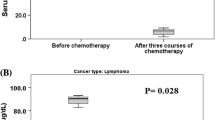
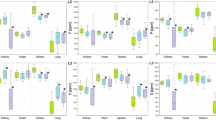
Abstract
The concentration of trace elements in samples of both colorectal cancer tumors and normal tissues of a Mexican population were irradiated for 30 s and 4 h and their elemental content were measured by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Ca, Cu, Co, I, Mg, Se, Fe, Zn, Hg, Ba, and Cr were analyzed. Alterations in Co, Fe, I, and Ba were found in tumors with respect to normal tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. P. Cheng, Study of the correlation of trace elements,J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 195 (1) (1995).
A. Mendoza-Rodriguez, I. Morillen, M. A. Cerbon, P. Luna, H. Santiago-Payon, and A. Quintero, Differential expression of c-fos, c-myc and c-Ki-ras oncogenes in colo- rectal cancer from Mexican patients,Bol. Est. Mod. Biol. Mex. 44, 77–79 (1996).
P. Vaughan, D. Kaye, S. Ball, H. Reeve, and C. Peers, The effect of barium on (3H) noradrenalin release from the human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y,Eur. J. Neurosci. 1, 875–80 (1995).
L. Xiao, and H. Zhang, INNA of elemental contents in fingernails of esophageal can- cer patients,J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 195 (1) (1995).
M. A. Lovell, and J. D. Robertson, Aplication of radioanalytical techniques to biolog- ical and biomedical sciences,J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 195 (1) (1995).
Y. L. Sziklai, and A. Cser, Selenium determination in biological materials,J. Anal. Nucl. Chem. 190 (1) (1995).
G. Friedlander, J. Kennedy, E. Macias, and M. Miller,Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Wiley, New York (1981).
J. T. Proudehomme. Texas Nuclear Corporation. USA (1962)
K. Way and L. Rose,Nuclear Data Tables, Academic, London (1971).
S. Toyokumi, Iron-induced carcinogenesis: the role of redox regulation,Free Radical Biol. Med. 20, 553–566 (1996).
P. Reizenstein, Free radicals and cancer,Med. Oncol. Tumour Pharmacother. 8, 229–233 (1991)
R. L. Nelson, S. J. Yoo, J. C. Tanure, G. Andrianopoulos, and A. Misumi, The effect of iron on experimental colorectal carcinogenesis,Anticancer Res. 6, 111–115 (1989).
P. Knekt, A. Reunanen, H. Takkunen, A. Aromaa, M. Heliovaara, and T. Hakulinen, Body iron stores and risk of cancer,Int. J. Cancer 56, 379–382 (1994).
R. Stevens, B. I. Graubard, M. S. Micozzi, K. Neriishi, and B. S. Blumberg, Moderate elevation of body iron level and increased risk of cancer occurrence and death,Int. J. Cancer 1, 364–369 (1994).
V. Zaichick, A. F. Tsyb, and B. M. Vtyurin, Trace elements and thyroid cancer,Ana- lyst 120, 817–821 (1995).
Y. P. Zhu, M. Bilous, and S. C. Boyages, Excess iodine induces the expression of thy- roid solid cell nests in lymphocytic thyroiditis-prone BB/W rats,Autoimmunity 20, 201–206 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arriola, H., Longoria, L., Quintero, A. et al. INAA of trace elements in colorectal cancer patients. Biol Trace Elem Res 71, 563–568 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784244
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784244