antigen presentation. J Immunol 1998;160:540–544.
Kovats S, Grubin CE, Eastman S, deRoos P, Dongre A, VanKaer L, et al.: Invariant chain-independent function of H-2M in the formation of endogenous peptide-major histocompatibility complex class II complexes in vivo. J Exp Med 1998;187:245–251.
Fairchild PJ, Wraith DC: Lowering the tone: mechanisms of immunodominance among epitopes with low affinity for MHC. Immunol Today 1996;17:80–85.
Fairchild PJ, Wildgoose R, Artherton E, Webb S, Wraith DC: An auto antigenic T cell epitope from unstable complexes with class II MHC: a novel route for escape from tolerance induction. Int Immunol 1993;5:1151–1158.
Joosten I, Wauben MH, Holewijn MC, Reske K, Pedersen LO, Roosenboom CF, et al.: Direct binding of autoimmune disease related T cell epitopes to purified Lewis rat MHC class II molecules. Int Immunol 1994;6:751–759.
Carrasco-Marin E, Shimizu J, Kanagawa O, Unanue ER: The class II MHC I-Ag7 molecules from non-obese diabetic mice are poor peptide binders. J Immunol 1996; 156:450–458.
Harrington CJ, Paez A, Hunkapiller T, Mannikko V, Brabb T, Ahearn M, et al.: Differential tolerance in induced T cells recognizing distinct epitopes of myelin basic protein. Immunity 1998; 8:571–580.
Cibotti R, Kanellopoulos JM, Cabaniols JP, Halle-Panenko O, Kosmatopoulos K, Sercarz E, et al.: Tolerance to a self-protein involves its immunodominant but does not involve its subdominant determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89:416–420.
Sercarz EE, Lehmann PV, Ametani A, Benichou G, Miller A, Moudgil K: Dominance and crypticity of T cell antigenic determinants. Annu Rev Immunol 1993;11:729–766.
Pinet V, Vergelli M, Martin R, Bakke O, Long EO: Antigen presentation mediated by recycling of surface HLA-DR molecules. Nature 1995;375:603–606.
Tompkins SM, Rota PA, Moore JC, Jensen PE: A europium fluoro-immunoassay for measuring binding of antigen to class II MHC glycoproteins. J Immunol Methods 1993;163:209–216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jensen, P.E., Weber, D.A., Thayer, W.P. et al. HLA-DM and the MHC class II antigen presentation pathway. Immunol Res 20, 195–205 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02790403
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02790403