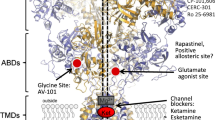
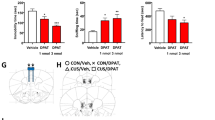
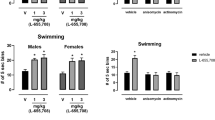
Abstract
Chronic administration of antidepressants produces region-specific adaptive changes in the radioligand binding properties ofN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. We hypothesized that this effect of chronic antidepressant administration was owing to an alteration in NMDA receptor subunit composition. This hypothesis was examined usingin situ hybridization with [35S]-labeled riboprobes to quantify the impact of chronic (16 d) injection with either imipramine (15 mg/kg) or citalopram (20 mg/kg) on the levels of transcripts encoding NMDA receptor subunits in mouse brain. These antidepressants altered the levels of mRNA encoding the ζ-subunit in a parallel fashion, with both drugs either reducing transcript levels (e.g., in the cortex, cerebellum, thalamus, and striatum) or producing no substantial effects (e.g., hippocampus). In contrast, these antidepressants often produced distinct, region-specific effects on mRNA levels encoding the ɛ family of subunits. For example, citalopram treatment produced widespread reductions in ɛ1-subunit mRNA levels (e.g., in frontal cortex, CA2 of hippocampus, and amygdala), whereas imipramine reduced levels of this transcript only in the amygdala. Conversely, imipramine treatment produced widespread reductions in ɛ2-subunit mRNA levels (e.g., in cortex, CA1-4 of hippocampus, and amygdala), whereas the effects of citalopram on levels of this transcript were largely restricted to amygdala. These findings indicate that long-term antidepressant treatment produces region-specific changes in expression of transcripts for NMDA receptor subunits, presumably altering NMDA receptor composition. Because subunit composition determines the physiological and pharmacological properties of NMDA receptors, these changes may play a critical role in the therapeutic actions of structurally diverse antidepressants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACPC:
-
1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid
- CA1-4:
-
Fields CA1-4 of Ammon’s horn of hippocampus
- DG:
-
dentate gyrus
- ECS:
-
electroconvulsive shock
- Fcx:
-
frontal cortex
- nt:
-
nucleotide
- Ocx:
-
occipital cortex
- Pcx:
-
parietal cortex
- SSRI:
-
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
References
Bovetto S., Boyer P. A., Skolnick P., and Fossom L. H. (1997) Chronic administration of a glycine partial agonist alters the expression of NMDA receptor subunit mRNAs.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283, 1503–1508.
Brunello N., Langer S. Z., Perez J., and Racagni G. (1995) Current understanding of the mechanism of action of classic and newer antidepressant drugs.Depression 2, 119–126.
Caldecott-Hazard S., Morgan D. G., DeLeon-Jones F., Overstreet D. H., and Janowsky D. (1991) Clinical and biochemical aspects of depressive disorders: II Transmitter receptor theories.Synapse 9, 251–301.
Drevets W. C., Videen T. O., Price J. L., Preskorn S.H., Carmichael S. T., and Raichle M. E. (1992) A functional anatomical study of unipolar depression.J. Neurosci. 12, 3628–3641.
Duman R. S., Nibuya M., and Vaidya V. A. (1997) A role for CREB in antidepressant action, inAntidepressants: New Pharmacological Strategies (Skolnick P., ed.), Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp. 173–194.
Fink M. (1979)Convulsive Therapy: Theory and Practice. Raven, New York.
Heninger G. and Charney D. (1987) Mechanism of action of antidepressant treatments: implications for the etiology and treatment of depressive disorders, inPsychopharmacology: the Third Generation of Progress (Meltzer H., ed.), Raven, New York, p. 535.
Heninger G. R., Delgado P. L., and Charney D. S. (1996) The revised monoamine theory of depression: A modulatory role for monoamines, based on new findings from monoamine depletion experiments in humans.Pharmacopsychiatry 29, 2–11.
Hjorth S. (1993) Serotonin 5HT1A autoreceptor blockade potentiates the ability of the 5-HT reuptake inhibitor citalopram to increase nerve terminal output of 5-HT in vivo: a microdialysis study.J. Neurochem. 60, 776–779.
Huang N., Layer R. T., and Skolnick P. (1997) Is an adaptation ofN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors an obligatory step in antidepressant action? inAntidepressants: New Pharmacological Strategies (Skolnick P., ed.), Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp. 125–143.
Ishii T., Moriyoshi K., Sugihara, H., Sakurada K., Kadotani H., Yokoi M., et al. (1993) Molecular characterization of the family of theN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits.J. Biol. Chem. 268, 2836–2843.
Kraus J. E., Nadler J. V., and McNamara J. O. (1996) Regulation of alternative splicing of NMDAR1 in the kindling model.Mol. Brain Res. 41, 97–104.
Kutsuwada T., Kashiwabuchi N., Mori H., Sakimura K., Kushiya E., Araki K., et al. (1992) Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel.Nature 358, 36–41.
Laurie D. J. and Seeburg P. H. (1994) Ligand affinities at recombinantN-methyl-d-aspartate receptors depend on subunit composition.Eur. J. Pharm. 268, 335–345.
Layer R. T., Popik P., Nowak G., Paul I. A., Trullas R., and Skolnick P. (1998) A unified theory of anti-depressant action: evidence for adaptation of theN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor complex following chronic antidepressant treatments, inIon Channel Pharmacology (Soria B. and Cena V., eds.), Oxford University Press, London, pp. 438–456.
Lin Y. J., Bovetto S., Carver J. M., and Giordano T. (1996) The cloning of the human NR2-C NMDA glutamate receptor and its expression in the central nervous system and periphery.Mol. Brain Res. 43, 57–64.
Lynch D. R., Anegawa N. J., Verdoorn T., and Pritchett D. B. (1994)N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors: different subunit requirements for binding of glutamate antagonists, glycine antagonists, and channel-blocking agents.Mol. Pharmacol. 45, 540–545.
Maccecchini M. L. (1995) Partial agonism and neuroprotection, inIschemic Stroke: Recent Advances in Understanding & Therapy (Grotta J., Miller L. P., and Buchan A. M., eds.), International Business Communications, Southboro, pp. 140–168.
Meshul C. K., Bunker G. L., Mason J. N., Allen C., and Janowsky A. (1996) Effects of subchronic clozapine and haloperidol on striatal glutamatergic synapses.J. Neurochem. 67, 1965–1973.
Milne R. J. and Goa K. L. (1991) Citalopram: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in depressive illness.Drugs 41, 450–477.
Monyer H., Sprengel R., Schoepfer R., Herb A., Higuchi M., Lomeli H., et al. (1992) Heteromeric NMDA receptors: molecular and functional distinction of subtypes.Science 256, 1217–1221.
Mori H. and Mishina M. (1995) Structure and function of the NMDA receptor channel.Neuropharmacology 34, 1219–1237.
Moriyoshi K., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., and Nakanishi S. (1991) Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat NMDA receptor.Nature 354, 31–36.
Moryl E., Dansyz W., and Quach G. (1993) Potential antidepressive properties of amantadine, memantine and bifelamine.Pharmacol. Toxicol. 72, 394–397.
Nakanishi S. (1992) Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function.Science 258, 597–603.
Naylor P., Stewart C. A., Wright S. R., Pearson R. C. A., and Reid I. C. (1996) Repeated ECS induces GluR1 mRNA but not NMDAR1A-G mRNA in the rat hippocampus.Mol. Brain Res. 35, 349–353.
Nibuya M., Nestler E. J., and Duman R. S. (1996) Chronic antidepressant administration increases the expression of cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) in rat hippocampus.J. Neurosci. 16, 2365–2372.
Nowak G., Trullas R., Layer R. T., Skolnick P., and Paul I. A. (1993) Adaptative changes in theN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor complex after chronic treatment with imipramine and 1-amino-cyclopropanecarboxylic acid.J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 265, 1380–1386.
Nowak G., Li Y., and Paul I. A. (1996) Adaptation of cortical but not hippocampal NMDA receptors after chronic citalopram treatment.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 295, 74–85.
Oretti R. G., Spurlock G., Buckland P. R., and McGuffin P. (1994) Lack of effect of antipsychotic and anti-depressant drugs on glutamate receptor mRNA levels in rat brains.Neurosci. Lett. 177, 39–43.
Oswald I., Brezinova V., and Dunleavy D. L. F. (1972) On the slowness of action of tricyclic antidepressant drugs.Br. J. Psychiatr. 120, 673–677.
Papp M. and Moryl E. (1993) Similar effect of chronic treatment with imipramine and the NMDA antagonist CGP 37849 and MK 801 in a chronic mild stress model of depression in rats.Eur. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 3, 348,349.
Papp M. and Moryl E. (1994) Antidepressant activity of non-competitive and competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in a chronic mild stress model of depression.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 263, 1–7.
Papp M. and Moryl E. (1996) Antidepressant-like effects of 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid andd-cycloserine in an animal model of depression.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 316, 145–151.
Paul I. A., Nowak G., Layer R. T., Popik P., and Skolnick P. (1994) Adaptation of theN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor complex following chronic antidepressants treatments.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 269, 95–102.
Paul S. M., Wu X., Liang Y., and Ginns E. I. (1997) Molecular strategies to novel antidepressant discovery, inAntidepressants: New Pharmacological Strategies (Skolnick P., ed.), Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp. 235–250.
Rigby M., Le Bourdelles B., Heavens R. P., Kelly S., Smith D., Butler A., et al. (1996) The messenger RNAs for theN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits show region-specific expression of different subunit composition in the human brain.Neuroscience 73, 429–447.
Rosenberg C. D., Damsbo N., Fuglum E., Jacobsen L. V., and Horsgard S. (1994) Citalopram and imipramine in the treatment of depressive patients in general practice. A nordic multicentre clinical study.Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 9 (Suppl. 1), 41–48.
Rossby S. P. and Sulser F. (1997) Antidepressants: beyond the synapse, inAntidepressants: New Pharmacological Strategies (Skolnick P., ed.), Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp. 195–212.
Sheng M., Cummings J., Roldan L. A., Jan Y. N., and Jan L. Y. (1994) Changing subunit composition of heteromeric NMDA receptors during development of rat cortex.Nature 368, 144–147.
Standaert D. G., Testa C. M., Young A. B., and Penney J. B. (1994) Organization ofN-methyl-d-aspartate glutamate receptor gene expression in the basal ganglia of the rat.J. Comp. Neurol. 343, 1–16.
Sugrue M. F. (1985) Delayed biochemical changes following antidepressant treatment.Psychopharmacology 21, 619–622.
Swerdlow N. R. and Koob G. F. (1987) Dopamine, schizophrenia, mania and depression: toward a unified hypothesis of cortico-striato-pallido-thalamic function.Behav. Brain Sci. 10, 197–245.
Trullas R. and Skolnick P. (1990) Functional antagonists at the NMDA receptor complex exhibit antidepressant actions.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 185, 1–10.
Vetulani J. (1991) The development of our understanding of the mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs.Polish J. Pharmacol. 43, 323–338.
Vetulani J. and Sulser F. (1975) Action of various antidepressant treatments reduces reactivity of noradrenergic cyclic AMP generating system in limbic forebrain.Nature 257, 495,496.
Von Lubitz D. K. J. E., Lin R. C.-S., McKenzie R. J., Devlin T. M., McCabe R. T., and Skolnick P. (1992) A novel treatment of global cerebral ischaemia with a glycine partial agonist.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 219, 153–158.
Wafford K. A., Bain C. J., Le Bourdelles B., Whiting P. J., and Kemp J. A. (1993) Preferential co-assembly of recombinant NMDA receptors composed of three different subunits.Neuroreport 4, 1347–1349.
Watanabe M., Inoue Y., Sakimura K., and Mishina M. (1993) Distinct distributions of fiveN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor channel subunit mRNAs in the forebrain.J. Comp. Neurol. 338, 377–390.
Watanabe M., Mishina M., and Inoue Y. (1994) Distinct distributions of five NMDA receptor channel subunit mRNAs in the brainstem.J. Comp. Neurol. 343, 520–531.
Zukin R. S. and Bennett M. V. L. (1995) Alternatively spliced isoforms of the NMDAR1 receptor subunit.Trends Neurosci. 18, 306–313.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyer, PA., Skolnick, P. & Fossom, L.H. Chronic administration of imipramine and citalopram alters the expression of NMDA receptor subunit mRNAs in mouse brain. J Mol Neurosci 10, 219–233 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02761776
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02761776