Abstract
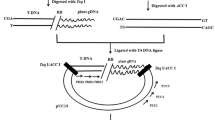
Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation is a method of choice for the development of transgenic plants. The presence of latentAgrobacterium that multiplies in the plant tissue in spite of antibiotic application confounds the results obtained by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of putative transgenic plants. The presence ofAgrobacterium can be confirmed by amplification of eitherAgrobacterium chromosomal genes or genes present out of transfer DNA (T-DNA) in the binary vector. However, the transgenic nature ofAgrobacterium-contaminated transgenic plants cannot be confirmed by PCR. Here we report a simple protocol for PCR analysis ofAgrobacterium-contaminated transgenic plants. This protocol is based on denaturation and renaturation of DNA. The contaminating plasmid vector becomes double-stranded after renaturation and is cut by a restriction enzyme having site(s) within the PCR amplicon. As a result, amplification by PCR is not possible. The genomic DNA with a few copies of the transgene remains single-stranded and unaffected by the restriction enzyme, leading to amplification by PCR. This protocol has been successfully tested with 4 different binary vectors and 3Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains: EHA105, LBA4404, and GV3101.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTAB:
-
hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RT:
-
reverse transcription
- T-DNA:
-
transfer DNA
- TE:
-
Tris-EDTA
References
Birnboim HC (1983) A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol 100: 243–255.
Chen PY, Wang CK, Soong SC, and To KY (2003) Complete sequence of the binary vector pBI121 and its application in cloning T-DNA from transgenic plants. Mol Breed 11: 287–293.
De Buck S, De Wilde C, Van Montagu M, and Depicker A (2000) T-DNA vector backbone sequences are frequently integrated into the genome of transgenic plants obtained byAgrobacterium-mediated transformation. Mol Breed 6: 459–468.
Doyle JJ and Doyle JI (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12: 13–15.
Gelvin SB (2003)Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation: the biology behind the “Gene-Jockeying” tool. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67: 16–37.
Hofgen R and Willmtzer L (1988) Storage of competent cells ofAgrobacterium transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 16(20): 9877.
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffman NL, Eichholtz D, Ragers SG, and Fraley RT (1985) A simple method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227: 1229–1231.
Nauerby B, Billing K, and Wyndaele R (1997) Influence of the antibiotic timentin on plant regeneration compared to carbenicillin and cefotaxime in concentrations suitable for elimination of plant cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 29: 153–160.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, and Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2d ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Sarma KS, Evans NE, and Selby C (1995) Effect of carbenicillin and cefotaxime on somatic embryogenesis of Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr.). J Exp Bot 46: 1779–1781.
Shackelford NJ and Chlan CA (1996) Identification of antibiotics that are effective in eliminatingAgrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Mol Biol Rep 14: 50–57.
Siritunga D and Sayre RT (2003) Generation of cyanogen-free transgenic cassava. Planta 217: 367–373.
Trontin JF, Harvengt L, Garin E, Lopez-Vernaza MLV, Arancio L, Hoebeke J, Canlet F, and Paques M (2002) Towards genetic engineering of maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Ait.) Ann Forest Sci 59: 687–697.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nain, V., Jaiswal, R., Dalal, M. et al. Polymerase chain reaction analysis of transgenic plants contaminated byAgrobacterium . Plant Mol Biol Rep 23, 59–65 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772647
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772647