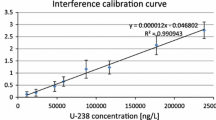
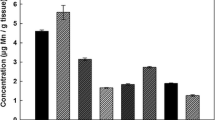
Abstract
Methods have been developed for the analyses of trace metals in various areas of porcine brains, (temporal, parietal, frontal cortex, both right and left hemispheres). Determinations were carried out using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (ETAAS). The elements investigated were Li, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cd, Hg, and Pb by ICP-MS and Cu, Cd, and Mn by ETAAS. For determination by ICP-MS, a method of standard additions calibration coupled with internal standards was used, and for ETAAS, standard additions calibrations were prepared. The accuracy of all methods was determined using NIST and IAEA certified reference material.
A small number of pig brains were analyzed by instrumental neutron activation analysis for Cr, Co, Cs, Fe, Rb, Se, Sc, Sb, and Zn using the comparator method of analysis. Four separate NIST standard reference materials have been used to examine the validity of the comparator method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Andrasi, E. Farkas, H. Scheibler, A. Reffy, and L. Bezur, Al, Zn, Cu, Mn and Fe levels in brain in Alzheimer’s Disease,Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 21, 89–97 (1995).
M. A. Deibel, W. D. Ehmann, and W. R. Markesbery, Copper, iron and zinc imbal- ances in severley degenerated brain regions in Alzheimer’s Disease: possible relation to oxidative stress,J. Neurol. Sci. 143, 137–142 (1996).
W. D. Ehmann, W. R. Markesbery, T. I. M. Hossain, M. Alzuddin, and D. T. Goodin, Trace elements in human brain tissue by INAA,J. Radioanal. Chem. 70 1–2, 57–65 (1982).
L. Tandon, B. F. Ni XX Ding, W. D. Ehmann, E. J. Kasarskis, and W. P. Markesbery, RNAA for arsenic, cadmium, copper and molybdenum in CNS tissues from subjects with age related neurodegenerative diseases,J. Radional. Nucl. Chem. 179, 331–339 (1994).
Y. K. Fung, A. G. Meade, E. P. Rack, and A. J. Blotcky, Brain mercury in neurode- generative disorders,Clin. Toxicol. 35(1), 49–54 (1997).
W. J. Nicklowitz and T. I. Mandybur, Neurofibrillary changes following childhood lead encephalopathy,J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 34, 445 (1975).
J. D. Stedman and N. M. Spyrou, A comparison of the techniques of PIXE, PIGE and INAA by reference to the elemental analysis of porcine brain samples,Nucl. lustrum. Methods Phys. Rese., Sect A,353, 436–439 (1994).
B. S. Iversen, R. Bottin, M. A. White, and E. Sabbioni, ICP-MS method for the deter- mination of trace elements in microwave oven mineralised Hair, In preparation.
R. Pietra and E. Sabbioni, Titanium nitride as a coating for surgical instruments used to collect human tissue for trace metal analysis,Analyst 115, 1025–1028 (1990).
H. Evans and J. Giglio, Interferences in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrom- etry,J. Atomic Absorpt. Spectrom. 8, 1–18 (1993).
Institute for Advanced Materials, Joint Research Centre (JRC), Petten, P.O. Box 2. 1755 ZG, Petten, Netherlands.
NEDA, Author, Aurelio Galbersanini ASCOM, 38, Via Clericetti, 20133, Milan, Italy.
G. V. Iyengar, W. E. Kollmer, and H. J. M. Bowen. The Elemental Compositon of Human Tissue and Body Fluids. A Compilation of Values for Adults, Verag Chemie, Weinheim (1978).
Porcine Food Supplements, Private Communication with Div. Sildamin, Agribands Europe, Italy, S.p.A. Pavia, Italy.
J. Steadman, PhD Thesis, 1996, Regional distribution of elemental concentrations in brain tissue of “normal” aging and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease subjects determined by PIXE, RBS and INA analysis, Physics Department, University of Surrey, Guildford. Surrey, GU2 5XH, U.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panayi, A.E., Spyrou, N.M., Ubertalli, L.C. et al. Determination of trace elements in porcine brain by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry, and instrumental neutron activation analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res 71, 529–540 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784241
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784241