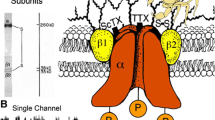
Abstract
Voltage-dependent sodium channels control the transient inward current responsible for the action potential in most excitable cells. Members of this multigene family have been cloned, sequenced, and functionally expressed from various tissues and species, and common features of their structure have clearly emerged. Site-directed mutagenesis coupled with in vitro expression has provided additional insight into the relationship between structure and function. Subtle differences between sodium channel isoforms are also important, and aspects of the regulation of sodium channel gene expression and the modulation of channel function are becoming topics of increasing importance. Finally, sodium channel mutations have been directly linked to human disease, yielding insight into both disease pathophysiology and normal channel function. After a brief discussion of previous work, this review will focus on recent advances in each of these areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed C. M. I., Ware D. H., Lee S. C., Patten C. D., Ferrermontiel A. V., Schinder A. F., McPherson J. D., Wagner-McPherson C. B., Wasmuth J. J., Evans G. A., and Montal M. (1992) Primary structure, chromosomal localization and functional expression of a voltage-gated sodium channel from human brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 8220–8224.
Aldrich R. W. (1986) Voltage-dependent gating of sodium channels: towards an integrated approach.Trends Neurosci. 9, 82–86.
Ambrose C., Cheng S., Fontaine B., Nadeau J. H., MacDonald M., and Gusella J. F. (1992) The α-subunit of the skeletal muscle sodium channel is encoded proximal to Tk-1 on mouse chromosome 11.Mammal. Gen. 3, 151–155.
Anderson C. S., MacKinnon R., Smith C., and Miller C. (1988) Charybdotoxin block of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Effects of channel gating, voltage, and ionic strength.J. Gen. Physiol. 91, 317–333.
Angelides K. J., Elmer L. W., Loftus D., and Elson E. (1988) Distribution and lateral mobility of voltage-dependent sodium channels in neurons.J. Cell. Biol. 106(6), 1911–1926.
Armstrong C. M. (1981) Sodium channels and gating currents.Physiol. Rev. 61, 644–683.
Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F., and Rojas E. (1973) Destruction of sodium conductance inactivation in squid axons perfused with pronase.J. Gen. Physiol. 62, 375–391.
Armstrong C. M. and Bezanilla F. (1973) Currents related to movement of the gating particles of the sodium channels.Nature (Lond.) 242, 459–461.
Armstrong C. M. and Bezanilla F. (1974) Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels.J. Gen. Physiol. 63, 533–552.
Armstrong C. M. and Bezanilla F. (1977) Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments.J. Gen. Physiol. 70, 567–590.
Atchison W. D., Luke V. S., Narahashi T., and Vogel S. M. (1986) Nerve membrane sodium channels as the target site of brevetoxins at neuromuscular junctions.Br. J. Pharmacol. 89(4), 731–738.
Auld V., Marshall J., Goldin A., Dowsett A., Catterall W., and Davidson, N. (1985) Cloning and characterization of the gene for the α-subunit of the mammalian voltage-gated sodium channel.J. Gen. Physiol. 86(2), 10a.
Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., and Dunn R. J. (1990) A neutral amino acid change in segment IIS4 dramatically alters the gating properties of the voltage-dependent sodium channel.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87(1), 323–327.
Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Marshall J., Dunn J. M., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., and Dunn R. J. (1988) A rat brain Na+ channel α-subunit with novel gating.Neuron 1, 449–461.
Backx P. H., Yue D. T., Lawrence J. H., Marban E., and Tomaselli G. F. (1992) Molecular localization of an ion-binding site within the pore of mammalian sodium channels.Science 257, 248–251.
Baker P. F. and Rubinson K. A. (1975) Chemical modification of crab nerves can make them insensitive to the local anesthetics tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin.Nature 257, 442–444.
Baker P. F. and Rubinson K. A. (1976) TTX-resistant action potentials in crab nerve after treatment with Meerwein’s reagent.J. Physiol. 266, 3–4P.
Balerna R., Ritchie J. M., and Strichartz G. R. (1975) Constitution and properties of axonal membranes of crustacean nerves.Biochemistry 14, 5500–5511.
Bambrick L. L. and Gordon T. (1988) Neural regulation of [3H]-saxitoxin binding site numbers in rat neonatal muscle.J. Physiol. 407, 263–274.
Bar-Sagi D. and Prives J. (1983) Tunicamycin inhibits the expression of surface sodium channels in cultured muscle cells.J. Cell. Physiol. 114, 77–81.
Bar-Sagi D. and Prives J. (1985) Negative modulation of sodium channels in cultured chick muscle cells by the channel activator batrachotoxin.J. Biol. Chem. 260(8), 4740–4744.
Barchi R. L. (1988) Probing the molecular structure of the voltage-dependent sodium channel.Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 455–495.
Barchi R. L. and Weigele J. B. (1979) Characteristics of saxitoxin binding to the sodium channel of sarcolemma isolated from rat skeletal muscle.J. Physiol. 295, 383–396.
Baumann A., Krah J. I., Mueller R., Mueller H. F., Seidel R., Kecskemethy N., Casal J., Ferrus A., and Pongs O. (1987) Molecular organization of the maternal effect region of the Shaker complex ofDrosophila characterization of an Ia channel transcript with homology to vertebrate sodium channel.EMBO J. 6(11), 3419–3430.
Beckh S. (1990) Differential expression of sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat peripheral nervous system and innervated tissues.FEBS Lett. 262(2), 317–322.
Beckh S., Noda M., Luebbert H., and Numa, S. (1989) Differential regulation of three sodium channel messenger RNA species in the rat central nervous system during development.EMBO J. 8(12), 3611–3616.
Behrens M. I., Oberhauser A., Bezanilla F., and Latorre R. (1989) Batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels from squid optic nerve in planar bilayers ion conduction and gating properties.J. Gen. Physiol. 93(1), 23–42.
Beneski C. A. and Catterall W. A. (1980) Covalent labeling of protein components of the sodium channel with a photoactivatable derivative of scorpion toxin.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 639–643.
Bennett P. B., Makita N., and George A. L. (1993) A molecular basis for gating mode transitions in human skeletal muscle sodium channels.FEBS Lett. 326, 21–24.
Berwald-Netter Y., Martin-Moutot N., Koulakoff A., and Couraud F. (1981) Na+ channel associated scorpion toxin receptor sites as probes for neuronal evolutionin vivo andin vitro.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 1245–1249.
Bessereau J. L., Fontaine B., and Changeux J. P. (1990) Denervation of mouse skeletal muscle differentially affects the expression of thejun andfos protooncogenes.New Biol. 2(4), 375–383.
Bishopric N. H. and Kedes L. (1991) Adrenergic regulation of the skeletal α-actin gene promoter during myocardial cell hypertrophy.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88(6), 2132–2136.
Bond J. M., Herman B., and Lemasters J. J. (1991) Protection by acidotic pH against anoxia/reoxygenation injury to rat neonatal cardiac myocytes.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 179(2), 798–803.
Boudier J. A., Berwald-Netter Y., Dellmann H. D., Boudier J. L., Couraud F., Koulakoff A., and Cau P. (1985) Ultrastructural visualization of Na+-channel associated [125I] α-scorpion toxin binding sites on fetal mouse nerve cells in culture.Dev. Brain Res. 352, 137–142.
Boudier, J. L., Letreut T., and Jover E. (1992) Autoradiographic localization of voltage-dependent sodium channels on the mouse neuromuscular junction using I-125-alpha scorpion toxin. 2. Sodium channel distribution on postsynaptic membranes.J. Neurosci. 12(2), 454–466.
Brodie C., Brody M., and Sampson S. R. (1989) Characterization of the relation between sodium channels and electrical activity in cultured rat skeletal myotubes: regulatory aspects.Brain Res. 488, 186–194.
Brodie C. and Sampson S. R. (1989) Characterization of thyroid hormone effects on sodium channel synthesis in cultured skeletal myotubes: role of Ca2+.Endocrinology 125(2), 842–849.
Brodie C. and Sampson S. R. (1990) Effects of ethanol on voltage-sensitive Na-channels in cultured skeletal muscle—up-regulation as a result of chronic treatment.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 255(3), 1195–1201.
Brodie C. and Sampson S. R. (1991) Verapamil regulation of Na-K pump levels in rat skeletal myotubes: role of spontaneous activity and Na channels.J. Neurosci. Res. 28, 229–235.
Brodwick M. S. and Eaton D. C. (1978) Sodium channel inactivation in squid axons is removed by high internal pH or tyrosine-specific reagents.Science 200, 1494–1496.
Brown G. B. (1988) Batrachotoxin a, window on the allosteric nature of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel.International Review Of Neurobiology (Smythies J. R. and Bradley R. J., eds.)29, 77–116.
Buja L. M. and Willerson J. T. (1991) Relationship of ischemic heart disease to sudden death.J. Forensic. Sci. 36(1), 25–33.
Burt J. M. and Spray D. C. (1989) Volatile anesthetics block intercellular communication between neonatal rat myocardial cells.Circ. Res. 65(3), 829–837.
Caffrey J. M., Brown A. M., and Schneider M. D. (1989) Ca2+ and Na+ currents in developing skeletal myoblasts are expressed in a sequential program: reversible suppression by transforming growth factor {ie420-1}, an inhibitor of the myogenic pathway.J. Neurosci. 9(10), 3443–3453.
Cannon S. C., Brown R. J., and Corey D. P. (1991) A sodium channel defect in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis: potassium-induced failure of inactivation.Neuron. 6(4), 619–626.
Cannon S. C. and Strittmatter S. M. (1993) Functional expression of sodium channel mutations identified in families with periodic paralysis.Neuron 10 (2), 317–326.
Catterall W. A. (1980) Neurotoxins that act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes.Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 20, 15–43.
Catterall W. A. (1986) Molecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels.Ann. Rev. Biochem. 55, 953–985.
Catterall W. A. (1988) Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels.Science 242, 50–61.
Catterall W. A. and Coppersmith J. (1981) Pharmacological properties of sodium channels in cultured rat heart cells.Mol. Pharmacol. 20(3), 533–542.
Chahine M., George A. L., Zhou M., Sun W., Barchi R., and Horn R. (1993) Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita destabilize inactivation.Neuron, in press.
Chatterjee T. K., Moy J. A., and Fisher R. A. (1991) Characterization and regulation of high affinity calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes.Endocrinology 128(6), 2731–2738.
Chen L.-Q., Chahine M., Kallen R. G., Barchi R. L., and Horn R. (1992) Chimeric study of sodium channels from rat skeletal and cardiac muscle.FEBS Lett. 309, 253–257.
Cohen S. A. and Barchi R. L. (1992a) Localization of epitopes for antibodies that differentially label sodium channels in skeletal muscle surface and t-tubular membranes.J. Memb. Biol. 128(3), 219–226.
Cohen S. A. and Barchi R. L. (1992b) Cardiac sodium channel structure and function.Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2(4), 133–140.
Cohen S. A. and Barchi R. L. (1992c) Probing the structure of sodium channel cytoplasmic domains. Submitted for publication.
Cohen S. A. and Levitt L. K. (1993) Partial characterization of the rH1 sodium channel protein from rat heart using subtype-specific antibodies.Circ. Res. 73, 735–742.
Coombs J., Scheuer T., Rossie S., and Catterall W. (1988) Evidence that cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation promotes inactivation in embryonic rat brain cells in primary culture.Biophys. J. 53, 542a.
Costa M. R. C., Casnellie J. E., and Catterall W. A. (1982) Selective phosphorylation of the α-subunit of the sodium channel by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase.J. Biol. Chem. 257(14), 7918–7921.
Costa M. R. C. and Catterall W. A. (1984a) Phosphorylation of the α-subunit of the sodium channel by protein kinase C.Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 4(3), 291–298.
Costa M. R. C. and Catterall W. A. (1984b) Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of the α-subunit of the sodium channel in synaptic nerve ending particles.J. Biol. Chem. 259(13), 8210–8218.
Couraud F., Martin-Moutot N., Koulakoff A., and Berwald-Netter, Y. (1986) Neurotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in neurons developing in vivo and in vitro.J. Neurosci. 6, 192–198.
Cribbs L. L., Satin J., Fozzard H. A., and Rogart R. B. (1990) Functional expression of the rat heart-I Na+ channel isoform-demonstration of properties characteristic of native cardiac Na+ channels.FEBS Lett. 275(1–2), 195–200.
Cruz L. J., Gray W. R., Olivera B. M., Zeikus R. D., Kerr L., Yoshikami D., and Moczydlowski E. (1985)Conus geographus toxins that discriminate between neuronal and muscle sodium channels.J. Biol. Chem. 260(16), 9280–9288.
Cummings T. R., Zhou J., Sigworth F. J., Ukomada C., Sephan M., Ptácek L. J., and Agnew W. S. (1993) Functional consequences of a Na+ channel mutation causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis.Neuron 10, 667–678.
Dargent B. and Couraud F. (1990) Down-regulation of voltage-dependent sodium channels initiated by sodium influx in developing neurons.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 5907–5911.
Dascal N. and Lotan I. (1991) Activation of protein kinase C alters voltage dependence of a Na+ channel.Neuron 6, 165–175.
Dascal N., Snutch T. P., Lubbert H., Davidson N., and Lester H. A. (1986) Expression and modulation of voltage-gated calcium channels after RNA injection inXenopus oocytes.Science 231, 1147–1150.
Dreyfus P., Rieger F., Murawsky M., Garcia L., Lombet A., Fosset M., Pauron D., Barhanin J., and Lazdunski M. (1986) The voltage-dependent sodium channel is co-localized with the acetylcholine receptor at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 139(1), 196–201.
Dunnmon P. M., Iwaki K., Henderson S. A., Sen A., and Chien K. R. (1990) Phorbol esters induce immediate-early genes and activate cardiac gene transcription in neonatal rat myocardial cells.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 22(8), 901–910.
Eaton D. C., Brodwick M. S., Oxford G. S., and Rudy B. (1978) Arginine-specific reagents remove sodium channel inactivation.Nature (Lond.) 271, 473–476.
Ebers G. C., George A. L., Barchi R. L., Ting-Passador S. S., Kallen R. G., Lathrop G. M., Beckmann J. S., Hahn A. F., Brown W. F., Campbell R. D., and Hudson A. J. (1991) Paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis are linked to the adult muscle sodium channel gene.Ann. Neurol. 30(6), 810–816.
Elmer L. W., Obrien B. J., Nutter T. J., and Angelides K. J. (1985) Physicochemical characterization of the α-peptide of the sodium channel from rat brain.Biochemistry 24(27), 8128–8137.
Emerick M. C. and Agnew W. S. (1989) Identification of phosphorylation sites for cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase on the voltage-sensitive sodium channel fromElectrophorus-electricus.Biochemistry 28(21), 8367–8380.
Estacion, M. (1990) Inhibition of voltage-dependent Na+ current in cell-fusion hybrids containing activatedc-Ha-ras.J. Membrane Biol. 113, 169–175.
Flamm R. E., Birnberg N. C., and Kaczmarek L. K. (1990) Transfection of activatedras into an excitable cell line (AtT-20) alters tetrodotoxin sensitivity of voltage-dependent sodium current.Pflugers Arch. 416, 120–125.
Fontaine B., Khurana T. S., Hoffman E. P., Bruns G. A., Haines J. L., Trofatter J. A., Hanson M. P., Rich J., McFarlane H., Yasek D. M., Romano D., Gusella J., and Brown R. (1990) Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and the adult muscle sodium channel α-subunit gene.Science 250, 1000–1002.
Fontecilla-Camps J. C., Habersetzer R. C., and Rochat H. (1988) Orthorhombic crystals and 3-dimensional structure of the potent toxin II from the scorpionAndroctonus Australis Hector.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 7443–7447.
Foster K. A., McDermott P. J., and Robishaw J. D. (1990) Expression of G proteins in rat cardiac myocotes: effect of KC1 depolarization.Am. J. Physiol. 259(2 Pt 2), h431–441.
Garber S. S. and Miller C. (1987) Single Na+ channels activated by veratridine and batrachotoxin.J. Gen. Physiol. 89(3), 459–480.
Gautron S., Dossantos G., Pintohenrique D., Koulakoff A., Gros F., and Berwaldnetter Y. (1992) The glial voltage-gated sodium channel: cell-specific and tissue-specific messenger RNA expression.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89(15), 7272–7276.
Gellens M. E., George A. L., Jr., Chen L., Chahine M., Horn R., Barchi R. L., and Kallen R. G. (1992) Primary structure and functional expression of the human cardiac voltage-sensitive sodium channel.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 554–558.
George A. F., Jr., Iyer G. S., Kleinfield R., Kallen R. G., and Barchi R. L. (1993) Genomic organization of the human skeletal muscle sodium channel gene.Genomics 15, 598–606.
George A. L., Jr, Knittle T. J., and Tamkun M. M. (1992a) Molecular cloning of an atypical voltage-gated sodium channel expressed in human heart and uterus: evidence for a distinct gene family.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89(11), 4893–4897.
George A. L., Jr., Komisarof J., Kallen R. G., and Barchi R. L. (1992b) Primary structure of the adult human skeletal muscle voltage-dependent sodium channel.Ann. Neurol. 31, 131–137.
George A. L., Jr., Ledbetter D. H., Kallen R. G., and Barchi R. L. (1991) Assignment of a human skeletal muscle sodium channel α-subunit gene (SCN4A) to 17q23. 1-25.3.Genomics 9, 555–556.
Gilly W. F., Lucero M. T., and Horrigan F. T. (1990) Control of the spatial distribution of sodium channels in giant fiber lobe neurons of the squid.Neuron 5(5), 663–674.
Ginty D. D., Fanger G. R., Wagner J. A., and Maue R. A. (1992) The activity of cAMP-dependent protein kinase is required at a posttranslational level for induction of voltage-dependent sodium channels by peptide growth factors in PC12 cells.J. Cell Biol. 116, 1465–1473.
Gonoi T., Ashida K., Feller D., Schmidt J., Fujiwara M., and Catterall W. A. (1986) Mechanism of action of a polypeptide neurotoxin from the coralGoniopora on sodium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells.Mol. Pharmacol. 29(4), 347–354.
Gordon R. D., Fieles W. E., Schotland D. L., Hogue A. R., and Barchi R. L. (1987) Topographical localization of the C-terminal region of the voltage-dependent sodium channel fromElectrophorus electricus using antibodies raised against a synthetic peptide.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84(1), 308–312.
Gordon R. D., Li Y., Fieles W. E., Schotland D. L., and Barchi R. L. (1988) Topological localization of a segment of the eel voltage-dependent sodium channel primary sequence aa 927–938 that discriminates between models of tertiary structure.J. Neurosci. 8(10), 3742–3749.
Gordon D., Merrick D., Wollner D. A., and Catterall W. A. (1988) Biochemical properties of sodium channels in a wide range of excitable tissues studied with site directed antibodies.Biochemistry 27, 7032–7038.
Greenblatt R. E., Blatt Y., and Montal M. (1985) The structure of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel.FEBS Lett. 193, 125–134.
Gunderson C. B., Miledi R., and Parker I. (1984a) Messenger RNA from human brain induces drug- and voltage-operated channels inXenopus oocytes.Nature 308, 421–424.
Gunderson C. B., Miledi R., and Parker I. (1984b) Properties of human brain glycine receptors expressed inXenopus oocytes.Proc. R. Soc. London (Series B)221, 235–244.
Guy H. R. and Conti F. (1990) Pursuing the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channel.Trends Neurosci. 13, 201–206.
Guy H. R. and Seetharamulu P. (1986) Molecular model of the action potential sodium channel.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83(2), 508–512.
Han J., Lu C. M., Brown G. B., and Rado T. A. (1991) Direct amplification of a single dissected chromosome polymerase chain reaction: A human brain sodium channel on chromosome 2q22-q23.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 335–339.
Harris J. B. and Thesleff S. (1971) Studies on tetrodotoxin resistant action potentials in denerated skeletal muscle.Acta. Physiol. Scand. 83, 382–388.
Hartmann H. A., Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Taglialatela M., Joho R. H., and Brown A. M. (1991) Exchange of conduction pathways between two related K+ channels.Science 251, 942–944.
Heginbotham L. and MacKinnon R. (1992) The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels.Neuron 8, 483–491.
Heinemann S. H., Terlau H., Stühmer W., Imoto K., and Numa S. (1992) Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations.NAT 356, 441–443.
Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., and Strichartz G. R. (1973) The binding of labeled saxitoxin to the sodium channels in nerve membranes.J. Physiol. 235, 783–804.
Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., and Strichartz G. R. (1974) Evidence that tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin act at a metal cation binding site in the sodium channels of nerve membrane.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71, 3936–3940.
Henrich C. J. and Simpson P. C. (1988) Differential acute and chronic response of protein kinase C in cultured neonatal rat heart myocytes to alpha 1-adrenergic and phorbol ester stimulation.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 20(12), 1081–1085.
Hille B. (1968) Charges and potentials at the nerve surface: divalent ions and pH.J. Gen. Physiol. 51, 221–236.
Hille B. (1971) The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve.J. Gen. Physiol. 58, 599–619.
Hille B. (1972) The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve.J. Gen. Physiol. 59, 637–658.
Hille B. (1977) Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for drug-receptor reaction.J. Gen. Physiol. 69, 497–515.
Hille B. (1984)Ionic Channels of Excitable Membanes. Sinauer Assoc., Inc., Sunderland, MA.
Hirono C., Yanagishi S., O'Hara R., Hisanaga Y., Nakayama T., and Sugiyama H. (1985) Characterization of mRNA responsible for induction of functional sodium channels inXenopus oocytes.Brain Res. 359, 57–61.
Hodgkin A. L. and Huxley A. F. (1952) The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon ofLoligo.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 116, 473–496.
Hondeghem L. M. and Katzung B. G. (1987) Antiarrhythmic agents: the modulated receptor mechanism of action of sodium channel-blocking drugs.Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 24, 387–423.
Horn R. (1984) Gating of channels in nerve and muscle: a stochastic approach, inIon Channels: Molecular and Physiological Aspects. Academic, New York, pp. 53–97.
Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., and Aldrich R. W. (1990) Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation.Science 250, 533–538.
Isom L. L., Dejongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F. X., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., and Catterall W. A. (1992) Primary structure and functional expression of the {ie423-1} of the rat brain sodium channel.Science 256, 839–842.
Ito H., Miller S. C., Billingham M. E., Akimoto H., Torti S. V., Wade R., Gahlmann R., Lyons G., Kedes L., and Torti F. M. (1990) Doxorubicin selectively inhibits muscle gene expression in cardiac muscle cellsin vivo andin vitro.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 87(11), 4275–4279.
Joho R. H., Moorman J. R., Van Dongen A. M., Kirsch G. E., Silberberg H., Schuster G., and Brown A. M. (1990) Toxin and kinetic profile of rat brain type III sodium channels expressed inXenopus oocytes.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 7(2), 105–113.
Joho R. H., Moorman J. R., Van Dongen A. M. J., Kirsch G. E., Silberberg H., Schuster G., and Brown A. M. (1988) Cloning and expression of the rat brain type III sodium channel gene.Cetus Upjohn UCLA Symposium on Molecular Biology Of The Cardiovascular System. Keystone, CO.
Jover E., Massacrier A., Cau P., Martin M. F., and Couraud F. (1988) The correlation between Na+ channel subunits and scorpion toxin-binding sites.J. Biol. Chem. 263, 1542–1548.
Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Yang, J., Chen L. Q., Rogart R. B., and Barchi R. L. (1990) Primary structure and expression of a sodium channel characteristic of denervated and immature rat skeletal muscle.Neuron 4(2), 233–242.
Kalman D., Wong B., Horvai A., Cline M., and O'Lague P. (1990) Nerve growth factor acts through cAMP-dependent protein kinase to increase the number of sodium channels in PC12 cells.Neuron 2, 355–366.
Kamb A., Iverson L. E., and Tanouye M. A. (1987) Molecular characterization of Shaker, aDrosophila gene that encodes a potassium channel.Cell 50(3) 405–413.
Kamb A., Tseng-Crank J. and Tanouye M. A. (1988) Multiple products of theDrosophila Shaker gene may contribute to potassium channel diversity.Neuron 1, 421.
Kayano T., Noda M., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., and Numa S. (1988) Primary structure of rat brain sodium channel III deduced from the cDNA sequence.FEBS Lett. 228(1), 187–194.
Kirsch G. E., Skattebol A., Possani L. D., and Brown A. M. (1989) Modification of Na channel gating by α-scorpion toxin fromTityus serrulatus.J. Gen. Physiol. 93(1), 67–83.
Klocke R., Kaupmann K., George A. L., Barchi R. L., and Jockusch H. (1992) Chromosomal mapping of muscle-expressed sodium channel genes in the mouse.Mouse Genome 90, 433–435.
Koch M. C., Ricker K., Otto M., Grimm T., Hoffman E., Rudel R., Bende K., Zoll B., Harper P., and Lehmann-Horn, F. (1991) Confirmation of linkage of hyperkalmeic periodic paralysis to chromosome 17.J. Med. Genet. 28, 583–586.
Komuro I., Kaida T., Shibazaki Y., Kurabayashi M., Katoh Y., Hoh E., Takaku F., and Yazaki, Y. (1990) Stretching cardiac myocytes stimulates protooncogene expression.J. Biol. Chem. 265(7), 3595–3598.
Kontis K. J. and Goldin A. L. (1993) Site-directed mutagenesis of the putative pore region of the rat IIA sodium channel.Mol. Pharmacol. 43, 635–644.
Kosower E. M. (1985) A structural and dynamic molecular model for the sodium channel ofElectrophorus electricus.FEBS Lett. 182, 234–242.
Krafte D. S., Goldin A. L., Auld V. J., Dunn R. J., Davidson N., and Lester H. A. (1990) Inactivation of cloned Na channels expressed inXenopus oocytes.J. Gen. Physiol. 96(4), 689–706.
Krafte D. S., Volberg W. A., Dillon K., and Ezrin A. M. (1991) Expression of cardiac Na channels with appropriate physiological and pharmacological properties inXenopus oocytes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88(10), 4071–4074.
Kraner S. D., Chong J. A., Tsay H.-J., and Mandel G. (1992) Silencing the type II sodium channel gene: a model for neural-specific gene regulation.Neuron 9, 37–44.
Kraner S., Yang J., and Barchi R. (1989) Structural inferences for the native skeletal muscle sodium channel as derived from patterns of endogenous proteolysis.J. Biol. Chem. 264(22), 13,273–13,280.
Lehmann-Horn F., Kuther G., Ricker K., Grafe P., Ballanyi K., and Rüdel R. (1987a) Adynamia episodica hereditaria with myotonia: a nonactivating sodium current and the effect of extracellular pH.Muscle Nerve 10, 363–374.
Lehmann-Horn F., Rüdel R., and Ricker K. (1987b) Membrane defects in paramyotonia congenita (Eulenburg).Muscle Nerve 10, 633–641.
Levine M. and Manley J. L. (1989) Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters.Cell 59(3), 405–408.
Li M., West J. W., Lai Y., Scheuer T., and Catterall W. A. (1992) Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation.Neuron 8, 1151–1159.
Liman E. R., Hess P., Weaver F., and Koren G. (1991) Voltage-sensing residues in the S4 region of a mammalian K+ channel.Nature 353, 752–756.
Litt M., Luty J., Kwak M., Allen L., Magenis R. E., and Mandel G. (1989) Localization of a human brain sodium channel gene SCN2A to chromosome 2.Genomics 5(2), 204–208.
Lloyd T. R. and Marvin W. J., Jr. (1990) Sympathetic innervation improves the contractile performance of neonatal cardiac ventricular myocytes in culture.J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 22(3), 333–342.
Logothetis D. E., Movahedi S., Satler C., Lindpaintner K., and Nada, G. B. (1992) Incremental reductions of positive charge within the S4 region of a voltagegated K+ channel result in corresponding decreases in gating charge.Neuron 8, 531–540.
Lopez G. A., Jan Y. N., and Jan L. Y. (1991) Hydrophobic substitution mutations in the S4-sequence alter voltage-dependent gating in Shaker K+-channels.Neuron 7(2), 327–336.
MacKinnon R. and Miller C. (1989) Mutant potassium channels with altered binding of charybdotoxin, a pore0blocking peptide inhibitor.Science 245, 1382–1385.
MacKinnon R. and Yellen G. (1990) Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels.Science 250, 276–279.
Makita N., Bennett P. A., and George A. L. (1993) Voltage-gated Na+ channel beta1 subunit mRNA expressed in adult human skeletal muscle, heart and brain is encoded by a single gene.J. Biol. Chem., in press.
Malo D., Schurr E., Dorfman J., Canfield V., Levenson R., and Gros P. (1991) Three brain sodium channel α-subunit genes are clustered on the proximal segment of mouse chromosome-2.Genomics 10(3), 666–672.
Mandel G., Cooperman S. S., Maue R. A., Goodman R. H., and Brehm P. (1988) Selective induction of brain type II Na+ channels by nerve growth factor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85(3), 924–928.
Matsuda J. J., Lee H., and Shibata E. F. (1992) Enhancement of rabbit cardiac sodium channels by β-adrenergic stimulation.Circulation Res. 70(1), 199–207.
Maue R. A., Kraner S. D., Goodman R. H., and Mandel G. (1990) Neuron specific expression of the rat brain type II sodium channel gene is directed by upstream regulatory elements.Neuron 4(2), 223–231.
McClatchey A. I., McKenna-Yasek D., Cros D., Worthen H. G., Kuncl R. W., De Silva S. M., Cornblath D. R., Gusella J. F., and Brown R. H. (1992) Novel mutations in families with unusual and variable disorders of the skeletal muscle sodium channel.Nature Genetics 2, 148–152.
McClatchey A. I., Cannon S. C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., and Gusella J. F. (1993) The cloning and expression of a sodium channel beta-1-subunit cDNA from human brain.Hum. Mol. Genet. 2, 745–749.
Messner D. J. and Catterall W. A. (1985) The sodium channel from rat brain. Separation and characterization of subunits.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 10,597–10,604.
Meves H. and Nagy K. (1989) Multiple conductance states of the sodium channel and of other ion channels.Biochim. Biophs. Acta. 988(1), 99–106.
Meves H., Simard J. M., and Watt D. D. (1985) Interactions of scorpion toxins with the sodium channel, inAnnals of The New York Academy of Sciences (Kao C. Y. and Levinson S. R., eds.),5, 897–966.
Moorman J. R., Kirsch G. E., Lacerda A. E., and Brown A. M. (1989) Angiotensin II modulates cardiac Na+ channels in neonatal rat.Circ. Res. 65(6), 1804–1809.
Moorman J. R., Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M., and Joho R. H. (1990) Changes in sodium channel gating produced by point mutations in a cytoplasmic linker.Science 250, 688–690.
Mori N., Schoenherr C., Vandenbergh D. J., and Anderson D. J. (1992) A common silencer element in the SCG10 and type II sodium channel genes binds a factor present in nonneuronal cells but not in neuronal cells.Neuron 9, 45–54.
Nilius B. (1988) Modal gating behavior of cardiac sodium channels in cell-free membrane patches.Biophys. J. 53(6), 857–862.
Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., and Numa S. (1986a) Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain.Nature 320(6058), 188–192.
Noda M., Ikeda T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Takahashi T., Kuno M., and Numa S. (1986b) Expression of functional sodium channels from cloned cDNA.Nature 322(6082), 826–828.
Noda M., Shimizu S., Tanabe T., Takai T., Kayano T., Ikeda T., Takahashi H., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Raftery M. A., Hirose T., Inayama S., Hayashida H., Miyata T., and Numa S. (1984) Primary structure ofElectrophorus-electricus sodium channel deduced from complementary DNA sequence.Nature 312(5990), 121–127.
Noda M., Suzuki H., Numa S., and Stühmer W. (1989) A single point mutation confers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin insensitivity on the sodium channel II.FEBS Lett. 259(1), 213–216.
Numann R., Catterall W. A., and Scheuer T. (1991) Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C phosphorylation.Science 254, 115–118.
Offord J. and Catterall W. A. (1989) Electrical activity, cAMP, and cytosolic calcium regulate mRNA encoding sodium channel α-subunits in rat muscle cells.Neuron 2, 1447–1452.
Orlowski J. and Lingrel J. B. (1990) Thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones regulate the expression of multiple Na, K-ATPase genes in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes.J. Biol. Chem. 265(6), 3462–3470.
Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., and Narahashi T. (1978) Removal of sodium channel inactivation in squid giant axons by N-bromoacetamide.J. Gen Physiol. 71, 227–247.
Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., and Jan L. Y. (1987) Cloning of genomic and complementary DNA from Shaker, a putative potassium channel gene fromDrosophila.Science 237(4816), 749–753.
Papazian D. M., Timpe L. C., Jan Y. N., and Jan L. Y. (1991) Alteration of voltage-dependence of Shaker potassium channel by mutations in the S4 sequence.Nature 349, 305–310.
Pappone P. A. (1980) Voltage-clamp experiments in normal and denervated mammalian skeletal muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 306, 377–410.
Parker T. G., Chow K. L., Schwartz R. J., and Schneider M. D. (1990) Differential regulation of skeletal alpha-actin transcription in cardiac muscle by two fibroblast growth factors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87(18), 7066–7070.
Patlak J. B. and Ortiz M. (1986) Two modes of gating during late Na+ channel currents in frog sartorius muscle.J. Gen. Physiol. 87, 305–326.
Patlak J. B. and Ortiz M. (1989) Kinetic diversity of sodium channel bursts in frog skeletal muscle.J. Gen. Physiol. 94(2), 279–302.
Patton D. E., West J. W., Catterall W. A., and Goldin A. L. (1992a) Amino acids residues required for fast sodium channel inactivation. Charge neutralizations and deletions in the III–IV linker.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10,905–10,909.
Patton D. E., West J. W., Catterall W. A., and Goldin A. L. (1992b) The sodium channel III–IV linker functions as an amino terminal inactivation particle in the MK1 potassium channel.Soc. Neurosci. Abs. 18, 922.
Poli M. A., Mende T. J., and Baden D. G. (1986) Brevetoxins, unique activators of voltage-sensitive sodium channels, bind to specific sites in rat brain synaptosomes.Mol. Pharmacol. 30(2), 129–135.
Pollock J. D., Krempin M., and Rudy B. (1990) Differential effects of NGF, EGF, cAMP, and dexamethasone on neurite outgrowth and sodium channel expression in PC12 cells.J. Neurosci. 10(8), 2626–2637.
Pongs O., Kecskemethy N., Muller R., Krah-Hentgens I., Baumann A., Kiltz H. H., Canal I., Llamazares S., and Ferrus A. (1988) Shaker encodes a family of putative potassium channel proteins in the nervous system ofDrosophila.EMBO J. 7, 1087–1096.
Ptácek L. J., George A. L., Jr, Barchi R. L., Griggs R. C., Riggs J. E., Robertson M., and Leppert M. F. (1992a) Mutations in an S4 segment of the adult skeletal muscle sodium channel cause paramyotonia congenita.Neuron 8(5), 891–897.
Ptácek L. J., Tawil R., Griggs R. C., Storvick D., and Leppert M. (1992b) Linkage of atypical myotoniacongenita to a sodium channel locus.Neurology 42(2), 431–433.
Ptácek L. J., George A. L., Griggs R. C., Tawil R., Kallen R. G., Barchi R. L., Robertson M., and Leppert M. (1991a) Identification of a mutation in the gene causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis.Cell 67, 1021–1027.
Ptácek L. F., Tyler F., Trimmer J. S., Agnew W. S., and Leppert M. (1991b) Analysis in a large hyperkalemic periodic paralysis pedigree supports tight linkage to a sodium channel locus.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 49, 378–382.
Ptácek L. J., Gouw L, Kwiecinski H., McManis P., Mendell J. R., Barohn R. J., George A. L., Barch, R. L., Robertson M., and Leppert M. F. (1993) Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita and periodic paralysis. Submitted for publication.
Reber B. F. X. and Catterall W. A. (1987) Hydrophobic properties of the {ie425-1} and {ie425-2} of the rat brain sodium channel.J. Biol. Chem. 262, 11,369–11,374.
Recio-Pinto E., Thornhill W. B., Duch D. S., Levinson S. r., and Urban B. W. (1990) Neuraminidase treatment modifies the function of electroplax sodium channels in planar lipid bilayers.Neuron 5(5), 675–684.
Redfern P. and Thesleff S. (1971) Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. II Action of tetrodotoxin.Acta. Physiol. Scand. 82, 70–78.
Reed J. K. and Raftery M. A. (1976) Properties of the t tetrodotoxin binding component in plasma membranes isolated fromElectrophorus electricus.Biochemistry 15, 944–953.
Renaud J.-F., Kazazoglou T., Lombat A., Chicheportiche R., Jaimovich E., Romey G., and Lazdunski M. (1983) The Na+ channel in mammalian cardiac cells—two kinds of tetrodoxin receptors in rat heart membranes.J. Biol. Chem. 258(14), 8799–8805.
Ricker K., Camacho L., Grafe P., Lehmann-Horn F., and Rudel R. (1989) Adynamia episodica hereditaria: what causes the weakness?Muscle Nerve 12, 883–891.
Roberts R. H. and Barchi R. L. (1987) The voltage-sensitive sodium channel from rabbit skeletal muscle: chemical characterization of subunits.J. Biol. Chem. 262(5), 2298–2303.
Rogart R. B., Regan L. J., Dziekan L. C., and Galper, J. B. (1983) Identification of two sodium channel subtypes in chick heart and brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 1106–1110.
Rogart R. B., Cribbs L. L., Muglia L. K., Kephart D. D., and Kaiser M. W. (1989) Molecular cloning of a putative tetrodotoxin-resistant rat heart Na+ channel isoform.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86(20), 8170–8174.
Rogart R. B. and Regan L. F. (1985) Two subtypes of sodium channel with tetrodotoxin sensitivity and insensitivity detected in denervated mammalian skeletal muscle.Brain Res. 329, 314–318.
Rojas E. and Armstrong C. M. (1971) Sodium conductance activation without inactivation in pronase-perfused axons.Nature (Lond.) 229, 177–178.
Rojas E. and Rudy B. (1976) Destruction of the sodium conductance inactivation by a specific protease in perfused nerve fibres fromLoligo.J. Physiol. 262, 501–531.
Rojas C., Wang J., Schwartz L., Hoffman E., Powell B., and Brown R. (1991) A Met to Val mutation in the skeletal muscle Na+ channel α-subunit in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis.Nature 254, 387–389.
Rossie S. and Catterall W. A. (1989) Phosphorylation of the α-subunit of rat brain sodium channels by cAMP-dependent protein kinase at a new site containing Ser686 and Ser687.J. Biol. Chem. 264(24), 14,220–14,224.
Rossie S., Gordon D., and Catterall W. A. (1987) Identification of an intracellular domain of the sodium channel having multiple cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation sites.J. Biol. Chem. 262(36), 17,530–17,535.
Rudel R., Lehmann-Horn F., Ricker K., and Kuther G. (1984) Hypokalemic periodic paralysis:in vitro investigation of muscle fiber membrane parameters.Muscle and Nerve 7, 110–120.
Rudolph J. A., Spier S. J., Byrns G., Rojas C. V., Bernoco D., and Hoffman E. P. (1992) Periodic paralysis in Quarter Horses: a sodium channel mutation disseminated by selective breeding.Nat. Gen. 2, 144–147.
Rudy B., Kirschenbaum B., Rukenstein A., and Greene L. A. (1987) Nerve growth factor increases the number of functional Na channels and induces TTX-resistant Na channels in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells.J. Neurosci. 7(6), 1613–1635.
Salgado V. L., Yeh J. Z., and Narahashi T. (1985) Voltage-dependent removal of sodium inactivation by N-bromoacetamide and pronase.Biophys. J. 47, 567–571.
Salkoff L., Baker K., Butler A., Covarrubia M., Pak M. D., and Wei A. (1992) An essential ‘set’ of K+ channels conserved in flies, mice and humans.Trends Neurosci. 15, 161–166.
Salkoff L., Butler A., Wei A., Scavarda A., Giffen K., Ifune C., Goodman R., and Mandel G. (1987) Genomic organization and deduced amino acid sequence of a putative sodium channel gene inDrosophila.Science 237(4816), 744–749.
Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., and Kedes L. (1990) Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1.Genes Dev. 4(10), 1811–1822.
Satin J., Kyle J. W., Chen M., Bell P., Cribbs L. L., Fozzard H. A., and Rogart R. B. (1992) A mutant of TTX-resistant cardiac sodium channels with X-sensitive properties.Science 256, 1202–1205.
Sato C. and Matsumoto G. (1992b) Proposed tertiary structure of the sodium channel.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 186, 61–68.
Schaller K. L., Krzemien D. M., McKenna N. M., and Caldwell J. H. (1992) Alternatively spliced sodium channel transcripts in brain and muscle.J. Neurosci. 12(4), 1370–1381.
Scheuer T., McHugh L., Tejedor F., and Catterall W. (1988) Functional properties of neuraminidasetreated rat brain sodium.Biophys. J. 53, 541a.
Schmidt J., Rossie S., and Catterall W. A. (1985) A large intracellular pool of inactive sodium channel α-subunits in developing rat brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82(14), 4847–4851.
Schmidt J. W. and Catterall W. A. (1986) Biosynthesis and processing of the α-subunit of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel in rat brain neurons.Cell 46(3), 437–446.
Schmidt J. W. and Catterall W. A. (1987). Palmitylation, sulfation, and glycosylation of the α-subunit of the sodium channel. Role of post-translational modifications in channel assembly.J. Biol. Chem. 262(28), 13,713–13,723.
Schreibmayer W., Dascal N., Lotan I., Wallner M., and Weigl L. (1991) Molecular mechanism of protein kinase C modulation of sodium channel α-subunits expressed inXenopus oocytes.FEBS Lett. 291(2), 341–344.
Schubert B., Van Dongen A. M., Kirsch G. E., and Brown A. M. (1989) β-Adrenergic inhibition of cardiac sodium channels by dual G-protein pathways.Science 245, 516–519.
Schwarz T., Tempel B., Papazian D., Jan Y., and Jan L. (1988) Multiple potassium channel components are produced by alternative splicing at the Shaker locus inDrosophila.Nature 331, 137–142.
Seelig T. L. and Kendig J. J. (1982) Cyclic nucleotide modulation of sodium and potassium currents in the isolated node of Ranvier.Brain Res. 245, 144–147.
Sheng Z.-H., Barchi R. L., and Kallen R. G. (1993) Multiple positive and negative 5′-flanking segments control rat skeletal muscle voltage-sensitive sodium channel subtype 2 (SkM2) expression in skeletal muscle.DNA Cell Biol., in press.
Sherman S., Chrivia W., and Catterall W. (1985) Cyclic adenosine-3′,5′-monophosphate and cytosolic calcium exert opposing effects on biosynthesis of tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in rat muscle.J. Neurosci. 5, 1570–1576.
Shrager P. and Profera C. (1973) Inhibition of the receptor for tetrodotoxin in nerve membranes by reagents modifying carboxyl groups.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 318(1), 141–146.
Sigel E. (1987) Properties of single sodium channels translated byXenopus oocytes after injection with messenger RNA.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 386, 73–90.
Sigworth F. J. and Neher E. (1980) Single Na+ channel currents observed in cultured rat muscle cells.Nature 287, 447–449.
Sills M. N., Xu Y. C., Baracchini E., Goodman R. H., Cooperman S. S., Mandel G., and Chien K. R. (1989) Expression of diverse Na+ channel messenger RNAs in rat myocardium. Evidence for a cardiac-specific Na+ channel.J. Clin. Invest. 84(1), 331–336.
Smith R. D. and Goldin A. L. (1992) Protein kinase-A phosphorylation enhances sodium channel currents inXenopus oocytes.Am. J. Physiol. 263(3 Part 1), C660-C666.
Sorbera L. A. and Morad M. (1990) Atrionatriuretic peptide transforms cardiac sodium channels into calcium-conducting channels.Science 247(4945), 73.
Sorbera L. A. and Morad M. (1991) Modulation of cardiac sodium channels by cAMP receptors on the myocyte surface.Science 253(5025), 1286–1289.
Stühmer W., Conti F., Stocker M., Pongs O., and Heinemann S. H. (1991) Gating currents of inactivating and non-inactivating potassium channels expressed inXenopus oocytes.Pflugers Arch. 418(4), 423–429.
Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., and Numa S. (1989) Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel.Nature 339, 597–603.
Stühmer W., Methfessel C., Sakmann B., Noda M., and Numa S. (1987) Patch clamp characterization of sodium channels expressed from rat brain cDNA.Eur. Biophys. J. 14(3), 131–138.
Sumikawa K., Parker L., and Miledi R. (1984) Partial purification and functional expression of brain mRNAs coding for neurotransmitter receptors and voltage-operated channels.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 7994–7998.
Sutkowski E. M. and Catterall W. A. (1990) Beta-1 subunits of sodium channels studies with subunit-specific antibodies.J. Biol. Chem. 265(21), 12,393–12,399.
Suzuki H., Beckh S., Kubo H., Yahagi N., Ishida H., Kayano T., Noda M., and Numa S. (1988) Functional expression of cloned complementary DNA encoding sodium channel III.FEBS Lett. 228(1), 195–200.
Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., and Numa S. (1987) Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle.Nature 328, 313–318.
Tanaka J. C., Doyle D. D., and Barr J. (1984) Sodium channels in vertebrate hearts three types of saxitoxin binding sites in hearts.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 775, 203–214.
Taouis M., Sheldon R. S., and Duff H. J. (1991a) Upregulation of the rat cardiac sodium channel by in vivo treatment with a class I antiarrhythmic drug.J. Clin. Invest. 88(2), 375–378.
Taouis M., Sheldon R. S., Hill R. J., and Duff H. J. (1991b) Cyclic AMP-dependent regulation of the number of [3H]-batrachotoxin benzoate binding sites on rat cardiac myocytes.J. Biol. Chem. 266(16), 10,300–10,304.
Tejedor F. J. and Catterall W. A. (1988) Site of covalent attachment of α-scorpion toxin derivatives in domain I of the sodium channel α-subunit.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 8742–8746.
Terlau J., Heinemann S. H., Stühmer W., Pusch M., Conti F., Imoto K., and Numa S. (1991) Mapping the site of block by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin of sodium channel II.FEBS Lett. 293(12), 93–96.
Thomsen W. J. and Catterall W. A. (1989) Localization of the receptor site for α scorpion toxins by antibody mapping: implications for sodium channel topology.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86(24), 10,161–10,165.
Thornhill W. B. and Levinson S. R. (1987) Post-translational processing of the voltage-regulated sodium channel from eel electroplax. Symposium on molecular biology of intracellular protein sorting and organelle assembly held at the 16th annual meeting ofThe UCLA Symposia On Molecular And Cellular Biology, Los Angeles, CA.
Trimmer J. S., Cooperman S. S., Tomiko S. A., Zhou J. Y., Crean S. M., Boyle M. B., Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Barchi R. L., and Sigworth F. J. (1989) Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel.Neuron 3(1), 33–49.
Tytgat J., and Hess P. (1992) Evidence for cooperative interactions in potassium channel gating.Nature 359, 420–423.
Vassilev P., Scheuer T., and Catterall W. A. (1989) Inhibition of inactivation of single sodium channels by a site-directed antibody.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 8147–8151.
Vassilev P. M., Scheuer T., and Catterall W. A. (1988) Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation.Science 241, 1658–1661.
Waechter C. J., Schmidt J. W., and Catterall W. A. (1983) Glycosylation is required for maintenance of functional sodium channels in neuro blastoma cells.J. Biol. Chem. 258(8), 5117–5123.
Warashina A., Ogura T., and Fujita S. (1988) Binding properties of sea anemone toxins to sodium channels in the crayfish giant axon.Com. Biochem. Physiol. C. Comp. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 90(2), 351–360.
Weigele J. and Barchi R. (1982) Functional reconstitution of the purified sodium channel from rat sarcolemma.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 3651–3655.
West J. W., Numann R., Murphy B. J., Scheuer T., and Catterall W. A. (1991) A phosphorylation site in the Na+ channel required for modulation by protein kinase C.Science 254, 866–868.
West J. W., Patton D. E., Scheuer T., Wang Y., Goldin A. L., and Catterall W. A. (1992) A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na+ channel inactivation.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10,910–10,914.
White M. M., Chen L., Kleinfield R., Kallen R. G., and Barchi R. L. (1991) SkM2, a Na+ channel cDNA clone from denervated skeletal muscle, encodes a TTX-insensitive Na+ channel.Mol. Pharmacol. 39, 604–608.
Woosley R. L. (1991) Antiarrhythmic drugs.Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 31, 427–455.
Yamamoto D. (1985) The operation of the sodium channel in nerve and muscle.Prog. Neurobiol. (Oxf.) 24(4), 257–292.
Yang J. and Barchi R. (1990) Phosphorylation of the rat skeletal muscle sodium channel by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase.J. Neurochem. 54(3), 954–962.
Yang J. S., Bennett P. B., Makita N., George A. F., and Barchi R. L. (1993) Expression of the sodium channel {ie428-1} subunit in rat skeletal muscle is selectively associated with the tetrodotoxin-sensitive α subunit isoform.Neuron 11, 915–922.
Yang J. R., Sladky J., Kallen R., and Barchi R. L. (1991) mRNA transcripts encoding the TTX sensitive and insensitive forms of the skeletal muscle sodium channel are independently regulated after denervation.Neuron 7, 421–427.
Yatani A., Okabe K., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., and Brown A. M. (1990) Heart rate regulation by G proteins acting on the cardiac pacemaker channel.Science 249(4973), 1163–1166.
Yellen G., Jurman M. E., Abramson T., and MacKinnon R. (1991) Mutations affecting internal TEA blockade identify the probable pore-forming region of a K+ channel.Science 251(4996), 939–942.
Yool A. J. and Schwarz T. L. (1991) Alteration of ionic selectivity of a K+ channel by mutation of the H5 region [see comments].NAT 349, 700–704.
Zagotta W. N. and Aldrich R. A. (1990) Voltage-dependent gating of Shaker a-type potassium channels inDrosophila muscle.J. Gen. Physiol. 95(1), 29–60.
Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., and Aldrich R. W. (1990) Restoration of inactivation in mutants of Shaker potassium channels by a peptide derived from ShB.Science 250, 568–570.
Zhang J.-F., Robinson R. B., and Siegelbaum S. A. (1992) Sympathetic neurons mediate developmental change in cardiac sodium channel gating through long-term neurotransmitter action.Neuron 9, 97–103.
Zhou J., Potts F. F., Trimmer J. S., Agnew W. A., and Sigworth F. J. (1992) Multiple gating modes and the effect of modulating factors on the μl sodium channel.Neuron 7(5), 775–785.
Zwerling S. J., Cohen S. A., and Barchi R. L. (1991) Analysis of protease-sensitive regions in the skeletal muscle sodium channelin vitro and implications for channel tertiary structure.J. Biol. Chem. 266(7), 4574–4580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kallen, R.G., Cohen, S.A. & Barchi, R.L. Structure, function and expression of voltage-dependent sodium channels. Mol Neurobiol 7, 383–428 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02769184
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02769184