Abstract
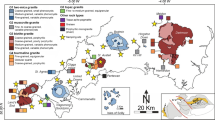
The Guilaizhuang gold deposit, with an average grade of 8.10 g/t Au and reserves of over 30 mt, is a subvolcanic epithermal deposit. The deposit is hosted in Paleozoic carbonate rocks in the western Shandong metallogenic terrane of the littorine Pacific metallogenic domain, eastern China, and is associated spatially with an early Mesozoic subvolcanic alkalic intrusive complex (188–190 Ma). The orebody was discovered at the end of the 1980s based on anomalies of Au in stream sediment samples at a map scale of 1∶200,000. The ore is rich in Au, Ag, Te, V, F, As, Sb, Tl, W, and Mo but poor in Cu, Pb, and Zn. The ore is similar in its trace elements to Carlin-type Au deposits. The transverse element association zonation of the deposit is as follows: (on the hanging wall) F⟸ W−Mo−As−Tl⟸Se−Sb−Bi⟸Au−Ag−Te (orebody) ⟹ Se−Sb−Bi (on the foot wall). The axial zonation is as follows: Au⟹Ag⟹Sb⟹V⟹Zn ⟹W⟹F⟹Mo⟹Tl⟹As. Indexes such as (Au+Sb) d / (As+Tl) d and (Au+ Ag) d /(As+Tl) d decrease with depth but dramatically increase at the level where the orebody pinches out, which indicates another orebody might exist at depth. Multivariate statistical analysis suggests that the ore (halo)-forming process can be divided into two stages: alteration and mineralization. The former includes: potash feldsparization, albitization, silicification, and fluoritization. The latter includes the following substages: arsenopyritization and scheelitization; pyritization, chalcopyritization, and sphaleritization; and native gold, electrum, and calaveritization. The last substage is considered to be the main ore-forming stage in the formation of the deposit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beus, A. A. and Grigorian, S. V., 1977, Geochemical Exploration Methods for Mineral Deposits: Calgary, Applied Publishing p. 92–98.
Chen, Y. Q., Ji, H. J., and Li, S. Q., 1995, Geochemical prospecting pattern of Tongshi gold field, eastern China: Geology & Prospecting, v. 31, n. 6, p. 49–53 (in Chinese).
Ji, H. J., Wu, X. S., and Chen, Y. Q., 1993, Correspondence cluster analysis: Journal of Changchun University of Earth Sciences, v. 23, n. 4, p. 459–464 (in Chinese).
Jin, L. Y., and Shen, K., 1995, Ore composition and genesis of the Guilaizhuang gold deposit in Pingyi, Shandong province: Geology of Shandong, v. 11, n. 1, p. 30–40 (in Chinese)
Li, H. F., 1995, A preliminary study of “three-stages & two series” prospecting model in Dongping gold deposit: Gold Geology, v. 1, n. 1, p. 42–45 (in Chinese).
Li, W. D., 1986, A discussion on a new type of gold deposit at the International Volcanology Symposium in New Zealand: External Volcanic Geology, v. 2, p. 1–18 (in Chinese).
Lin, J. Q., Tan, D. J., and Yu, X. F., 1995, Genesis and metallogenic model of Guilaizhuang gold deposit: Journal of Changchun University of Earth Sciences, v. 25, n. 3, p. 286–293 (in Chinese).
Qiu, J. S., Wang, D. Z., and Zhu, X. Y., 1994, The first example of Te−Au type epithermal deposit in China—The Guilaizhuang gold deposit: Geology & Prospecting, v. 30, n. 1, p. 7–12 (in Chinese).
Quan, Z. W., 1992, Ore-forming geological characteristics of Guilaizhuang gold deposit: Geological information of Shandong, v. 76, n. 2, p. 18–26 (in Chinese).
Richards, J. P., and Ledlie, I., 1993, Alkalic intrusive rocks associated with the Mount Kare gold deposit, Papua New Guinea: Comparison with the Porgera intrusive complex. Economic Geology, v. 88, n. 4, p. 755–781.
Xiang, S. Y., and Ye, J. L., 1995, A new type of gold deposit related to alkalic intrusive rocks: Mineral Resources & Geology, v. 9, n. 46, p. 73–76 (in Chinese).
Yu, X. F., 1996, Geological characteristics and genesis of the Guilaizhuang gold deposit,in Shandong Bureau of Geology & Mineral Resources, ed., Proceedings of researches on the geology & mineral resources in Shandong province: Jinan, Shandong Science & Technology Press, p. 129–139 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yongqing, C., Pengda, Z. Zonation in primary halos and geochemical prospecting pattern for the Guilaizhuang gold deposit, eastern China. Nat Resour Res 7, 37–44 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782507
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782507